CHAPTER 2 GENERAL VARIETY OF ORGANISMS
advertisement

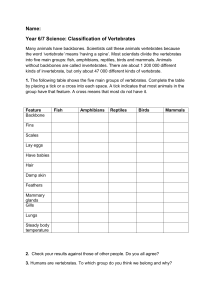
CHAPTER 2 GENERAL VARIETY OF ORGANISMS 2.1 The Diversity of Organisms 1. 2. There are a large variety of living things in the world. There are about 1,000,000 different kinds (species) of animals and 500,000 different plants. 2.2 Classification 1. Classifying organisms can help us to identify and study them. 2. The plan of classification is based on the similarities and differences in their external and internal features among the living organisms. 3. Simple classification : a. The animals in Animal Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Invertebrates: animals without backbones. Vertebrates: animals with backbones. b. The plants in Plant Kingdom can be divided into 2 large groups : Non-flowering plants : plants without flowers. Flowering plants : plants with flowers. 3. Scientific classification: Kingdom --> Phylum --> ......... --> Genus --> Species 4. A species is a type of organisms which are a. similar to each other; b. can breed among themselves to produce offspring. fertile 2.3 Different Plant and Animal Groups 1. The seven characteristics of living things are nutrition, respiration, excretion, movement, irritability, growth and reproduction. They are also made up of cells. matter non-living things living-things plants animals 2. General differences between plants and animals nutrition excretion growth response movement 3. Plants by photosynthesis no definite excretory organ 1. at special regions such as stem tips, root tips and cambium. 2. grow throughout their live slow restricted to some parts of the plants Animals feed on organic food has special excretory organ 1. grow evenly throughout the body 2. stop growing when mature fast can move from place to place General classification of animals animals invertebrates fish 4. vertebrates amphibians reptiles General classification of plants : birds mammals plants flowering plants dicotyledons non-flowering plants monocotyledons gymnosperms ferns mosses algae fungi 2.4 Characteristics of the Animal Groups 1. Invertebrates -- animals without a backbone. e.g. single-cell animals, jelly-fish, coral, earthworm, insect, shrimp, crab, snail, clams, octopus, starfish, etc. 2. Vertebrates -- animals with a backbone. a. fish ------- aquatic vertebrates with moist scales on the skin; breathing by gill; with fins; body temperature changes with the environment. external fertilization e.g. carp, shark, (all fish) b. amphibian --- vertebrates with moist skin; with aquatic larva stage breathing with gills. -- Adult may live on land and breathe with lungs, skin and mouth cavity. -- body temperature changes with environment. -- external fertilization -- e.g. frog, toad c. reptile ------ d. bird ---- vertebrates with feather on skin; the fore-limbs modified into wings; body temperature does not change environment internal fertilization e.g. hens, eagle, (all birds) --e. mammal ------ 3. vertebrates with dry, scaly skin; breathe by lungs, egg-laying. body temperature changes with environment; internal fertilization e.g. snake, crocodile, tortoise vertebrates with hair on skin; mother has mammary glands; body temperature not change environment internal fertilization e.g. rat, monkey, man, bat, whale with with Summary of vertebrates Fish Amphibian Reptile Birds Body covering Breathing structure Body temperature Fertilization Other special features. 2.5 Characteristics of the Plant Groups Mammals 1. Fungi (singular : fungus) a. simple plants without root, stem and leaf. b. do not have chlorophyll and cannot photosynthesis. c. live either saprophytic or parasitic. d. e.g. bread mould, yeast, mushroom carry 2. Algae (singular : alga) a. simple plants without root, stem and leaf. b. with chlorophyll (or other pigments) photosynthesis. c. e.g. spirogyra out for 3. Mosses a. simple plants with simple leaves and stems but no true roots. b. usually grow in moist and damp places. 4. Ferns a. plants with true leaves, stems and roots. b. have vascular tissues for transporting materials c. no flower, reproduce by spores. 5. Gymnosperms a. plants with true leaves, stems and roots. b. have vascular tissues for transporting materials c. no flower, naked seeds produced in cones. d. the leaves are usually needle-shaped. e. e.g. pine, cypresses (柏), fir (杉), etc. 6. Flowering Plants a. plants with true leaves, stems and roots. b. have vascular tissues for transporting materials. c. with flower. d. There are two main types: (i) Dicotyledonous plants -- leaves with net-venation -- e.g. rose, Bauhinia, broad bean, mungo bean. (ii) Monocotyledonous plants -- leaves with parallel venation. -- e.g. grass, rice, orchid (蘭花), gladiolus (劍蘭) 7. Summary Fungi Algae Mosses Ferns Gymnosperm Flowering plants chlorophyll root, stem and leaf vascular bundle seed flower 2.6 Use of keys 1. Keys can help us to name an organism. 2. A dichotomous key provides a way to identify organisms by choosing between two alternative features at each stage of the key. 3. A dichotomous key for classification of plants: 1. plants with flowers plants without flowers go to 2 go to 3 2. leaves with network veins leaves with parallel veins dicot plant monocot plant 3. have true roots, stems and leaves no true roots, stems and leaves go to 4 go to 5 4. have seeds do not have seeds gymnosperms fern 5. have simple "stems" and "leaves" no such simple "stems" and "leaves" mosses go to 6 6. with chlorophyll without chlorophyll algae fungi ============================================================= Important words diversity of organisms classification of organisms plants backbone fish reptiles mammals monocotyledonous plants fungi mosses gymnosperms dichotomous key habitat animals invertebrates vertebrates amphibians birds non-flowering plants dicotyledonous plants algae ferns key ============================================================== Checklist After studying this chapter, you should be able to 1. point out that there is a large variety of living things. 2. classify animals into vertebrates and invertebrates. 3. classify vertebrates birds and mammals. 4. classify plants into flowering and non-flowering plants using external features. 5. classify non-flowering plants into algae, fungi, mosses, ferns and gymnosperms. 6. use a dichotomous key for identification. into fishes, amphibians, reptiles, ==============================================================