Thermal Energy
advertisement

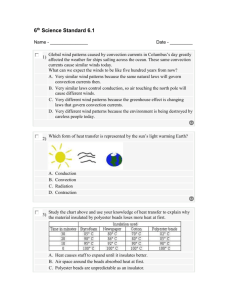
Transfer of Thermal (heat) Energy Heat is a form of energy. Heat (energy) can be transferred or MOVED from one thing to another. Examples of thermal energy being transferred: In each of these examples heat is being transferred from one thing to another, but is being transferred in a different way (through radiation, conduction or convection). If you are outside on a hot day and you get warm from the sun (radiation) If you touch the hot blacktop, your bare feet will feel the heat (conduction) If water is boiled on a stove, bubbles can be seen moving in the pot (convection). There THREE methods of transferring heat from one thing to another are: 1. Radiation 2. Conduction 3. Convection 1. RADIATION Radiation is the transfer of heat from a distance. Heat travels from the sun to the Earth by a process called radiation. The objects (sun and Earth) DO NOT COME IN DIRECT CONTACT with one another. The sun gives off energy. It can be moved to me on a warm, sunny day when I go outside. The closer the sun or other heat source, the stronger the energy. Being warmed from a fire is another example of heat transfer through radiation. In addition to the sun, some other things that radiate heat include: light bulbs, a fire in a fireplace and toasters. 2. CONDUCTION Conduction is a way that heat is transferred between objects that are in direct contact. Conduction is the transfer of energy from one particle to another. This occurs when particles hit against one another. Conduction is the strongest in solids because the particles are so close together. Metals are good conductors of heat. Wood and plastics are NOT good conductors. Examples of Conduction: The burner on the stove is heating the frying pan because it is in direct contact with the pan. Heat is being transferred from the burner to the pan. The bowl and the spoon are in direct contact with the hot soup. The heat flows from the hot soup to the bowl and spoon. The boy is roasting marshmallows over a fire using a metal rod. The rod begins to get warm, as the thermal energy (heat) from the fire is being transferred to the rod. The rod is in direct contact with the fire. 3. CONVECTION: Convection is the movement of heat by a liquid, such as water or through a gas – such as air. The liquid or gas moves from one location to another carrying heat along with it. In convection, the heat source DOES NOT touch the objects being heated. Examples of convection: Convection is the reason that macaroni rises and falls in a pot of heated water. Convection occurs in the heated water. The warm water brings some of the macaroni up, and the cool water brings some of the macaroni down. Heat is circulated through the water. This happens because the hot water is less dense than the cool water that is at the top. The cool water at the top then sinks since it is denser. This movement creates convection current (like a cycle). Convection is also involved in a hot air balloon. The balloon rises in the air because the hot air in the balloon is less dense than the air around it. To lower a hot air balloon that is in the sky, it would be necessary to turn down the burner in the balloon. This would slowly cool the air inside the balloon. The cool air is more dense. As the air inside the balloon cools, it sinks and gently brings down the balloon.