Appendix A
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
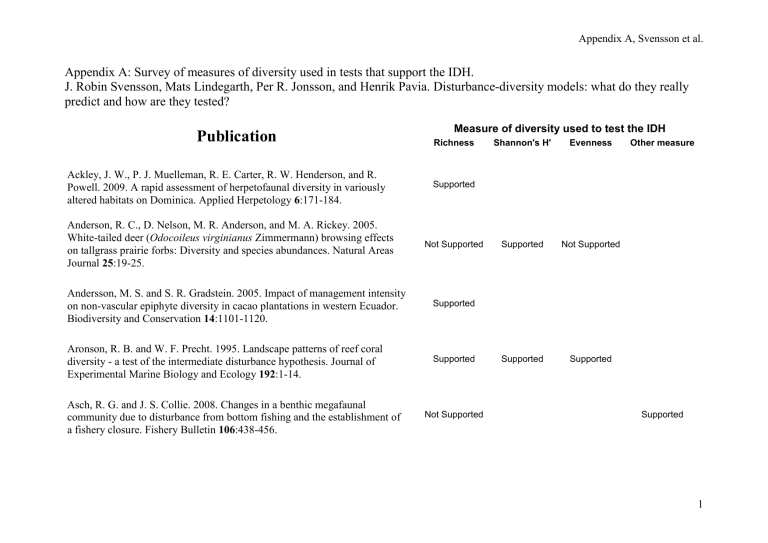
Appendix A: Survey of measures of diversity used in tests that support the IDH.
J. Robin Svensson, Mats Lindegarth, Per R. Jonsson, and Henrik Pavia. Disturbance-diversity models: what do they really predict and how are they tested?
Measure of diversity used to test the IDH
Publication
Richness Shannon's H' Evenness Other measure
Ackley, J. W., P. J. Muelleman, R. E. Carter, R. W. Henderson, and R.
Powell. 2009. A rapid assessment of herpetofaunal diversity in variously altered habitats on Dominica. Applied Herpetology 6 :171-184.
Anderson, R. C., D. Nelson, M. R. Anderson, and M. A. Rickey. 2005.
White-tailed deer ( Odocoileus virginianus Zimmermann) browsing effects on tallgrass prairie forbs: Diversity and species abundances. Natural Areas
Journal 25 :19-25.
Andersson, M. S. and S. R. Gradstein. 2005. Impact of management intensity on non-vascular epiphyte diversity in cacao plantations in western Ecuador.
Biodiversity and Conservation 14 :1101-1120.
Supported
Not Supported Supported Not Supported
Supported
Aronson, R. B. and W. F. Precht. 1995. Landscape patterns of reef coral diversity - a test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Journal of
Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 192 :1-14.
Asch, R. G. and J. S. Collie. 2008. Changes in a benthic megafaunal community due to disturbance from bottom fishing and the establishment of a fishery closure. Fishery Bulletin 106 :438-456.
Supported
Not Supported
Supported Supported
Supported
1
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Atauri, J. A., C. L. De Pablo, P. M. De Agar, M. F. Schmitz, and F. D.
Pineda. 2004. Effects of management on understory diversity in the forest ecosystems of Northern Spain. Environmental Management 34 :819-828.
Austen, M. C., S. Widdicombe, and N. Villano-Pitacco. 1998. Effects of biological disturbance on diversity and structure of meiobenthic nematode communities. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 174 :233-246.
Austen, M. C., S. Widdicombe, and N. Villano-Pitacco. 1998. Second test within the same study
Banitz, T., A. Huth, V. Grimm, and K. Johst. 2008. Clumped versus scattered: how does the spatial correlation of disturbance events affect biodiversity? Theoretical Ecology 1 :231-240.
Baniya, C. B., T. Solhoy, and O. R. Vetaas. 2009. Temporal changes in species diversity and composition in abandoned fields in a trans-Himalayan landscape, Nepal. Plant Ecology 201 :383-399.
Benmayor, R., A. Buckling, M. B. Bonsall, M. A. Brockhurst, and D. J.
Hodgson. 2008. The interactive effects of parasitesf disturbance, and productivity on experimental adaptive radiations. Evolution 62 :467-477.
Bertrand, C., E. Franquet, N. Chomerat, and A. Cazaubon. 2004. An approach to the Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis at the landscape scale: the effects of hydrodynamic disturbance on phytoplankton communities.
Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 161 :351-369.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported
Supported Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported
Supported
2
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Biswas, S. R. and A. U. Mallik. 2010. Disturbance effects on species diversity and functional diversity in riparian and upland plant communities.
Ecology 91 :28-35.
Biswas, S. R. and A. U. Mallik. 2010.Second test within the same experiment
Supported
Supported
Bongers, F., L. Poorter, W. D. Hawthorne, and D. Sheil. 2009. The intermediate disturbance hypothesis applies to tropical forests, but disturbance contributes little to tree diversity. Ecology Letters 12 :798-805.
Bowers, M. A. 1993. Influence of herbivorous mammals on an old-field plant community - years 1-4 after disturbance. Oikos 67 :129-141.
Bowers, M. A. 1993. Second test within the same study
Supported
Supported
Supported
Braccia, A. and J. R. Voshell. 2007. Benthic macroinvertebrate responses to increasing levels of cattle grazing in Blue Ridge Mountain streams, Virginia,
USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 131 :185-200.
Brockhurst, M. A., A. Buckling, and A. Gardner. 2007. Cooperation peaks at intermediate disturbance. Current Biology 17 :761-765.
Brown, C. S., A. F. Mark, G. P. Kershaw, and K. J. M. Dickinson. 2006.
Secondar succession 24 years after disturbance of a New Zealand high-alpine cushionfield. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research 38 :325-334.
Buckling, A., R. Kassen, G. Bell, and P. B. Rainey. 2000. Disturbance and diversity in experimental microcosms. Nature 408 :961-964.
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
3
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Buddle, C. M., D. W. Langor, G. R. Pohl, and J. R. Spence. 2006. Arthropod responses to harvesting and wildfire: Implications for emulation of natural disturbance in forest management. Biological Conservation 128 :346-357.
Burt, J. W. and K. J. Rice. 2009. Not all ski slopes are created equal:
Disturbance intensity affects ecosystem properties. Ecological Applications
19 :2242-2253.
Cadotte, M. W. 2007. Competition-colonization trade-offs and disturbance effects at multiple scales. Ecology 88 :823-829.
Cardinale, B. J., H. Hillebrand, and D. F. Charles. 2006. Geographic patterns of diversity in streams are predicted by a multivariate model of disturbance and productivity. Journal of Ecology 94 :609-618.
Supported
Not Supported Supported
Supported
Supported
Cleary, D. F. R., A. O. Mooers, K. A. O. Eichhorn, J. van Tol, R. de Jong, and S. B. J. Menken. 2004. Diversity and community composition of butterflies and odonates in an ENSO-induced fire affected habitat mosaic: a case study from East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Oikos 105 :426-446.
Cleary DFR, Mooers AO, Eichhorn KAO, et al. ii
Collins, S. L., S. M. Glenn, and D. J. Gibson. 1995. Experimental-Analysis of Intermediate Disturbance and Initial Floristic Composition - Decoupling
Cause and Effect. Ecology 76 :486-492.
Connell, J. H., T. E. Hughes, C. C. Wallace, J. E. Tanner, K. E. Harms, and
A. M. Kerr. 2004. A long-term study of competition and diversity of corals.
Ecological Monographs 74 :179-210.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported
4
Connell, J. H., T. E. Hughes, C. C. Wallace, J. E. Tanner, K. E. Harms, and
A. M. Kerr. 2004. Second test within the same study
Connell, J. H., T. E. Hughes, C. C. Wallace, J. E. Tanner, K. E. Harms, and
A. M. Kerr. 2004. Third test within the same study
Connell, J. H., T. E. Hughes, C. C. Wallace, J. E. Tanner, K. E. Harms, and
A. M. Kerr. 2004. Fourth test within the same study
Crooks, K. R., A. V. Suarez, and D. T. Bolger. 2004. Avian assemblages along a gradient of urbanization in a highly fragmented landscape. Biological
Conservation 115 :451-462.
De Cauwer, B., D. Reheul, K. D'Hooghe, I. Nijs, and A. Milbau. 2006.
Disturbance effects on early succession of field margins along the shaded and unshaded side of a tree lane. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment
112 :78-86. del Pozo, A., C. Ovalle, M. A. Casado, B. Acosta, and J. M. de Miguel.
2006. Effects of grazing intensity in grasslands of the Espinal of central
Chile. Journal of Vegetation Science 17 :791-798.
Devictor, V. and A. Robert. 2009. Measuring community responses to largescale disturbance in conservation biogeography. Diversity and Distributions
15 :122-130.
Doak, D. F. and M. G. Loso. 2003. Effects of grizzly bear digging on alpine plant community structure. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research 35 :421-
428.
Not Supported Supported
Not Supported Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported Supported
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Not Supported
5
Doak, D. F. and M. G. Loso. 2003. Second test within the same study
D'Odorico, P., F. Laio, L. Ridolfi, and M. T. Lerdau. 2008. Biodiversity enhancement induced by environmental noise. Journal of Theoretical
Biology 255 :332-337.
Dorrough, J., J. Ash, and S. McIntyre. 2004. Plant responses to livestock grazing frequency in an Australian temperate grassland. Ecography 27 :798-
810.
Engelmoer, D. J. P. and D. E. Rozen. 2009. Fitness trade-offs modify community composition under contrasting disturbance regimes in
Pseudomonas flouresens microcosms. Evolution 63 :3031-3037.
England, P. R., J. Phillips, J. R. Waring, G. Symonds, and R. Babcock. 2008.
Modelling wave-induced disturbance in highly biodiverse marine macroalgal communities: support for the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Marine and Freshwater Research 59 :515-520.
English, E. I. and M. A. Bowers. 1994. Vegetational gradients and proximity to Woodchuck ( Marmota monax ) borrows in an old field. Journal of
Mammalogy 75 :775-780.
Fedoroff, E., J. F. Ponge, F. Dubs, F. Fernandez-Gonzalez, and P. Lavelle.
2005. Small-scale response of plant species to land-use intensification.
Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment 105 :283-290.
Ferreira, M. N. and S. Rosso. 2009. Effects of human trampling on a rocky shore fauna on the Sao Paulo coast, southeastern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of
Biology 69 :993-999.
Supported Not Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Supported
6
Flecker, A. S. and B. W. Taylor. 2004. Tropical fishes as biological bulldozers: Density effects on resource heterogeneity and species diversity.
Ecology 85 :2267-2278.
Fleming, G. M., J. E. Diffendorfer, and P. H. Zedler. 2009. The relative importance of disturbance and exotic-plant abundance in California coastal sage scrub. Ecological Applications 19 :2210-2227.
Flöder, S. and U. Sommer. 1999. Diversity in planktonic communities: An experimental test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Limnology and
Oceanography 44 :1114-1119.
Fox, J. F. 1981. Intermediate levels of soil disturbance maximize alpine plant diversity. Nature 293 :564-565.
Gallet, R., S. Alizon, P. A. Comte, A. Gutierrez, F. Depaulis, M. van Baalen,
E. Michel, and C. D. M. Muller-Graf. 2007. Predation and disturbance interact to shape prey species diversity. American Naturalist 170 :143-154.
Graham, J. H., A. J. Krzysik, D. A. Kouacic, J. J. Duda, D. C. Freeman, J. M.
Emlen, J. C. Zak, W. R. Long, M. P. Wallace, C. Chamberlin-Graham, J. P.
Nutter, and H. E. Balbach. 2009. Species richness, equitability, and abundance of ants in disturbed landscapes. Ecological Indicators 9 :866-877.
Guo, Q. F. 1996. Effects of bannertail kangaroo rat mounds on small-scale plant community structure. Oecologia 106 :247-256.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
7
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Gutt, J., P. Koubbi, and M. Eleaume. 2007. Mega-epibenthic diversity off
Terre Adelie (Antarctica) in relation to disturbance. Polar Biology 30 :1323-
1329.
Hacker, S. D. and M. D. Bertness. 1999. Experimental evidence for factors maintaining plant species diversity in a New England salt marsh. Ecology
80 :2064-2073.
Hiltunen, T., J. Laakso, and V. Kaitala. 2006. Interactions between environmental variability and immigration rate control patterns of species diversity. Ecological Modelling 194:125-131.
Hiura, T. 1995. Gap formation and species diversity in Japanese beech forests - a test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis on a geographic scale. Oecologia 104 :265-271.
Hixon, M. A. and W. N. Brostoff. 1983. Damselfish as keystone species in reverse - intermediate disturbance and diversity of reef algae. Science
220 :511-513.
Huang, H., J. S. Lian, X. P. Huang, L. M. Huang, R. L. Zou, and D. R.
Wang. 2006. Coral cover as a proxy of disturbance: A case study of the biodiversity of the hermatypic corals in Yongxing Island, Xisha Islands in the South China Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin 51 :129-135.
Hughes, A. R., J. E. Byrnes, D. L. Kimbro, and J. J. Stachowicz. 2007.
Reciprocal relationships and potential feedbacks between biodiversity and disturbance. Ecology Letters 10 :849-864.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported Supported
8
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Ikeda, H. 2003. Testing the intermediate disturbance hypothesis on species diversity in herbaceous plant communities along a human trampling gradient using a 4-year experiment in an old-field. Ecological Research 18 :185-197.
Not Supported Not Supported Supported
Jara, V. C., J. H. S. Miyamoto, B. A. P. da Gama, M. Molis, M. Wahl, and R.
C. Pereira. 2006. Limited evidence of interactive disturbance and nutrient effects on the diversity of macrobenthic assemblages. Marine Ecology-
Progress Series 308 :37-48.
Jiang, L. and S. N. Patel. 2008. Community assembly in the presence of disturbance: A microcosm experiment. Ecology 89 :1931-1940.
Johst, K., J. Gutt, C. Wissel, and V. Grimm. 2006. Diversity and disturbances in the antarctic megabenthos: Feasible versus theoretical disturbance ranges. Ecosystems 9 :1145-1155.
Johst, K. and A. Huth. 2005. Testing the intermediate disturbance hypothesis: when will there be two peaks of diversity? Diversity and
Distributions 11 :111-120.
Kadmon, R. and Y. Benjamini. 2006. Effects of productivity and disturbance on species richness: A neutral model. American Naturalist 167 :939-946.
Kammer, P. M. and A. Mohl. 2002. Factors controlling species richness in alpine plant communities: An assessment of the importance of stress and disturbance. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research 34 :398-407.
Kimbro, D. L. and E. D. Grosholz. 2006. Disturbance influences oyster community richness and evenness, but not diversity. Ecology 87 :2378.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
9
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Kobayashi, T., B. G. Sanderson, and G. N. G. Gordon. 2005. A phytoplankton community in a temperate reservoir in New South Wales,
Australia: relationships between similarity and diversity indices and measures of hydrological disturbance. Marine and Freshwater Research
56 :203-214.
Kuznetsova, N. A. 2009. Soil-dwelling Collembola in coniferous forests along the gradient of pollution with emissions from the Middle Ural Copper
Smelter. Russian Journal of Ecology 40 :415-423.
Köhler, P. and A. Huth. 2007. Impacts of recruitment limitation and canopy disturbance on tropical tree species richness. Ecological Modelling 203 :511-
517.
Lafon, C. W. 2004. Ice-storm disturbance and long-term forest dynamics in the Adirondack Mountains. Journal of Vegetation Science 15 :267-276.
Leis, S. A., D. M. Engle, D. M. Leslie, and J. S. Fehmi. 2005. Effects of short- and long-term disturbance resulting from military maneuvers on vegetation and soils in a mixed prairie area. Environmental Management
36 :849-861.
Lenz, M., M. Molis, and M. Wahl. 2004a. Experimental test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis: frequency effects of emersion on fouling communities. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology
305 :247-266.
Lenz, M., M. Molis, and M. Wahl. 2004b. Testing the intermediate disturbance hypothesis: response of fouling communities to various levels of emersion intensity. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 278 :53-65.
Not Supported Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
10
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Lepczyk, C. A., C. H. Flather, V. C. Radeloff, A. M. Pidgeon, R. B.
Hammer, and J. G. Liu. 2008. Human impacts on regional avian diversity and abundance. Conservation Biology 22 :405-416.
Li, J., W. A. Loneragan, J. A. Duggin, and C. D. Grant. 2004. Issues affecting the measurement of disturbance response patterns in herbaceous vegetation - A test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Plant Ecology
172 :11-26.
Li, J., W. A. Loneragan, J. A. Duggin, and C. D. Grant. 2004. Second test within the same study
Li, J., W. A. Loneragan, J. A. Duggin, and C. D. Grant. 2004. Third test within the same study
Lindholm, M., D. O. Hessen, and L. Ramberg. 2009. Diversity, dispersal and disturbance: cladoceran species composition in the Okavango Delta. African
Zoology 44 :24-35.
Lite, S. J., K. J. Bagstad, and J. C. Stromberg. 2005. Riparian plant species richness along lateral and longitudinal gradients of water stress and flood disturbance, San Pedro River, Arizona, USA. Journal of Arid Environments
63 :785-813.
Liu, B., W. Z. Zhao, Z. J. Wen, J. R. Teng, and X. H. Li. 2009. Floristic
Characteristics and Biodiversity Patterns in the Baishuijiang River Basin,
China. Environmental Management 44 :73-83.
Supported
Supported Not Supported Not Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported Not Supported Supported
11
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Lubchenco, J. 1978. Plant species diversity in a marine intertidal community
- importance of herbivore food preference and algal competitive abilities.
American Naturalist 112 :23-39.
Martinsen, G. D., J. H. Cushman, and T. G. Whitham. 1990. Impact of
Pocket Gopher disturbance on plant species diversity in a shortgrass prairie community. Oecologia 83 :132-138.
McGuinness, K. A. 1987. Disturbance And Organisms On Boulders .2.
Causes Of Patterns In Diversity And Abundance. Oecologia 71 :420-430.
McIntire, E. J. B. and D. S. Hik. 2005. Influences of chronic and current season grazing by collared pikas on above-ground biomass and species richness in subarctic alpine meadows. Oecologia 145 :288-297.
Melis, C., M. Sundby, R. Andersen, A. Moksnes, B. Pedersen, and E.
Roskaft. 2007. The role of moose Alces alces L. in boreal forest - the effect on ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) abundance and diversity.
Biodiversity and Conservation 16 :1321-1335.
Michalet, R., R. W. Brooker, L. A. Cavieres, Z. Kikvidze, C. J. Lortie, F. I.
Pugnaire, A. Valiente-Banuet, and R. M. Callaway. 2006. Do biotic interactions shape both sides of the humped-back model of species richness in plant communities? Ecology Letters 9 :767-773.
Miyake, Y. and S. Nakano. 2002. Effects of substratum stability on diversity of stream invertebrates during baseflow at two spatial scales. Freshwater
Biology 47 :219-230.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
12
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Miyake, Y. and S. Nakano. 2002. Second test within the same study
Molino, J. F. and D. Sabatier. 2001. Tree diversity in tropical rain forests: A validation of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Science 294 :1702-
1704.
Molis, M., M. Lenz, and M. Wahl. 2003. Radiation effects along a UV-B gradient on species composition and diversity of a shallow-water macrobenthic community in the western Baltic. Marine Ecology-Progress
Series 263 :113-125.
Morabito, G., A. Oggioni, and P. Panzani. 2003. Phytoplankton assemblage at equilibrium in large and deep subalpine lakes: a case study from Lago
Maggiore (N. Italy). Hydrobiologia 502 :37-48.
Morgan, A. D. and A. Buckling. 2004. Parasites mediate the relationship between host diversity and disturbance frequency. Ecology Letters 7 :1029-
1034.
Mouritsen, K. N. and R. Poulin. 2005. Parasites boosts biodiversity and changes animal community structure by trait-mediated indirect effects. Oikos
108 :344-350.
Niedrist, G., E. Tasser, C. Luth, J. Dalla Via, and U. Tappeiner. 2009. Plant diversity declines with recent land use changes in European Alps. Plant
Ecology 202 :195-210.
Not Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported Supported
Supported
Not Supported Supported Not Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported
Supported Not Supported
Oba, G., R. B. Weladji, W. J. Lusigi, and N. C. Stenseth. 2003. Scaledependent effects of grazing on rangeland degradation in northern Kenya: A test of equilibrium and non-equilibrium hypotheses. Land Degradation &
Development 14 :83-94.
Supported
Supported
13
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Olofsson, J. and H. Shams. 2007. Determinants of plant species richness in an alpine meadow. Journal of Ecology 95 :916-925.
Paidere, J., D. Gruberts, A. Skute, and I. Druvietis. 2007. Impact of two different flood pulses on planktonic communities of the largest floodplain lakes of the Daugava River (Latvia). Hydrobiologia 592 :303-314.
Parvinen, K. and G. Meszena. 2009. Disturbance-generated nichesegregation in a structured metapopulation model. Evolutionary Ecology
Research 11 :651-666.
Patricio, J., F. Salas, M. A. Pardal, S. E. Jorgensen, and J. C. Marques. 2006.
Ecological indicators performance during a re-colonisation field experiment and its compliance with ecosystem theories. Ecological Indicators 6 :43-57.
Patricio, J., R. Ulanowicz, M. A. Pardal, and J. C. Marques. 2004.
Ascendency as an ecological indicator: a case study of estuarine pulse eutrophication. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 60 :23-35.
Peterson, D. W. and P. B. Reich. 2008. Fire frequency and tree canopy structure influence plant species diversity in a forest-grassland ecotone. Plant
Ecology 194 :5-16.
Pfauder, A. and M. Zimmer. 2005. Intermediate tidal stress promotes the detritivore-mediated decomposition of Spartina litter. European Journal of
Soil Biology 41 :135-141.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported Not Supported Not Supported
Supported
Supported Not Supported
Supported
14
Piou, C., U. Berger, H. Hildenbrandt, and I. C. Feller. 2008. Testing the intermediate disturbance hypothesis in species-poor systems: A simulation experiment for mangrove forests. Journal of Vegetation Science 19 :417-
U153.
Pöyry, J., M. Luoto, J. Paukkunen, J. Pykälä, K. Raatikainen, and M.
Kuussaari. 2006. Different responses of plants and herbivore insects to a gradient of vegetation height: an indicator of the vertebrate grazing intensity and successional age. Oikos 115 :401-412.
Rejmanek, M., E. Rejmankova, and W. Holzner. 2004. Species diversity of plant communities on calcareous screes: the role of intermediate disturbance.
Preslia 76 :207-222.
Renöfält, B. M., C. Nilsson, and R. Jansson. 2005. Spatial and temporal patterns of species richness in a riparian landscape. Journal of Biogeography
32 :2025-2037.
Ritter, C., P. A. Montagna, and S. Applebaum. 2005. Short-term succession dynamics of macrobenthos in a salinity-stressed estuary. Journal of
Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 323 :57-69.
Roxburgh, S. H., K. Shea, and J. B. Wilson. 2004. The intermediate disturbance hypothesis: Patch dynamics and mechanisms of species coexistence. Ecology 85 :359-371.
Sasaki, T., S. Okubo, T. Okayasu, U. Jamsran, T. Ohkuro, and K. Takeuchi.
2009. Management applicability of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis across Mongolian rangeland ecosystems. Ecological Applications 19 :423-
432.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Supported
15
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Scheffler, P. Y. 2005. Dung beetle (Coleoptera : Scarabaeidae) diversity and community structure across three disturbance regimes in eastern Amazonia.
Journal of Tropical Ecology 21 :9-19.
Scholes, L., P. H. Warren, and A. P. Beckerman. 2005. The combined effects of energy and disturbance on species richness in protist microcosms.
Ecology Letters 8 :730-738.
Not Supported Not Supported
Supported
Schratzberger, M. and R. M. Warwick. 1998. Effects of physical disturbance on nematode communities in sand and mud: a microcosm experiment.
Marine Biology 130 :643-650.
Not Supported Supported
Schratzberger, M., N. Lampadariou, P. Somerfield, L. Vandepitte, and E.
Vanden Berghe. 2009. The impact of seabed disturbance on nematode communities: linking field and laboratory observations. Marine Biology
156 :709-724.
Sheil, D. 2001. Long-term observations of rain forest succession, tree diversity and responses to disturbance. Plant Ecology 155 :183-199.
Sheil, D. and D. Burslem. 2003. Disturbing hypotheses in tropical forests.
Trends in Ecology & Evolution 18 :18-26.
Sommer, U. 1995. An experimental test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis using cultures of marine phytoplankton. Limnology and
Oceanography 40 :1271-1277.
Supported
Supported
Supported Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
16
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Sousa, W. P. 1979a. Disturbance in marine intertidal boulder fields: the nonequilibrium maintenance of species diversity. Ecology 60 :1225 – 1239.
Sousa, W. P. 1979b. Experimental investigations of disturbance and ecological succession in a rocky intertidal algal community. Ecological
Monographs 49 :227-254.
Stone, W. E. and M. L. Wolfe. 1996. Response of understory vegetation to variable tree mortality following a mountain pine beetle epidemic in lodgepole pine stands in northern Utah. Vegetatio 122 :1-12.
Suominen, O., J. Niemela, P. Martikainen, P. Niemela, and I. Kojola. 2003.
Impact of reindeer grazing on ground-dwelling Carabidae and Curculionidae assemblages in Lapland. Ecography 26 :503-513.
Suren, A. M. and M. J. Duncan. 1999. Rolling stones and mosses: effect of substrate stability on bryophyte communities in streams. Journal of the North
American Benthological Society 18 :457-467.
Svensson, J. R., M. Lindegarth, M. Siccha, M. Lenz, M. Molis, M. Wahl, and H. Pavia. 2007. Maximum species richness at intermediate frequencies of disturbance: Consistency among levels of productivity. Ecology 88 :830-
838.
Svensson, J. R., M. Lindegarth, and H. Pavia. 2009. Equal rates of disturbance cause different patterns of diversity. Ecology 90 :496-505.
Szentkiralyi, F. and F. Kozar. 1991. How many species are there in apple insect communities - testing the resource diversity and intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Ecological Entomology 16 :491-503.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
17
Supported
Supported
Tam, T. W. and P. O. Ang. 2009. Catastrophic regime shifts in coral communities exposed to physical disturbances: Simulation results from object-oriented 3-dimensional coral reef model. Journal of Theoretical
Biology 259 :193-208.
Thorp, J. H. and M. L. Cothran. 1984. Regulation of fresh water community structure at multiple intensities of Dragonfly predation. Ecology 65 :1546-
1555.
Townsend, C. R., M. R. Scarsbrook, and S. Doledec. 1997. The intermediate disturbance hypothesis, refugia, and biodiversity in streams. Limnology and
Oceanography 42 :938-949.
Valdivia, N., A. Heidemann, M. Thiel, M. Molis, and M. Wahl. 2005.
Effects of disturbance on the diversity of hard-bottom macrobenthic communities on the coast of Chile. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 299 :45-
54.
Vanselow, K. A., M. Kolb, and T. Fickert. 2007. Destruction and regeneration of terrestrial, littoral and marine ecosystems on the Island of
Guanaja/Honduras seven years after Hurricane Mitch. Erdkunde 61 :358-371.
Weider, L. J. 1992. Disturbance, competition and the maintenance of clonal diversity in Daphnia pulex . Journal of Evolutionary Biology 5 :505-522.
Weithoff, G., N. Walz, and U. Gaedke. 2001. The intermediate, disturbance hypothesis - species diversity or functional diversity? Journal of Plankton
Research 23 :1147-1155.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Supported Not Supported
Not Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
18
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Vetaas, O. R. 1997. The effect of canopy disturbance on species richness in a central Himalayan oak forest. Plant Ecology 132 :29-38.
Widdicombe, S. and M. C. Austen. 1998. Experimental evidence for the role of Brissopsis lyrifera (Forbes, 1841) as a critical species in the maintenance of benthic diversity and the modification of sediment chemistry. Journal of
Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 228 :241-255.
Wilson, S. D. and D. Tilman. 2002. Quadratic variation in old-field species richness along gradients of disturbance and nitrogen. Ecology 83 :492-504.
Vonlanthen, C. M., P. M. Kammer, W. Eugster, A. Buhler, and H. Veit.
2006. Alpine vascular plant species richness: the importance of daily maximum temperature and pH. Plant Ecology 184 :13-25.
Vujnovic, K. 2002. Predicting plant species diversity in response to disturbance magnitude in grassland remnants of central Alberta. Canadian
Journal of Botany 80 :504.
Xavier, E. D., B. A. P. da Gama, T. F. Porto, B. L. Antunes, and R. C.
Pereira. 2008. Effects of disturbance area on fouling communities from a tropical environment: Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Brazilian
Journal of Oceanography 56 :73-84.
Zacharias, M. A. and J. C. Roff. 2001. Explanations of patterns of intertidal diversity at regional scales. Journal of Biogeography 28 :471-483.
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported Supported
Supported Supported
19
Appendix A, Svensson et al.
Zerbe, S., U. Maurer, S. Schmitz, and H. Sukopp. 2003. Biodiversity in
Berlin and its potential for nature conservation. Landscape and Urban
Planning 62 :139-148.
Zhang, Z. D., R. G. Zang, and Y. D. Qi. 2008. Spatiotemporal patterns and dynamics of species richness and abundance of woody plant functional groups in a tropical forest landscape of Hainan Island, south China. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 50 :547-558.
Zhu, W. Z., S. Cheng, X. H. Cai, F. He, and J. X. Wang. 2009. Changes in plant species diversity along a chronosequence of vegetation restoration in the humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Rainy Zone of West China.
Ecological Research 24 :315-325.
Zinck, R. D., K. Johst, and V. Grimm. 2010. Wildfire, landscape diversity and the Drossel-Schwabl model. Ecological Modelling 221 :98-105.
Supported
Supported
Supported Supported Not Supported
Supported
20