Folds: Descriptive
advertisement

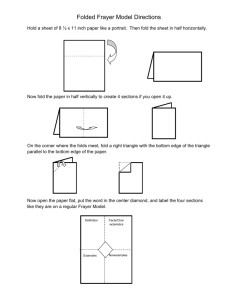
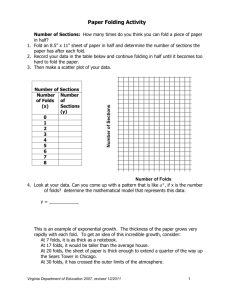
Folds, descriptive Goals: 1) To understand the basic geometric elements of folds and 2) to classify folds based on their shape. 1) Anticlines and Synclines a) Monocline: Fold pair with two long, horizontal limbs connected by a short inclined limb b) Antiforms: Convex upwards folds Anticline: Fold that is convex in the direction of the youngest beds Antiformal syncline: Antiform with oldest beds on top b) Synforms: Convex downwards folds Syncline: Fold that is convex in the direction of the oldest beds Synformal anticline: Synform with oldest beds on top 2) Basic geometric elements of a fold Fold profile plane: Plane normal to folding axis Fold hinge: Line of maximum curvature Hinge zone: Zone of maximum curvature around hinge Fold limb: Flanks of folded layer Inflection point: Point where limb segments change convexity between folds Axial plane: Axial trace: Axial-planar foliation: Fold axial surfaces commonly approximate the maximum shortening directions. 3) Fold classification based on the orientation of hinge/axial surface Display diagram in ppt. and draw on board. Axial surface: upright, steeply inclined, moderately inclined, gently inclined, recumbent Hinge line: subhorizontal, gently plunging, moderately plunging, steeply plunging, reclined Doubly plunging fold: Fold plunges in two directions Overturned fold: One limb rotated through vertical Show block diagram models of folds and have students classify. Show pictures of folds in the field and have students classify (at least hinge-line orientation) 4) Classification based on interlimb angle Define interlimb angle: Draw on board and write down Classifications: Gentle 180–170°, Open 170–90°, Tight 90–10°, Isoclinal 10–0° Show pictures of folds in the field and have students classify. Outcrop and regional scale. ASSUMES YOU ARE LOOKING AT PROFILE PLANE!!! Pass around isoclinal, recumbent fold. 5) Classification based on shape Cylindrical folds: Introduce poles-to-plane. Poles to surface in cylindrical fold form half circle Chevron or kink folds Cuspate folds Box folds Symmetrical vs. Asymmetrical folds Show pictures of folds in the field and have students classify 6) Classification based on layer thickness Parallel or concentric folds: Constant layer thickness — Because of space issues in the hinge-zones, these folds must die-out. Similar folds: Each folded surface has the same shape — Can be propagated ad infinitum Show pictures of folds in the field and have students classify Ramsay’s dip-isogon classification: Define dip isogons — Class-1A, Class-1B (parallel), Class-1C, Class-2 (similar), and Class-3 7) Additional terms and ideas Parasitic folds: Small folds that occur systematically along the limbs and in the hinge zone of larger folds Disharmonic folds: Die out within a couple of half wavelengths Mechanisms of maintaining strain compatibility in non-similar folds 8) Map symbols for folds Go over map symbols for anticlines, synclines, over-turned anticlines and synclines, and plunging folds Notes Bring fold hand samples