Attachment - Business Information Management

BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Chapter 10 / EXERCISE
Part A – Multiple Choice Questions
1.
A human newborn’s motor capacities are characterized by: a) b) reflexes. self-directed responses. c) d) skilled motor control. voluntary movement.
2.
At which age does the object permenance achieved? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 5
3. A theory of mind is: a) b) c)
Understanding actions/thoughts of other people
Comprehension of others’ intentions able to take another’s perspective the primacy effect d)
4. Concrete and Formal operations require that child has mastered ____ schema a) operational b) assimilation c) sensorimotor d) conservational
5. Brian is a two-month-old infant who is easily upset and frightened by new objects or people; his sister, Sara, was more easy-going and calm as an infant. These siblings have different: a) imprinting styles. b) temperaments. c) stages of moral development. d) prosocial instincts.
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.A firm, close, enduring emotional bond between the baby and the primary caregiver is called: a) b) c) d)
Locomotion
Attachment
Emotion Regulation
Social Referencing
7Harley Hallow’s experiment was about attachment, and it was to test____: a) whether the babies will show seperation anxiety when the caregiver leaves the room b) if human voice frequently bring relief from stress c) the stability of attachment d) if the babies are attached to caregivers on the basis of nutrition
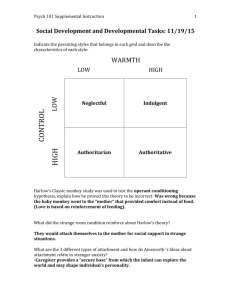
8.According to Mary Ainsworth, when considering different patterns of ways that children form bonds with parents , which of the following is not one of the parenting styles? a) b) c)
Securely attached
Anxious / resistant attachment
Anxious / avoidant attachment d) Organized attachment
9.In ______ parenting style, there are many rules and demands, few explanations and little sensitivity to the child’s perspective. a) Authoritative b) Authoritatian c) Permissive d) Uninvolved
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
Part B – Match the Followings
In the first column you will see some terms related with “Physical and
Cognitive Development”. In the second column, there are the descriptions of these terms. Please match them accordingly
Memory Related Terms
1. Genetic inheritance
Explanations
( 3 ) He was first to propose that a child’s thinking was qualitatively
2. Representational thought different from that of adults
( 5 ) he carried out experiments to find out whether babies attach to caregivers on the basis of nutrition
3. Piaget
4. Permissive
5. Harry Harlow
(4 ) _____ A parenting style
( 2 )
In the Preoperational period, with development of object permanence comes ____
( 1 ) _________ may set up learning pathways, specific processing paths for certain types of information
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
Part C - Short Answer Questions
1. Please explain what “attachment” is, by taking into account “contact comfort”, Harlow’s experiment, Bowlby, differences in attachment (Mary
Ainsworth), attachment to father and absence of attachment.
Attachment
6-8 months: with locomotive ability frequently comes… Separation
Anxiety
Separation Anxiety: Baby becomes upset when CG leaves room/goes out of sight
Implies that formation of attachment has occurred
Attachment: A firm, close, enduring emotional bond between the baby and the primary caregiver
Harry Harlow’s experiments
Do babies attach to caregivers on the basis of nutrition?
Infant rhesus monkeys raised in cages with two fixed objects:
terry-cloth covered wire-mesh object, wire-mesh object that held a bottle of milk
In times of stress/fear/uncertainty, monkeys always went to terry-cloth
“mother”
-- not the “mother” where they had been fed
Contact comfort: more important than where/how fed for purposes of attachment
Humans?
Contact comfort: also important
Children’s fondness for stuffed animals, blankets, etc: attachment formed for comfort, not for food
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
Other implications of contact comfort:
Many animals, including humans, need contact/physical comfort for normal development
Bowlby: among the first to describe a theory of attachment in humans
Differences Among Children
Temperament: most important difference in very young children
Some common descriptors: “easy” “difficult,” and “slow to warm up”
Based on structural/biological innate differences seen even from a very young age
Differences in Experience:
socially and environmentally, exposure varies across children differences in attachment patterns
Differences in Attachment: Mary Ainsworth
Different patterns of ways that children form bonds with parents differ with parental style:
Securely attached
Anxious / resistant attachment
Anxious / avoidant attachment
Disorganized attachment
Stability of attachment
Does child project same type of attachment across situations?
Mixed research results.
( a
A t t
) : a c
T h h e m e s n e t t c u a r n e d t t h e r e c a u s e a g n o d o d o e
( f u
B f f t
) t e c
: c o t t
T m
.
.
h e e a r s e a o u t t c o m e e
( t t f f t f f t h a e e c c t t h s s m e o n e f f s i i n a t a t e i i t t r c e v t t u a h e i r n i e d r m t t h e b o t t h d h o f f t a t h c h e t t g e r o o r o d o
) .
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
Attachment to Father
Fathers can form the “secure base” for children as easily as mothers
Fathers: different interaction style with children
More physical, more vigorous
Usually less likely to provide hugs/kisses
Some social, some biological reasons likely responsible
Absence of Attachment
Absence of any parenting/absent physical contact extremely disordered behavior
Seen in experimentally induced isolated animal models (this experimentation is no longer permitted)
Seen in rare instances of orphanages
Romanian orphans: little or no physical contact
This kind of disordered parenting: permanent social and emotional scars
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring
BILKENT UNIVERSITY
APPLIED SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
BUSINESS INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
92 100 Introduction to Psychology
Ebru İNANÇ
Instructor
07-08 Spring