compare_unimolecular..
advertisement
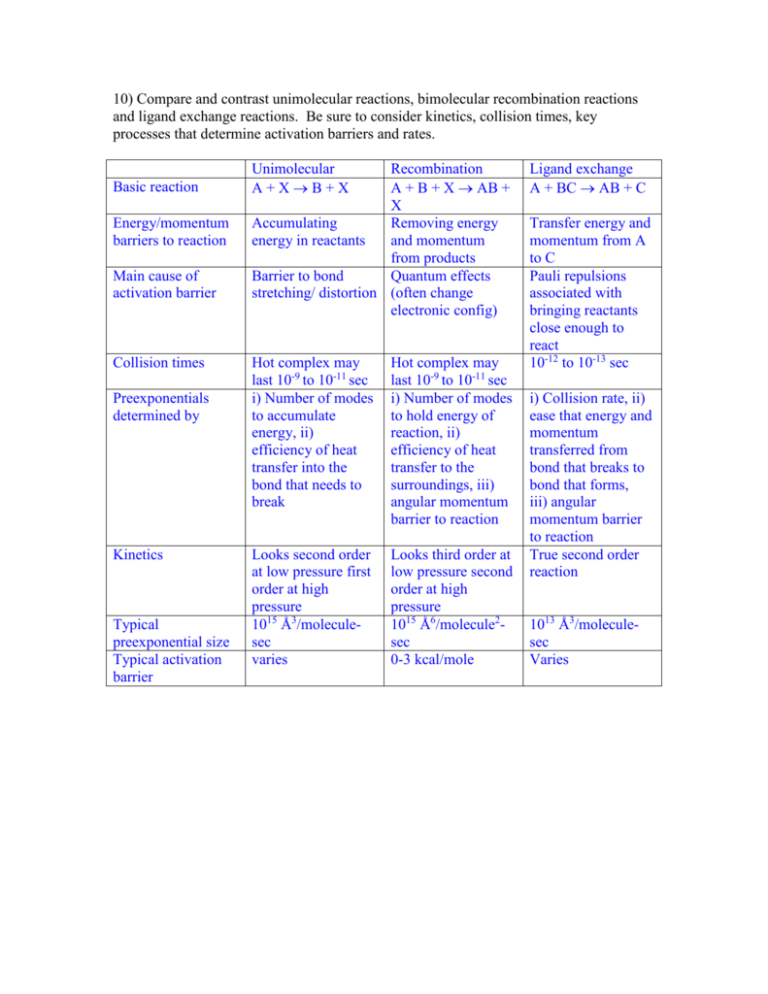
10) Compare and contrast unimolecular reactions, bimolecular recombination reactions and ligand exchange reactions. Be sure to consider kinetics, collision times, key processes that determine activation barriers and rates. Basic reaction Energy/momentum barriers to reaction Main cause of activation barrier Collision times Preexponentials determined by Kinetics Typical preexponential size Typical activation barrier Unimolecular A+XB+X Recombination A + B + X AB + X Accumulating Removing energy energy in reactants and momentum from products Barrier to bond Quantum effects stretching/ distortion (often change electronic config) Hot complex may last 10-9 to 10-11 sec i) Number of modes to accumulate energy, ii) efficiency of heat transfer into the bond that needs to break Hot complex may last 10-9 to 10-11 sec i) Number of modes to hold energy of reaction, ii) efficiency of heat transfer to the surroundings, iii) angular momentum barrier to reaction Looks second order at low pressure first order at high pressure 1015 Ǻ3/moleculesec varies Looks third order at low pressure second order at high pressure 1015 Ǻ6/molecule2sec 0-3 kcal/mole Ligand exchange A + BC AB + C Transfer energy and momentum from A to C Pauli repulsions associated with bringing reactants close enough to react 10-12 to 10-13 sec i) Collision rate, ii) ease that energy and momentum transferred from bond that breaks to bond that forms, iii) angular momentum barrier to reaction True second order reaction 1013 Ǻ3/moleculesec Varies











