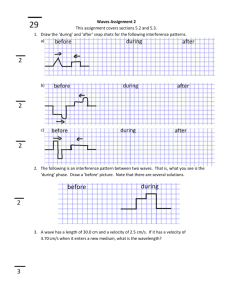
Refraction of Water Waves: Practice Problems & Examples
advertisement
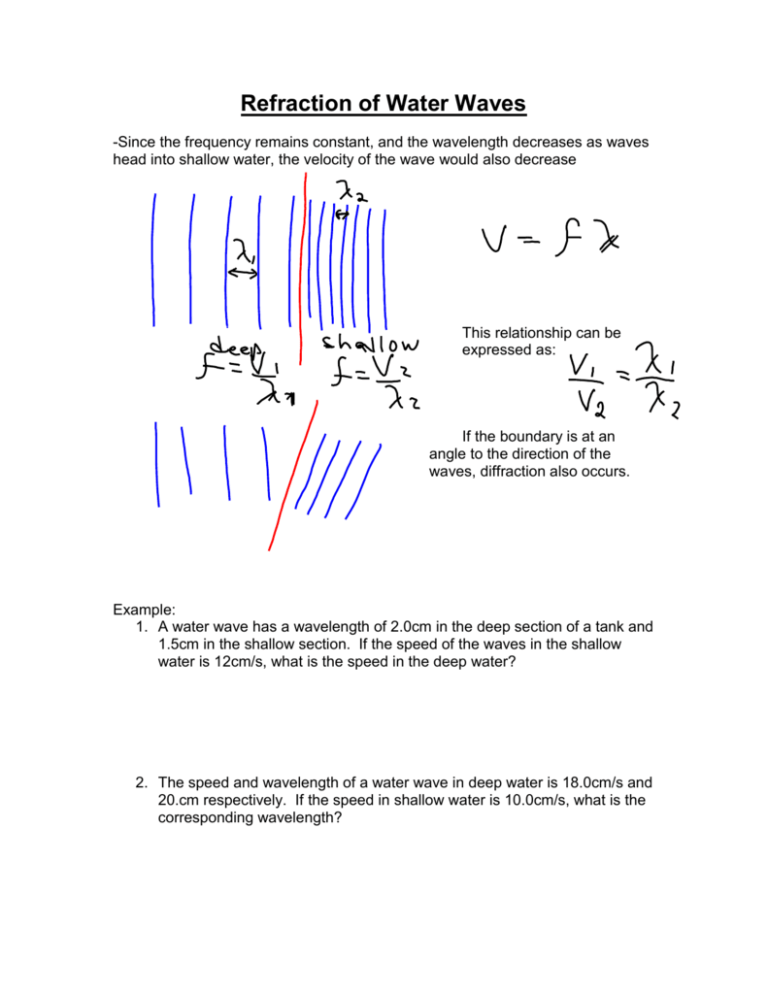
Refraction of Water Waves -Since the frequency remains constant, and the wavelength decreases as waves head into shallow water, the velocity of the wave would also decrease This relationship can be expressed as: If the boundary is at an angle to the direction of the waves, diffraction also occurs. Example: 1. A water wave has a wavelength of 2.0cm in the deep section of a tank and 1.5cm in the shallow section. If the speed of the waves in the shallow water is 12cm/s, what is the speed in the deep water? 2. The speed and wavelength of a water wave in deep water is 18.0cm/s and 20.cm respectively. If the speed in shallow water is 10.0cm/s, what is the corresponding wavelength? Refraction problems: 1. A water wave is approaching a beach from deep water. The wavelength of the waves in deep water is 2.0m while the velocity of the wave is 20 m/s. If the wavelength of the wave in the shallow water is 1.75m, what is it’s velocity in the shallow water? 2. A ski boat passes a beach in deep water. The wavelength of the waves produced in deep water is 2.5m. If the wavelength & velocity of the waves when they hit the beach is 1.8m & 2.2m/s, what is the original velocity of the wave?