Agglutination tests
advertisement

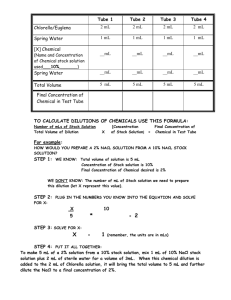
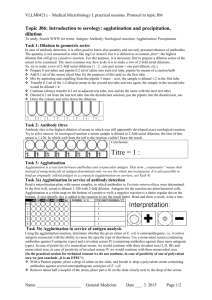
Agglutination tests -1 In this reaction the antigen is is part of the surface of some particulate material such as Red Blood Cell, Bacterium or perhaps an inorganic particles (e.g. poly styrene latex) which has been coated with antigen. Antibody added to a suspension of such particles combines with the surface antigens and links them together to form visible aggregates or agglutinate. It is of two types: 1- Direct: Ag is used to detect the Ab in the patient's serum. 2- Indirect:passive/ carrier particles Ag. In it's simplest form, an agglutination test is set up in round bottomed test tubes or Perspex plates and doubling dilutions of the antiserum are made up in the tubes (neat, 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, etc..). The particulate antigen is then added, and after incubation at 37OC, agglutination may be seen in the bottom of the tubes. The last tube clearly showing visible agglutination is the end point of the test, e.g. 1/320 is known as the titre of the antiserum and is a measure of the number of the antibody units per unit volume of serum ( if the end point occurs at 1/320 dilution, and the test is carried out in one ml volumes, the titre of the serum is 320 units per ml of serum. One practical difficulty of importance in agglutination tests is the occasional inhibition agglutination in the first tubes of an antiserum dilution series, were the tubes containing more dilute antiserum. This is known as the PROZONE PHENOMENON, we can eliminate this phenomena by diluting the serum in normal saline 1- Tube agglutination tests For laboratory diagnosis of brucellosis For laboratory diagnosis of salmonellosis (Widal test) 2- Slide agglutination tests In determination of ABO blood group In determination of Rh factor In salmonellosis 3- Carrier latex particle agglutination tests: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA factor) In pregnancy, using agglutination inhibition In measurement of serum C-reactive protein (CRP) 1- Tube agglutination test: Exercise- 1- laboratory diagnosis of brucellosis (direct) 1- Qualitative test: using clean slides. 2- Quantitative test Used to detect Brucella ( Abortus, suis) antibodies in the serum Materials: a. Antigen b. Test sera c. Control positive sera d. 10 tubes e. Phenol saline f. Pipettes 1ml g. Rack and Water bath 37C o Method: Prepare serial doubling dilution Place 0.8 ml of phenol saline in the first tube and 0.5 ml in each succeeding tube. Place 0.2 ml of the serum in the first only and mix. Using clean pipette, transfer 0.5 ml of the mixture to the second tube…..take 0.5 ml from tube 9 and discard it. By this way the dilution be 1/5, 1/10, 1/20 and so on. To each tube add 0.5 ml of the Brucella abortus antigen. Mix well, thus giving the final; dilution 1/10, 1/20, 1\40,1/80, 1/160. The tenth tube is a negative control tube containing the diluent and the antigen only. The same number of tubes and the same dilution should be performed using the positive control. After both sets are prepared, place in 370C for 24 hours before the result are read. Result: The tube are read most readily by reflected rather by than transmitted light. The degree of agglutination is assessed on the amount of clearing that has taken place in the tube as compared with a standard tube. Complete agglutination is indicated by complete clearing of the fluid and the presence of a thin veil-like film at the bottom of the tube. When no agglutination has occurred, the fluid will be as turbid as that of the control tube. According to that record your observation as follow: 4+ All bacterium appears agglutinated on the bottom of the tube and supernatant fluid is clear. 3+ Approximately 75% of bacterium are agglutinated and supernatant fluid is slightly cloudy. 2+ Approximately 50 % of bacterium are agglutinated and supernatant fluid is moderately cloudy. 1+ Approximately 25 % of bacterium are agglutinated and supernatant fluid is cloudy. the the the the Negative : no agglutination is observed and the supernatant fluid is turbed. Titre : reciprocal value of serum dilution in which at least 2+ (50 %) agglutination occurs. Exercise- 2- Widal Test To detect the presence of Salmonella Typhi antibodies. The procedure is the same as brocelosis test but change the reagnt and the water bath is at 45- 50 0C and time depend on the reagent. Result: 1: 80 is significant. Exercise- 3- Erythrocyte agglutination Test To demonstrate the titre of the Ab in the patient's serum using sheep RBCs. 2- Slide agglutination test: Exercise- 1- ABO blood grouping To detect antigen present on the surface of RBCs using anti-A, anti B and anti-D 3- Carrier latex particle agglutination tests (Indirect): Rheumatoid arthritis (RA factor) Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease, it is systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks the joints producing an inflammatory synovitis that often progresses to destruction of the articular cartilage of the joints. Rheumatoid factor (RF or RhF) is an autoantibody (antibody directed against an organism's own tissues) most relevant in rheumatoid arthritis. It is an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG, which is itself an antibody. RF and IgG join to form immune complexes which contribute to the disease process. Not all people with rheumatoid arthritis have detectable rheumatoid factor. Those who do not are said to be "seronegative".