Wave Erosion - energy is concentrated on headlands due to
advertisement

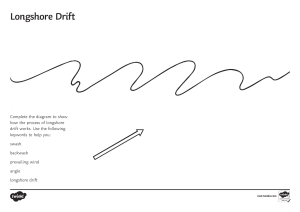
Wave Erosion - energy is concentrated on headlands due to refraction (bending of waves) & the energy is reduced in bays Wave-cut Cliff - produced by wave action cutting away its base. The cliff develops as the upper portions collapse after being undermined - may be evident in sea caves; Continued erosion of sea caves produces sea arches & as they crumble stacks are created. Rate of Wave Erosion 1) composition of coastal bedrock - igneous, metamorphic & hard sedimentary rocks are relatively resistant while weak sedimentary (sandstone, shale) are easily eroded 2) degree of exposure 3) size of waves 4) tidal range - smaller the range, greater the erosion Features of Depositional-Type Shores Longshore Currents - a current located in the surf zone and running parallel to the shore as a result of breaking waves. Longshore Drift (large scale) & Littoral Drift (small scale) - movement of sediment by the process just described Numerous depositional features result from longshore drift & other processes Spit - a linear ridge of sediment attached to the land at one end with the other end in the direction of the longshore drift Baymouth Bar (Bay Barrier) - ridge of sediment that cuts a bay off from the ocean; when the longshore drift comes to an embayment, the waves lose some of their force as they are refracted into the embayment & drop part of their sediment and a bar builds up across the mouth of the bay. Tombolo - a sand ridge that connects an island with another island or with the mainland.