Tasksheet
advertisement

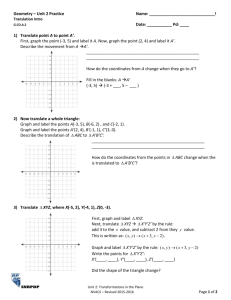
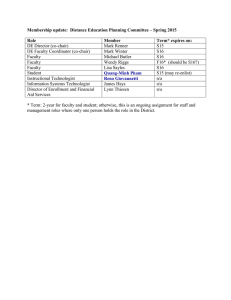
Tentative steps for translation Step 1 Read through once: to have an idea of what the text is about, its flavour and intention. Step 2: Identify words and phrases difficult to translate: words and phrases that imply a technical concept or a national (or local) character) E.g. 1. (Language is) productive: (ng«n ng÷ ................................) ................................ 2. 'deep down' Nhãm tõ cã hµm ý chØ lo¹i cÊu tróc s©u (®çi lËp víi cÊu tróc mÆt), theo lý thuyÕt 'ng÷ ph¸p t¹o sinh' (generative grammar) cña Noam Chomsky. 3. superficial features: nÐt thuéc cÊu tróc mÆt Step 3: Identify sentence structure; to understand it grammatically. This will help the translator understand correctly the sentence, hence correct translation. E.g. That the language is highly complex is shown by the fact that up to now it has not proved possible to translate mechanically from one language to another. Step 4: Translate: translate sentence by sentence, paragraph by paragraph. Principle: accuracy and partiality. Step 5: Sanitize: make the sentence sound more of the TL (communicative instead of semantic) E.g. It has been calculated that if the brain used anu of the known methods of computing langauge, it would take several minutes to produce or to understand a simple short sentence. Initial version: Nã ®· ®-îc tÝnh to¸n r»ng nÕu bé ãc sö dông mét trong nh÷ng ph-¬ng ph¸p ®-îc biÕt ®Õn vÒ ng«n ng÷ m¸y tÝnh th× nã sÏ ph¶i mÊt tíi vµi phót ®Ó s¶n sinh hoÆc hiÓu mét c©u ng¾n. Sanitized version. _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Step 6: Criticize the translated version. at word level, levels. sentence and text Correct vs. incorrect; accuracy vs. inaccuracy; appropriate vs. inappropriate. To find out the best possible translation Good luck