Relative Dating Worksheet: Geology Layers & Principles
advertisement
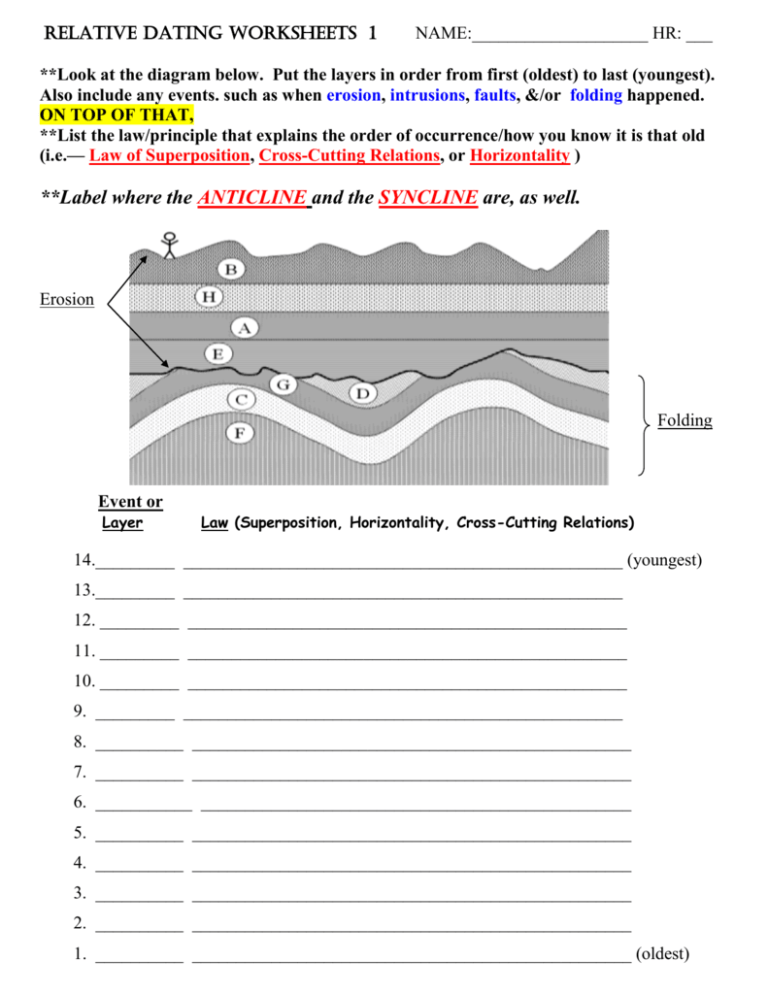
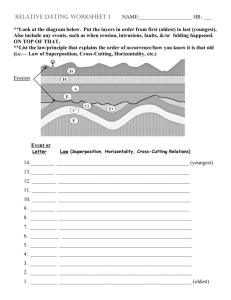
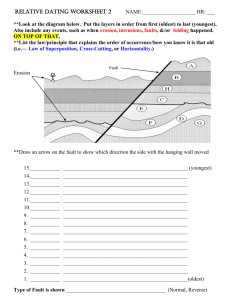
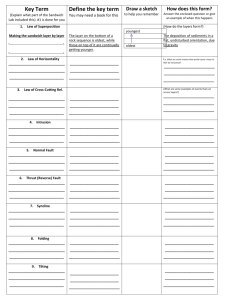
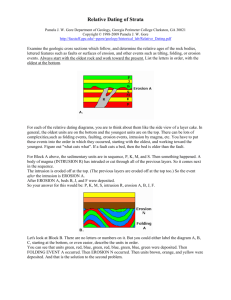
Relative Dating Worksheets 1 NAME:____________________ HR: ___ **Look at the diagram below. Put the layers in order from first (oldest) to last (youngest). Also include any events. such as when erosion, intrusions, faults, &/or folding happened. ON TOP OF THAT, **List the law/principle that explains the order of occurrence/how you know it is that old (i.e.— Law of Superposition, Cross-Cutting Relations, or Horizontality ) **Label where the ANTICLINE and the SYNCLINE are, as well. Erosion Folding Event or Layer Law (Superposition, Horizontality, Cross-Cutting Relations) 14._________ __________________________________________________ (youngest) 13._________ __________________________________________________ 12. _________ __________________________________________________ 11. _________ __________________________________________________ 10. _________ __________________________________________________ 9. _________ __________________________________________________ 8. __________ __________________________________________________ 7. __________ __________________________________________________ 6. ___________ _________________________________________________ 5. __________ __________________________________________________ 4. __________ __________________________________________________ 3. __________ __________________________________________________ 2. __________ __________________________________________________ 1. __________ __________________________________________________ (oldest) **Look at the diagram below. Put the layers in order from first (oldest) to last (youngest). Also include any events. such as when erosion, intrusions, faults, &/or folding happened. ON TOP OF THAT, **List the law/principle that explains the order of occurrence/how you know it is that old (i.e.— Law of Superposition, Cross-Cutting Relations, or Horizontality ) Still layer E Note: The various sedimentary layers above are labeled as B, E, K and W. The timing of the fault (break) in the rocks ( labeled Q ) must be included in the sequence of events. Event or Layer Law (Superposition, Horizontality, Cross-Cutting Relations) 5. __________ __________________________________________________ 4. __________ __________________________________________________ 3. __________ __________________________________________________ 2. __________ __________________________________________________ 1. __________ __________________________________________________ (oldest) Rule of Thumb: If you are considering where to put a layer into the sequence = Law of Superposition When you are considering where an event belongs in the mix, then, -if it has to do with the actions of folding, tilting, or erosion = Law of Horizontality -if it has to do with the action of faulting or intrusions = Law of Cross-Cutting Relations **Look at the diagram below. Put the layers in order from first (oldest) to last (youngest). Also include any events. such as when erosion, intrusions, faults, &/or folding happened. ON TOP OF THAT, **List the law/principle that explains the order of occurrence/how you know it is that old (i.e.— Law of Superposition, Cross-Cutting Relations, or Horizontality ) Note: The two intrusions above are labeled as X and Z; the surrounding rock is labeled D. Event or Layer Law (Superposition, Horizontality, Cross-Cutting Relations) 5. __________ __________________________________________________ 4. __________ __________________________________________________ 3. __________ __________________________________________________ 2. __________ __________________________________________________ 1. __________ __________________________________________________ (oldest)