Water
advertisement

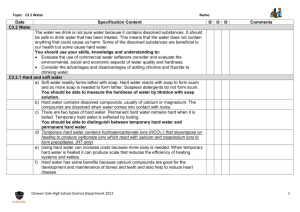
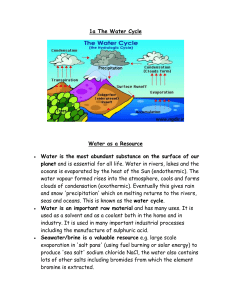
HARDNESS OF WATER The Cause of Hardness Hardness is caused by dissolved calcium and magnesium ions. Calcium hydrogencarbonate is the most common cause of hard water. It forms when rain falls and flows over rocks of limestone, chalk or marble. These are mostly calcium carbonate, which is not soluble in water. However, rainwater is not pure. As it falls through the air, it dissolves carbon dioxide, and this solution then attacks the calcium carbonate, forming calcium hydrogencarbonate. Calcium hydrogencarbonate is soluble in water. CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) Ca(HCO3)2(aq) Other compounds which cause hardness are magnesium hydrogencarbonate, calcium sulphate and magnesium sulphate, which are dissolved from rocks such as dolomite (CaCO3.MgCO3) and gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O). Hardness caused by calcium or magnesium hydrogencarbonate is called temporary hardness. Hardness caused by other calcium or magnesium compounds is called permanent hardness. How Hard Water is Recognised a) Scum In some places, the tap water lathers easily with soap. This is soft water. In other places, the same amount of soap gives a scum and hardly any lather. This is a sign of hard water. The scum forms because calcium or magnesium ions in solution react with soap, giving an insoluble off-white product that floats on water. Ca2+(aq) + 2C17H35COO-(aq) stearate ion, from soap (C17H35COO)2Ca(s) scum A proper lather cannot form until the soap has reacted with all the dissolved calcium or magnesium ions in the water. b) Scale Water containing calcium hydrogen carbonate, when boiled, produces a hard white deposit on the sides of a kettle. This deposit, called scale or fur, is calcium carbonate, which is formed when calcium hydrogencarbonate decomposes. Ca(HCO3)2(aq) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) Note that this reaction is the reverse of the process by which calcium hydrogencarbonate is formed. TOPIC 11.3.2: WATER 1 Softening water Softening water involves the removal of dissolved calcium and magnesium ions. Water can be softened in the following ways: 1) Distillation Distilling water gets rid of both sorts of hardness. The water is heated and boils off as steam, leaving any dissolved calcium and magnesium ions behind. The steam is condensed to pure water. Distilled water is the softest water available. Distillation is not used on a large scale because of the high fuel costs. 2) Boiling This removes temporary hardness. Calcium and magnesium hydrogencarbonates, which are soluble in water, decompose on heating to give the insoluble carbonates, which form a precipitate. The calcium and magnesium ions are, therefore, no longer in solution. Ca(HCO3)2(aq) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) 3) Adding Sodium Carbonate (Washing Soda) When sodium carbonate is added to hard water, the carbonate ions in the washing soda combine with the calcium or magnesium ions in the hard water to form a precipitate of calcium or magnesium carbonate. The calcium and magnesium ions are, therefore, no longer in solution. Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) CaCO3(s) Bath salts consist mainly of sodium carbonate. 4) Ion-Exchange Resins Ion-exchange resins soften water by removing all calcium and magnesium ions. An ion-exchanger is a container full of small beads of ion-exchange resin, a special negatively-charged plastic which has positive ions weakly attached to it; typically the positive ions are sodium ions. When hard water flows through the ion-exchanger, the calcium and magnesium ions dissolved in it change places with the sodium ions and attach themselves to the resin. The sodium ions dissolve in the water. After a time, when all the sodium ions from the resin have gone, no more hardness can be removed until the resin has been regenerated. To do this, a concentrated solution of sodium chloride (salt) is poured in. The sodium ions push the calcium and magnesium ions off the resin and replace them, making the resin ready for use again. TOPIC 11.3.2: WATER 2 Advantages & Disadvantages of Hard Water Hard water has advantages and disadvantages for industry and the home. Advantages The dissolved compounds in hard water are good for health. Calcium compounds help in the development of strong bones and teeth to reduce heart disease Disadvantages Using hard water leads to the formation of deposits (scale) in heating systems. This can block pipes and can increase electricity costs. Using hard water leads to the formation of deposits (scale) in kettles. Using hard water can increase costs because more soap in needed. Purifying Water Water is made safe to drink by removing solids and killing bacteria Solids are removed by filtration and sedimentation. Water is allowed to flow through stone and sand filter beds to remove solid materials. The sand becomes finer near to the bottom of the filter to remove small solids. Tiny particles which are still suspended in the water are allowed to settle out and fall to the bottom. This is called sedimentation. Chlorine (or ozone) is bubbled through the water to kill bacteria. Ultraviolet light can also be used to disinfect water. The safe clear water is pumped through underground pipes to houses. The quality of drinking water is monitored by environmental agencies for dissolved ions such as nitrate. Some people use water filters in their homes to make tap water nicer to drink. Water filters may contain silver which has an anti-bacterial effect and carbon which is good at removing tiny particles. Pure water can only be produced by distillation but this is an expensive process because of the energy involved. Water issues The addition of chlorine to water is not without its problems. Scientists have found that chlorine can react with harmless organic compounds dissolved in water to form toxic products. This is more likely to occur when chlorine is used in high concentrations to treat sewage and the risks to human health in treating drinking water are very low indeed. However ozone can be used as an alternative to kill bacteria. Fluoride is also added to public water supplies to protect teeth from decay. It is added to toothpaste for this reason. Some people believe that it should not be added to water and that we should be able to choose whether to drink water with fluoride in it or not. TOPIC 11.3.2: WATER 3