Chemical Kinetics
advertisement
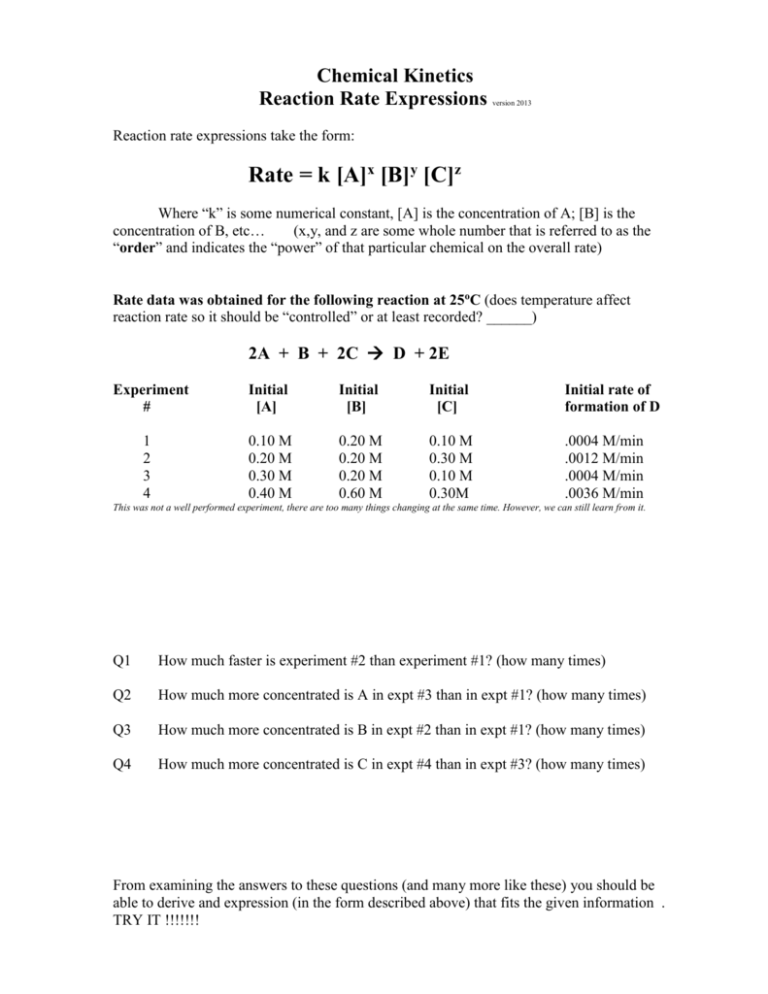
Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate Expressions version 2013 Reaction rate expressions take the form: Rate = k [A]x [B]y [C]z Where “k” is some numerical constant, [A] is the concentration of A; [B] is the concentration of B, etc… (x,y, and z are some whole number that is referred to as the “order” and indicates the “power” of that particular chemical on the overall rate) Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC (does temperature affect reaction rate so it should be “controlled” or at least recorded? ______) 2A + B + 2C D + 2E Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial [C] Initial rate of formation of D 1 2 3 4 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.30 M 0.40 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.60 M 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.10 M 0.30M .0004 M/min .0012 M/min .0004 M/min .0036 M/min This was not a well performed experiment, there are too many things changing at the same time. However, we can still learn from it. Q1 How much faster is experiment #2 than experiment #1? (how many times) Q2 How much more concentrated is A in expt #3 than in expt #1? (how many times) Q3 How much more concentrated is B in expt #2 than in expt #1? (how many times) Q4 How much more concentrated is C in expt #4 than in expt #3? (how many times) From examining the answers to these questions (and many more like these) you should be able to derive and expression (in the form described above) that fits the given information . TRY IT !!!!!!! Now try this one: Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC A + B + C Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 0.10 M 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.20 M .0006 M/min .0012 M/min .0096 M/min Now try this one: Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC 2A + B C Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.10 M .0003 M/min .0024 M/min .0006 M/min Try # 64 and 66 on page 587 of your textbook(Glencoe) More practice problems: (Taken from page 653 of 4th edition General Chem by Whitten, Gailey and Davis) Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC #13) A + 2B C +2D Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 4 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.30 M 0.40 M 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.10 M 0.20 M .0002 M/min .0006 M/min .0002 M/min .0004 M/min Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 904oC #15) 2NO + 2H2 N2 +2H2O Experiment # Initial [NO] Initial [H2] Initial rate of formation of N2 0.420 M 0.210 M 0.210 M 0.105 M 0.122 M 0.122 M 0.244 M 0.488 M 0.136 M/s 0.0339 M/s 0.0678 M/s 0.0339 M/s 1 2 3 4 Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. Find the rate of formation of N2 at the instant when [NO] = 0.550 M and [H2] = 0.199 M Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC #14) 2A + B +2C D +2E Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial [C] Initial rate of formation of D 1 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.10 5.0 x 10-4 M/min 2 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.30 1.5 x 10-3 M/min 3 0.30 M 0.20 M 0.10 5.0 x 10-4 M/min 4 0.40 M 0.60 M 0.30 4.5 x 10-3 M/min Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. (including the constant “k”) The following reaction gives the following information 2NO + O2 2NO2 #16) Experiment # Initial [NO] Initial [O2] 1 2 3 0.020 M 0.040 M 0.020 M 0.010 M 0.010 M 0.040 M Initial rate of disappearance of NO forward rate calculated 1.0 x 10-4 M/min 4.0 x 10-4 M/min 4.0 x 10-4 M/min __________ __________ __________ Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. (including the constant “k”) (Remember that the rate is usually based upon the formation of product not the rate of disappearance of reactant) Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate Expressions ANSWERS Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rate Expressions version 2013 Reaction rate expressions take the form: Rate = k [A]x [B]y [C]z Where “k” is some numerical constant, [A] is the concentration of A; [B] is the concentration of B, etc… (x,y, and z are some whole number that is referred to as the “order” and indicates the “power” of that particular chemical on the overall rate) Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC (does temperature affect reaction rate so it should be “controlled” or at least recorded? __YES!____) 2A + B + 2C D + 2E Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial [C] Initial rate of formation of D 1 2 3 4 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.30 M 0.40 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.60 M 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.10 M 0.30M .0004 M/min .0012 M/min .0004 M/min .0036 M/min Q1 How much faster is experiment #2 than experiment #1? (how many times) 3X Q2 How much more concentrated is A in expt #3 than in expt #1? (how many times) 3X Q3 How much more concentrated is B in expt #2 than in expt #1? (how many times) 1X Q4 How much more concentrated is C in expt #4 than in expt #3? (how many times) 3X From examining the answers to these questions (and many more like these) you should be able to derive and expression (in the form described above) that fits the given information . TRY IT !!!!!!! Rate = k [A]0 [B]1 [C]1 ; k=.02 M-1 min-1 Now try this one: Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC A + B + C Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 0.10 M 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.20 M .0006 M/min .0012 M/min .0096 M/min Rate = k [A]3 [B]1 ; k= 6.0 M-3 min-1 Now try this one: Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC 2A + B C Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.10 M .0003 M/min .0024 M/min .0006 M/min Rate = k [A]3 [B]2 ; k= 7.5 M-4 min-1 Try # 64 and 66 on page 587 of your textbook(Glencoe) More practice problems: (Taken from page 653 of 4th edition General Chem by Whitten, Gailey and Davis) Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC #13) A + 2B C +2D Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of formation of C 1 2 3 4 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.30 M 0.40 M 0.10 M 0.30 M 0.10 M 0.20 M .0002 M/min .0006 M/min .0002 M/min .0004 M/min Rate = k [A]0 [B]1 ; k= .002 M0 min-1 Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 904oC #15) 2NO + 2H2 N2 +2H2O Experiment # Initial [NO] Initial [H2] Initial rate of formation of N2 0.420 M 0.210 M 0.210 M 0.105 M 0.122 M 0.122 M 0.244 M 0.488 M 0.136 M/s 0.0339 M/s 0.0678 M/s 0.0339 M/s 1 2 3 4 Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. Rate = k [NO]2 [H2]1 ; k= 6.3 M-2 sec-1 Find the rate of formation of N2 at the instant when [NO] = 0.550 M and [H2] = 0.199 M 2 -1 Rate = 6.32 [.55] [.199] ; k= 0.38 M sec Rate data was obtained for the following reaction at 25oC #14) 2A + B +2C D +2E Experiment # Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial [C] Initial rate of formation of D 1 2 3 4 0.10 M 0.20 M 0.30 M 0.40 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.20 M 0.60 M 0.10 0.30 0.10 0.30 5.0 x 10-4 M/min 1.5 x 10-3 M/min 5.0 x 10-4 M/min 4.5 x 10-3 M/min Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. (including the constant “k”) Rate = k [A]0 [B]1[C]1 ; k= 0.025 M-1 min-1 The following reaction gives the following information 2NO + O2 2NO2 #16) Experiment # Initial [NO] Initial [O2] 1 2 3 0.020 M 0.040 M 0.020 M 0.010 M 0.010 M 0.040 M Initial rate of disappearance of NO 1.0 x 10-4 M/min 4.0 x 10-4 M/min 4.0 x 10-4 M/min forward rate calculated __.0001 M____ __.0004 M____ __.0004 M____ Find the rate-law expression for this reaction. (including the constant “k”) (Remember that the rate is usually based upon the formation of product not the rate of disappearance of reactant) Rate = k [NO]2 [O2]1 ; k= 25.0 M-2 min-1