oxidation extraction
advertisement
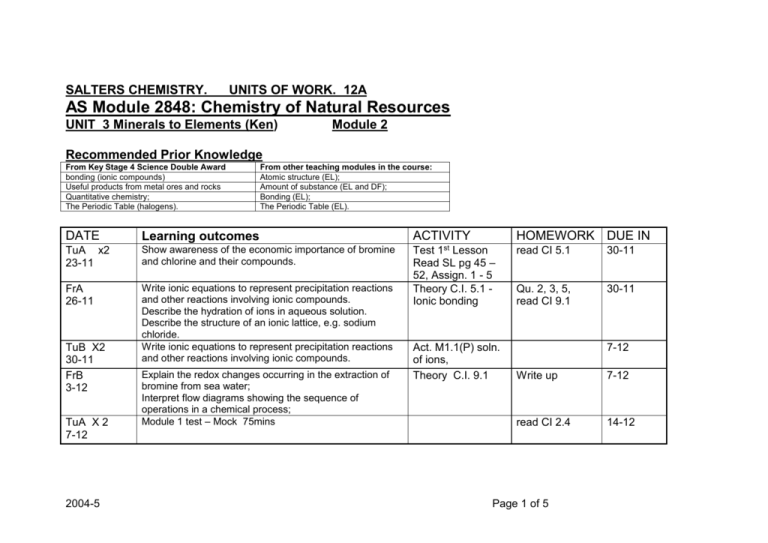
SALTERS CHEMISTRY. UNITS OF WORK. 12A AS Module 2848: Chemistry of Natural Resources UNIT 3 Minerals to Elements (Ken) Module 2 Recommended Prior Knowledge From Key Stage 4 Science Double Award bonding (ionic compounds) Useful products from metal ores and rocks Quantitative chemistry; The Periodic Table (halogens). DATE From other teaching modules in the course: Atomic structure (EL); Amount of substance (EL and DF); Bonding (EL); The Periodic Table (EL). Learning outcomes TuA x2 23-11 Show awareness of the economic importance of bromine and chlorine and their compounds. FrA 26-11 Write ionic equations to represent precipitation reactions and other reactions involving ionic compounds. Describe the hydration of ions in aqueous solution. Describe the structure of an ionic lattice, e.g. sodium chloride. Write ionic equations to represent precipitation reactions and other reactions involving ionic compounds. TuB X2 30-11 FrB 3-12 TuA X 2 7-12 2004-5 Explain the redox changes occurring in the extraction of bromine from sea water; Interpret flow diagrams showing the sequence of operations in a chemical process; Module 1 test – Mock 75mins ACTIVITY HOMEWORK DUE IN 1st Test Lesson Read SL pg 45 – 52, Assign. 1 - 5 Theory C.I. 5.1 Ionic bonding Act. M1.1(P) soln. of ions, Theory C.I. 9.1 read CI 5.1 30-11 Qu. 2, 3, 5, read CI 9.1 30-11 7-12 Write up 7-12 read CI 2.4 14-12 Page 1 of 5 DATE Learning outcomes ACTIVITY HOMEWORK DUE IN FrA 10-12 Use conventions for representing the distribution of electrons in atomic orbitals (no treatment of the shapes of atomic orbitals is expected); Recall the classification of elements into s, p and d blocks; Deduce (given the atomic number) the electronic configuration of atoms from hydrogen to krypton in terms of main energy levels and s, p and d atomic orbitals; Assign oxidation states to the elements in a compound; Use oxidation states to decide which species have been oxidised and which reduced in a redox reaction; Describe redox reactions of s- and p-block elements in terms of electron transfer, using half-equations to represent the oxidation and reduction reaction Explain the redox changes which take place when chlorine, bromine and iodine react with other halide ions; Compare the relative reactivity of the halogens; Recall the reaction between halide ions and silver ions; Recall the following physical properties of the halogens: appearance and state at room temperature, volatility, and solubility in water and organic solvents. Show awareness of the scale and importance of mineral extractive industries and discuss the environmental implications of mineral extraction Describe and explain the major stages in the extraction of a pure metal from its ore. Interpret flow diagrams showing the sequence of operations in a chemical process; Show awareness of the health and safety precautions needed in industry when hazardous chemicals are being stored, transported and used Theory CI 2.4 questions Read CI 11.4 14-12 Act M1.2 Write up, 18-1 CI 11.4 p-block, Gp 7 Even Qus 18-1 Act M1.3 (P) Halogens Write up, 25-1 Read SL M2(pages 53 – 58) do Assign 6 – 8 Ass for M2 25-1 Act M 1.4, M 1.5 theory sheets, Complete 1-2 TuB x2 14-12 FrB 14-1 TuA X2 18-1 FrA 21-1 TuB x2 25-1 2004-5 Page 2 of 5 DATE Learning outcomes ACTIVITY HOMEWORK DUE IN FrB 28-1 TuA x2 1-2 Use the concept of amount of substance to perform calculations involving concentrations of solutions Recap CI 1.5, All Quests Describe and explain he major stages in the extraction of a pure metal from its ore. Act M2.1 (P), M2.2 (P) FrA 4-2 Recognise from the balanced equation for a reaction whether it Is an acid-base, redox, or precipitation reaction. Recall that acid-base reactions involve proton transfer; identify the proton donor and proton acceptor in an acidbase reaction; Describe and explain the major stages in the extraction of a pure metal from its ore. Interpret flow diagrams showing the sequence of operations in a chemical process; Recall the procedure for vacuum filtration Describe examples of giant covalent (network) structures, such as diamond and silicon(IV) oxide; Interpret differences in the physical properties of CO2 and SiO2 in terms of their different structures. Recall the procedure for carrying out an acid-alkali titration and be able to work out the results; CI 8.1 Acid/base TuB X2 8-2 FrB 11-2 TuA 22-2 x2 FrA 25-2 Describe examples of giant covalent (network) structures, such as diamond and silicon (IV) oxide. Interpret differences in the physical properties of CO2 and SiO2 in terms of their different structures. TuB X2 1-3 Preparation for coursework. (EUT next lesson) 2004-5 1-2 8-2 Even Qu.Read CI 5.2 8-2 Begin Act M 2.3(P) Assign 9-10 (2 lessons needed) Complete SL pg 58 - 60 22-2 CI 5.2 molecules Even Qu 22-2 Complete Act. M2.3 (P) – Titration end Act M2.6 Check notes M3 write up M2.3 Read CI 8.1 1-3 Act M2.5 1-3 Act M 2.4 (P) Write up 4-3 Page 3 of 5 DATE Learning outcomes FrB 4-3 TuA x2 8-3 FrA 11-3 TuB x2 15-3 FrB 18-3 TuA X2 22-3 TuB X2 12-4 FrB 15-4 TuA X2 19-4 FrA 22-4 TuB X2 26-4 FrB 29-4 EUT , We begin coursework 2 -3 weeks 2004-5 ACTIVITY HOMEWORK DUE IN Page 4 of 5 DATE Learning outcomes ACTIVITY HOMEWORK DUE IN TuA X2 3-5 FrA 6-5 TuB X2 10-5 FrB 13-5 TuA X2 17-5 FrB 20-5 TuA X2 24-5 FrA 27-5 2004-5 Page 5 of 5