2.6 security
advertisement

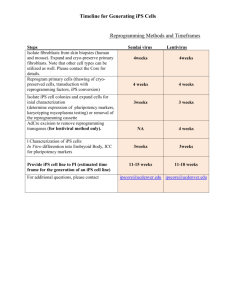
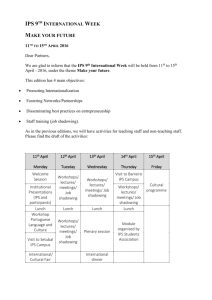
ACP-WG I-06/WP-09 International Civil Aviation Organization 3/17/2008 WORKING PAPER Aeronautical Communication Panel Working Group I – Internet Protocol Suite (IPS) March 17-20, 2008 Montreal Canada Updated Security Requirements for the “Manual for the ATN using IPS Standards and Protocols” Prepared by: Vic Patel and Tom McParland Presented by: Vic Patel SUMMARY This paper provides updated security requirements for Doc 9896, “Manual for the ATN using IPS Standards and Protocols.” This paper is an update of working paper 9 from the 5th meeting of Working Group I. Several changes to WP 9 were suggested during the 5th meeting as described in the meeting minutes. In addition this papers incorporates chages based on the adoption of Mobile IPv6 for air-ground mobility. The working group is invited to consider these requirements as a baseline set of air-ground security requirements. CHANGES TO 2.6 INCORPORATED 2.6 SECURITY This section contains provisions for ground-ground and air-ground security in the ATN/IPS. Note. - Support for security is to be based on a system threat and vulnerability analysis. 2.6.1 Ground-Ground Network Layer Security Note . – Network layer security in the ATN/IPS internetwork is implemented using IPsec. 2.6.1.1 Ground-Ground IPsec 2.6.1.1.1 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol as specified in RFC-4301 2.6.1.1.2. ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol as specified in RFC-4303. 2.6.1.1.3 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment may implement the IP Authentication Header (AH) protocol as specified in RFC-4302. 2.6.1.1.4 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement manual configuration 2.6.1.1.5 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol as specified in RFC-4306. 2.6.1.1.6 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Cryptographic Algorithm Implementation Requirements for the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) as specified in RFC-4305.. 2.6.1.1.7 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement The Null Encryption Algorithm and Its Use With IPsec as specified in RFC-4305, but not the Null Authentication Algorithm. Note - ESP encryption is optional, but authentication is always performed. 2.6.1.1.8 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Cryptographic Algorithms for Use in the Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) required algorithms for key exchange as specified in RFC-4307. Note. – Algorithms of equivalent or greater strength than those identified in RFC-4307 are implemented as a local matter on a bi-lateral basis. 2.6.2 Air-Ground Security 2.6.2.1 Acess Network Security 2.6.2.1.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes shall implement the security provisions of the accces network. Note. – For example, the WiMAX, 3GPP, and 3GPP2 access networks have authentication and authorization provisions. 2.6.2.2 Air-Ground IPsec 2.6.2.2.1 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol as specified in RFC 4301. 2.6.2.2.2 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol as specified in RFC 4303. 2.6.2.2.3 ATN/IPS nodes, which implement MIPv6, may implement the Authentication Protocol for Mobile IPv6 as specified in RFC 4285. 2.6.2.2.4 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol as specified in RFC 4306. 2.6.2.2.5 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment, which implement MIPv6, shall implement Mobile IPv6 Operation with IKEv2 and the Revised IPsec Architecture as specified in RFC 4877. 2.6.2.3 Air-Ground Transport Layer Security 2.6.2.3.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes may implement the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol as specified in RFC 4346. 2.6.2.6 If TLS is used for air-ground security, mobile nodes and correspondent nodes shall implement the Cipher Suite TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA as specified in RFC 4492. 2.6.2.4 Air-Ground Application Layer Security 2.6.2.4.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes may implement air-ground security as specified in Doc 9705/9880. 2.6.2.4.2 If application layer security is used for air-ground security, IKEv2 shall be used for key establishment as specified in section 2.6.2. 2.6.2.4.3 If application layer security is used for air-ground security, mobile nodes may use a shared secret or HTTP_CERT_LOOKUP as the authentication mechanism for IKEv2. Note 1.-- In IKEv2 the authentication mechaism may be different in each direction. Note 2. – With the shared secret method the ground system may retrieve the mobile node’s shared secret from a AAA server. Note 3. – With HTTP_CERT_LOOKUP the mobile node does not have to transmit an actual certificate but rather transmits a hash value and a URL where the ground system can retrieve the mobile node’s certificate and CRL. 2.6.2.4.4 If application layer security is used for air-ground security, ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes shall implement the following transforms: a) AUTH_HMAC_SHA2_256-128 as the Integrity Algorithm for ESP authentication as specified in RFC 4868. b) PRF_HMAC_SHA_256 as the pseudo-random function in IKEv2 as specified in RFC 4868. c) 256-bit random ECP group for Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange values in IKEv2 as specified in RFC 4753. d) ECDSA with SHA-256 on the P-256 curve as the IKEv2 authentication method as specified in RFC 4754. CHANGES TO 2.6 REDLINED 2.6 SECURITY This section contains provisions for ground-ground and air-ground security in the ATN/IPS. Note. - Support for security is to be based on a system threat and vulnerability analysis. 2.6.1 Ground-Ground Network Layer Security Note . – Network layer security in the ATN/IPS internetwork is implemented using IPsec. 2.6.1.1 Ground-Ground IPsec 2.6.1.1.1 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol as specified in RFC-4301 2.6.1.1.2. ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol as specified in RFC-4303. 2.6.1.1.3 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment may implement the IP Authentication Header (AH) protocol as specified in RFC-4302. 2.6.1.1.4 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement manual configuration 2.6.1.1.5 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol as specified in RFC-4306. 2.6.1.1.6 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Cryptographic Algorithm Implementation Requirements for the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) as specified in RFC-4305.. 2.6.1.1.7 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement The Null Encryption Algorithm and Its Use With IPsec as specified in RFC-4305, but not the Null Authentication Algorithm. Note - ESP encryption is optional, but authentication is always performed. 2.6.1.1.8 ATN/IPS nodes in the ground-ground environment shall implement the Cryptographic Algorithms for Use in the Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) required algorithms for key exchange as specified in RFC-4307. 5 Note. – Algorithms of equivalent or greater strength than those identified in RFC-4307 are implemented as a local matter on a bi-lateral basis. 2.6.2 Air-Ground Security 2.6.2.1 Acess Network Security 2.6.2.1.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes shall implement the security provisions of the accces network. Note. – For example, the WiMAX, 3GPP, and 3GPP2 access networks have authentication and authorization provisions. 2.6.2.2 Air-Ground IPsec 2.6.2.2.1 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol as specified in RFC 4301. 2.6.2.2.2 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol as specified in RFC 4303. 2.6.2.2.3 ATN/IPS nodes, which implement MIPv6, may implement the Authentication Protocol for Mobile IPv6 as specified in RFC 4285. 2.6.2.2.4 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment shall implement the Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol as specified in RFC 4306. 2.6.2.2.5 ATN/IPS nodes in the air-ground environment, which implement MIPv6, shall implement Mobile IPv6 Operation with IKEv2 and the Revised IPsec Architecture as specified in RFC 4877. 2.6.2.3 Air-Ground Transport Layer Security 2.6.2.3.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes may implement the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol as specified in RFC 4346. 2.6.2.6 If TLS is used for air-ground security, mobile nodes and correspondent nodes shall implement the Cipher Suite TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA as specified in RFC 4492. 2.6.2.4 Air-Ground Application Layer Security 6 2.6.2.4.1 ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes may implement air-ground security as specified in Doc 9705/9880. 2.6.2.4.2 If Doc application layer security is used for air-ground security, IKEv2 shall be used for key establishment as specified in section 2.6.2.2. 2.6.2.4.3 If application layer security is used for air-ground security, mobile nodes may use a shared secret or HTTP_CERT_LOOKUP as the authentication mechanism for IKEv2. Note 1.-- In IKEv2 the authentication mechaism may be different in each direction. Note 2. – With the shared secret method the ground system may retrieve the mobile node’s shared secret from a AAA server. Note 3. – With HTTP_CERT_LOOKUP the mobile node does not have to transmit an actual certificate but rather transmits a hash value and a URL where the ground system can retrieve the mobile node’s certificate and CRL. 2.6.2.4.4 If application layer security is used for air-ground security, ATN/IPS mobile nodes and correspondent nodes shall implement the following transforms: e) AUTH_HMAC_SHA2_256-128 as the Integrity Algorithm for ESP authentication as specified in RFC 4868. f) PRF_HMAC_SHA_256 as the pseudo-random function in IKEv2 as specified in RFC 4868. g) 256-bit random ECP group for Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange values in IKEv2 as specified in RFC 4753. h) ECDSA with SHA-256 on the P-256 curve as the IKEv2 authentication method as specified in RFC 4754. 7 CHANGES TO APPENDIX A REDLINED APPENDIX A – REFERENCE DOCUMENTS IETF STANDARDS AND PROTOCOLS The following documents are available publicly at http://www.ietf.org and form part of this manual to the extent specified herein. In the event of conflict between the documents referenced herein and the contents of this manual, the provisions of this manual shall take precedence. Request for Comments (RFCs) netlmm-mn-ar-if Network-based Localized Mobility Management Interface between Mobile Node and Mobility Access Gateway, May 2007 netlmm-proxymip6 Proxy Mobile IPv6, February 2008 RFC-768 User Datagram Protocol, August 1980 RFC-793 Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), September 1981 RFC-1006 ISO Transport Service on top of TCP, May 1987 RFC-1323 TCP Extensions for High Performance May 1992 RFC-1981 Path Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Discovery for IP Version 6, August 1996 RFC-2126 ISO Transport Service on top of TCP, March 1997 RFC-2460 Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification, December 1998 RFC-2474 Differential Services Field, December 1998 RFC-2488 Enhancing TCP over Satellite Channels, January 1999 RFC-2858 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Multiprotocol Extensions June 2000 RFC-3775 Mobility Support in IPv6, June 2004 RFC-4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4), January 2006 RFC-4285 Authentication Protocol for Mobile IPv6 , January 2006 RFC-4291 IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture, February 2006 RFC-4301 Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol, December, 2005 RFC-4302 Internet Protocol (IP) Authentication Header, December 2005 RFC-4303 IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP), December 2005RFC-4305 Cryptographic Algorithm Implementation Requirements for Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) – (NB proposed standard, obsoletes RFC-2402, RFC-2406), December 2005 RFC-4306 Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol, December 2005 RFC-4307 Cryptographic Algorithms for Use in the Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2), December 2005 RFC-4346 The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.1, April 2006 RFC 4423 Host Identity Protocol (HIP) Architecture, May 2006 RFC-4443 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Specification, March 2006 1 RFC-4492 RFC-4555 RFC-4753 RFC-4754 RFC-4830 RFC-4831 RFC-4868 RFC-4877 Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) Cipher Suites for Transport Layer Security, May 2006 IKEv2 Mobility and Multihoming Protocol (MOBIKE), June 2006 ECP Groups for IKE and IKEv2, January 2007 IKE and IKEv2 Authentication Using the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm, (ECDSA), January 2007 Problem Statement for Network-Based Localized Mobility Management (NETLMM), April 2007 Goals for Network-Based Localized Mobility Management (NETLMM), April 2007 Using HMAC-SHA-256, HMAC-SHA-384, and HMAC-SHA-512 with IPsec Mobile IPv6 Operation with IKEv2 and the Revised IPsec Architecture, April 2007 2