Faults - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

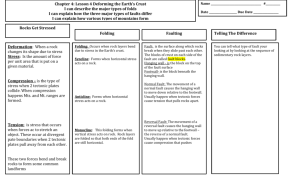
5.1 Earth’s Crust in Motion Notes Questions / Notes What is an earthquake? Earthquake: The shaking and trembling that comes from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. What causes earthquakes? When the tectonic plates of Earth’s lithosphere move they cause stress on the crust. What is stress? How does it create earthquakes? Stress: A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume. Stress adds energy to the rock. Stress is a force; it adds energy to the rock. Stress builds up until there is enough energy to overcome the friction, and the land shifts. The more energy built up, the bigger the quake. Three Types of Stress Are there different types of stress? What are they? Shearing Pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions. Rock breaks, slips apart or changes its shape. Tension Pulls on the crust, stretching rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle. It occurs where two plates are moving apart. Compression Squeezes rock until it breaks. One plate pushing on another compresses rock like a trash compactor. What are faults? Where do they occur? Faults Fault: A break in Earth’s crust where slabs of crust slip past each other. Faults occur when enough stress builds up in rock to make it break. Three Types of Faults Describe and draw the three types of Faults. 1) Strike Slip Faults Found at transform boundaries The rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other sideways with little up or down motion Ex: San Andreas Fault. 2) Normal Faults Found at divergent boundaries. Tension forces in Earth’s crust cause normal faults. The fault is at an angle, so one block of rock lies above the fault while the other block lies below the fault. There is up and down motion. What is the difference between a hanging wall and a footwall? Hanging Wall lies above Footwall lies below When movement occurs along a normal fault, the Hanging Wall slips downward. Tension forces create normal faults where plates diverge, or pull apart. 3) Reverse Faults. Found at convergent boundaries The same structure as a normal fault, but the blocks move in the opposite direction. The rock forming the hanging rock slides UP & OVER the foot wall. What is friction? Friction is the force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another surface. Friction exists because surfaces are not perfectly smooth. Rocks move along a fault depending on how much friction there is between opposite sides of the fault.