ADHD: Medication Guide for Family Physicians
advertisement

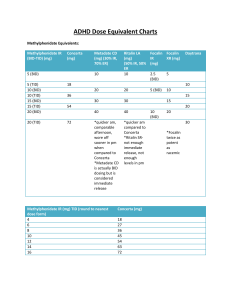
Rev. Fri, Aug 13, 2010 Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (AD/HD) in Children and Youth: Medication Guide for Physicians Compiled by Michael Cheng, Child and Family Psychiatrist, Ottawa Purpose of this Handout This handout is only a very brief summary of key ADHD medications and dosages. For more detailed information, please see: the excellent Canadian ADHD Practice Guidelines at http://www.caddra.ca as well as the Revised Texas Mediation Algorithm for ADHD, in the June 2006 issue of the Journal of the Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Where to Get this Handout This handout is available from http://www.drcheng.ca in the Mental Health Information section. Any comments and suggestions are welcome and will help ensure this handout is helpful. Disclaimer The content of this document is for general information and education only. It is not to be used in any other manner, and is not intended as medical, psychiatric or psychological advice. No doctor/patient relationship is formed. The accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the content is not warranted or guaranteed. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Users should always seek the advice of physicians or other qualified health providers with any questions regarding a medical condition. Any procedure or practice described here should be applied by a health professional under appropriate supervision in accordance with professional standards of care used with regard to the unique circumstances that apply in each practice situation. The authors disclaim any liability, loss, injury, or damage incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, or the use and application of any of the contents of this document. This work is “licensed” under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-Non Commercial-Sharelike 2.0, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/) which means that you are free to copy, distribute, display and perform the work, and make derivative works as long as you give the original author credit, the work is not used for commercial purposes, and if you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under a license identical to this one. 2 of 9 Table of Contents ADHD Strategies from the Texas Algorithm Project, 2006 ............................................................. 3 ADHD Medications: Dextroamphetamine Formulations .................................................................. 4 ADHD Medications: Methylphenidate Formulations ........................................................................ 5 Conversion Chart Comparing Immediate Release (IR) to Long-Acting Preparations ..................... 6 ADHD Medications: Non-Stimulants................................................................................................ 7 ADHD Medications: Non-Stimulants (Continued) ............................................................................ 8 Medical Issues for ADHD Medications ............................................................................................ 9 ADHD and Comorbid Conditions ..................................................................................................... 9 3 of 9 ADHD Strategies from the Texas Algorithm Project, 2006 (Reproduced under Fair Use Provision of U.S. Copyright Law) 4 of 9 ADHD Medications: Dextroamphetamine Formulations Medication Trade name Adderall XR (5, 7.5,10, 12.5, 15, 20,30 mg tabs) www.adderall.com (Capsule can be opened and beads sprinkled on apple sauce, but not chewed) Dextroamphetaminelevoamphetamine Adderall (5.10,20 mg tabs) www.adderall.com (Not commonly used in Canada due to availability of XR) Dextroamphetamine Dexedrine (regular) (5 mg scored tabs) Dextroamphetamine sustained release Dexedrine spansules (10, 15 mg sustained release capsule – cannot be split) Lisdexamfetamine Vyvanse (20,30,40,50,60 mg capsules) For all Dextroamphetamine formulations (including Dexedrine, Dexedrine spansules, Adderall, Adderall XR), use Dosage range of 2.5-40 mg/day or 0.1-0.8 mg/kg/day (1), usually target for 0.5 mg/kg/day Dosage range of 2.5-40 mg/day or 0.1-0.8 mg/kg/day (1), usually target for 0.5 mg/kg/day Given only once daily due to extended release formulation Give 10-30 mg in morning Half-life 11-13 hours; Onset of action 1-2 hr min; Peak effect bimodal; Duration of action 10-12 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage range <25 kg 5 mg q morning Up to 15 mg q morning 25-35 kg 10 mg q morning Up to 20 mg q morning >35 kg 10 mg q morning Up to 30 mg q morning Dosage range of 2.5-40 mg/day or 0.1-0.8 mg/kg/day (1), usually target for 0.5 mg/kg/day Generally given morning, lunch, possibly lunch Half-life 4-6 hours; Onset of action 30-60 min; Peak effect 1-2 hr; Duration of action 4-6 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage range <25 kg 2.5-5 mg q morning Up to 10 mg q morning or bid 25-35 kg 5-10 mg q morning Up to 10-15 mg q morning or bid >35 kg 10 mg q morning Up to 20-40 mg q morning or bid Dosage range of 2.5-40 mg/day or 0.1-0.8 mg/kg/day, usually target for 0.5 mg/kg/day Generally given morning, lunch, possibly lunch Half-life 4-6 hours; Onset of action 20-60 min; Peak effect in 1-2 hr; Duration of action 4-6 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage range <25 kg 2.5 mg q morning Up to 10-15 mg bid 25-35 kg 5 mg bid Up to 10 mg tid >35 kg 10 mg bid Up to 15 mg tid Dosage range of 2.5-40 mg/day or 0.1-0.8 mg/kg/day (1), usually target for 0.5 mg/kg/day Generally given once daily, but may need afternoon dosage of the regular shortacting Half-life 6-10 hrs; Onset of action 60-90 min, Peak effect (info not available); Duration of action 6-8 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage range <25 kg Per clinical judgement Per clinical judgement 25-35 kg 10 mg spansule q morning >35 kg 20 mg spansule q morning Up to 30 mg spansule q morning Up to 45 mg spansule q morning Start 20-30 mg od q AM Increase up to 60 mg daily Capsule contents may be dissolved in glass of water Consider starting first with long-acting formulation, e.g. Dexedrine spansules. 5 of 9 ADHD Medications: Methylphenidate Formulations Medication Name Trade Name Comments Methylphenidate (standard) Ritalin (5,10,20 mg scored tabs) www.adhdinfo.com Generic Dosage range 0.6-2.1 mg/kg/day, usually target for 1 mg/kg/day in divided doses Usually given morning, lunch, often afternoon as well Half-life 4-6 hrs; Onset of action 20-60 min, Peak effect ~ 2-hr; Duration of action 3-6 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage Range <25 kg 2.5 mg bid Up to 15 mg tid 25-35 kg 5 mg bid Up to 20 mg tid >35 kg 10 mg bid Up to 20 mg tid Dosage range 0.6-2.1 mg/kg/day, usually target for 1 mg/kg/day in divided doses Usually given once in morning only, but may need afternoon dosage Half-life 8 hrs; Onset of action 60-90 min, Peak effect ~ 5-hr; Duration of action 5-8 hr Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage Range < 25 kg Per clinical judgement Per clinical judgement 25-35 kg 20 mg SR in morning Up to 20 mg SR in morning + 10 mg tid >35 kg 20 mg SR in morning Up to 40 mg SR in morning, or 20 mg SR in morning + 20 mg tid Target for 1 mg/kg/day, maximum of 2 mg/kg/day Given only once daily, since controlled release Half-life 12-hr; Onset of action 30-120 min, Peak effect bimodal; Duration of action 12-hr Methylphenidate (longacting) Ritalin SR (20 mg slow or sustained release capsule) www.adhdinfo.com Concerta (controlled release) (18,27,36,54 mg controlled release tabs with immediate release outer coating – cannot be split) www.concerta.net For patients not currently taking methylphenidate, or for patients who are on stimulants other than methylphenidate Child’s Size Starting Dose Dosage Range < 25 kg Per clinical judgement Per clinical judgement 25-35 kg 18 mg daily, increase by 18 mg weekly 18 mg daily, increase by 18 mg weekly 18-36 mg daily >35 kg 36-54 mg daily For patients already on methylphenidate: Previous Methylphenidate (MPH) Daily Dose 5 mg bid or 5 mg tid or 20 mg SR 10 mg bid or 10 mg tid or 40 mg SR 15 mg bid or 15 mg tid or 60 mg SR Biphentin (10,15,20,30,40,50,60, 80 mg controlled release capsule) Concerta Dose ~ 18 mg q am ~ 36 mg q am ~ 54 mg q am Capsules may be sprinkled on soft foods (e.g. apple sauce, yogurt, ice cream), and must be swallowed without chewing or crushing Age 6-18: Start at 10-20 mg daily, titrate upwards weekly by 10 mg, up to 1 mg /kg/day or max daily dosage of 60 mg Age 18+: Start 10-20 mg daily, titrate upwards weekly by 10 mg, up to 1 mg/kg/day, or max daily dosage 80 mg 6 of 9 Switching Guide Dosing schedule for switching medications (from Clinical Focus, from ShireBioChem) If you prescribe Dexedrine Prescribe Adderall XR 5 mg bid, or Spansule 10 mg 10 mg bid, or Spansule 20 mg 15 mg bid or Spansule 30 mg Plus a delayed release dose of… 10 mg qAM This provides an immediate release dose of.. 5 mg 20 mg qAM 10 mg 10 mg 30 mg qAM 15 mg 15 mg If you prescribe Methylphenidate Prescribe Concerta Plus a delayed release dose of… 5 mg bid/tid, or 20 mg SR 10 mg bid/tid or 40 mg SR 15 mg bid/tid or 60 mg SR 18 mg qAM This provides an immediate release dose of.. 4 mg 36 mg qAM 8 mg 28 mg 54 mg qAM 12 mg 42 mg 5 mg 14 mg Conversion Chart Comparing Immediate Release (IR) to LongActing Preparations* Methylphenidate-IR 5 mg po tid 10 mg po tid 15 mg po tid 20 mg po tid Dextroamphetamine-IR 2.5 mg po tid 5 mg po tid 7.5 mg po tid 10 mg po tid Adderall XR 5-10 mg po daily 15 mg po daily 25 mg po daily 30 mg po daily Concerta 18 mg po daily 36 mg po daily 54 mg po daily 2 x 36 mg po daily Note: 1 mg/day dextroamphetamine = 1 mg/day Adderall XR = 2 mg/day methyphenidate Note: for Concerta, approximate the first-of-the-day IR dosage with 22% of the Concerta dose, e.g. the first 5 mg of a 5 mg tid dose approximates 22% of the 18 mg Concerta dose, the first 10 mg of a 10 mg tid dose approximates 22% of the 36 mg dose = 8 mg, etc. If your patient is on 105-5 rather than 10-10-10, then s/he will probably need the 36 mg Concerta dose. * Dr. Catharine Robertson, Psychiatrist, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd, Ottawa, ON, K1H 8L1 7 of 9 ADHD Medications: Non-Stimulants Drug Name Trade Name Comments Bupropion (Wellbutrin) Wellbutrin SR (supplied as 100,150 mg tabs) Consider for ADHD plus depression, or substance use problems Child maximum: 6 mg/kg/day; Adolescent maximum 400 mg/day Sample Titration: Initial target: 100 bid for children; 150 mg bid for teens In adults, target of 300-450 mg daily divided bid Thus Week 1: 100 mg mornings Week 2: 100 mg morning + 100 mg dinner – leave at this initial target dose with children, and reassess Week 3: 150 mg morning and 100 mg dinner Week 4: 150 morning and 150 mg dinner then reassess – leave at this initial target dosage for adolescents For child: Start at 100 mg daily; may increase up to 150 mg daily if necessary For teens/adults: Start at 100 mg daily; increase up to 300-450 mg daily Non-stimulant treatment, may be helpful in situations where stimulant side effects are not tolerated Do not break capsules Target dosage range of 1.2 mg/kg/day Sample Titration: Week 1 : 0.5 mg/kg/day Week 2 : 0.8 mg/kg/day Week 3 : 1.2 mg/kg/day Dosage for youth > 70 kg and for adults Week 1: Start at 40 mg daily Week 2: 60 mg daily Week 3: 80 mg After 30 days, re-assess and readjust dosage Maximum dosage: 1.4 mg/kg/day or 100 mg/day, whichever is less Wellbutrin XL Atomoxetine Strattera www.strattera.com (supplied as 10,18,25,40,60 mg capsule) Recommended Atomoxetine (Strattera) Dose Titration in Children and Adolescents up to 70 kg Body Weight (from Strattera Product Monograph, Dec 22, 2004) Body Weight Start Dose (~ 0.5 mg/kg/day) Intermediate Dosage (~0.8 mg/kg/day) 20-29 kg 30-44 kg 45-64 kg 65-70 kg 10 mg 18 mg 25 mg 40 mg 18 mg 25 mg 40 mg 60 mg Initial Target Dosage (“High Dose”) (~ 1.2 mg/kg/day) 25 mg 40 mg 60 mg 80 mg 8 of 9 ADHD Medications: Non-Stimulants (Continued) Drug Name Trade Name Comments Modafinil Provigil (supplied as 100,200mg tablets) Novel ‘stimulant’, which appears to increase arousal where needed, but without causing typical stimulant side effects such as insomnia For adults: 100-200 mg once daily in the morning For children/youth (Cephalon study): dosages used in studies included 300 mg once in the morning; alternatively, 100 mg morning; then gradually increase to 200 mg morning and 100 mg lunchtime; (Note that Cephalon will be releasing a new proprietary 340 mg/425 mg formulation specifically for ADHD) Primarily for impulsivity, or used at bedtime as sleep-aid 0.05 mg given orally qhs Target: up to 0.4 mg/day (4-5 mcg/kg/day). Bid/tid for daytime impulsivity (or QHS if just for sleep) Start: 10-25 mg Target: up to 100-150 mg daily Clonidine Catapres (supplied as 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 / tab) Desipramine Norpramin (supplied as 10,35,50,75,100,150 mg tabs) Imipramine Tofranil (supplied as 10,25,50 mg tabs) Nortriptyline Pamelor (supplied as 10,25,50,75 mg capsules) Start: 10-25 mg Target 100-150 mg daily Max: 5 mg/kg/day Start 10-25 mg Target: 100-150 mg daily Max: 3 mg/kg/day References for Modafinil : Recent study by Cephalon in summer 2004 showed effectiveness with youth aged 6-17 with mean dosage of 300 mg daily, given 200 mg morning and 100 mg lunchtime Rugino et al.: Modafinil in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatr Neurol. 2003 Aug;29(2):136-42. Turner DC et al.: Modafinil improves cognition and response inhibition in adult attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2004 May 15;55(10):1031-40. Biederman J, Swanson JM, Wigal SB, et al. Efficacy and safety of modafinil film-coated tablets in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: results of a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study. Pediatrics 2005;116:E777–84. 9 of 9 Medical Issues for ADHD Medications Recommended Baseline Testing by American Heart Association (published in Circulation on Apr 21, 2008) To help identify children who are at potentially increased risk, including those already taking stimulant medication, AHA recommends: History Take a patient history, including fainting, dizziness, seizures, chest pain or shortness of breath Take a family history, including sudden cardiac death at young ages (<30 years old) and cardiac arrhythmias; Physical Examination Always assess blood pressure and heart rate, particularly in adults Look for abnormal heart murmur, hypertension, arrhythmia and findings suggestive of Marfan syndrome; and Investigations Baseline ECG and have it read by a pediatric cardiologist or physician with expertise in reading pediatric ECGs. For pediatric patients, holter or graded exercise is not necessary unless clinically indicated If any significant findings on physical exam, ECG or history consult pediatric cardiologist Monitoring Regular assessments of blood pressure and pulse, repeat ECGs in certain situations, Careful monitoring and possible discontinuation of stimulant medication in children found to be at increased risk. ADHD and Comorbid Conditions With ADHD and comorbid conditions, generally need to treat the comorbidity prior to treating the ADHD First, treat depression, bipolar disorder, severe anxiety, or addiction prior to ADHD For adults, consider dual action agents or combined medications