Sales Despite Recalls
advertisement

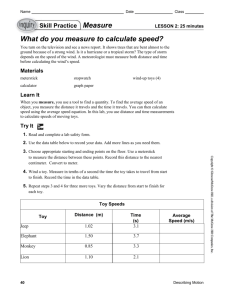
Chapter 13 Getting Products to Customers Sales Despite Recalls Retail sales in the U.S. toy industry totaled $21.3 billion in 2005. Mass marketers and discounters represented 54 percent of total toy sales, while toy stores represented 20 percent. Online toy sales generated more than $1.3 billion in 2005. Building sets and learning/exploration toys showed the greatest growth during the year. Entertainment franchises such as Dora the Explorer and Star Wars drove toy sales. Toys associated with popular youth movies are often sold or given away at fast-food restaurants. Recent toy recalls have become a concern for fast-food restaurants that attract family business from the popular toys. Most toys in the United States are safe; deaths associated with toys are taken very seriously. Manufacturers use recalls to avoid lawsuits associated with defective products. Hasbro Inc. recalled 255,000 Playskool toy tool benches after toddlers in West Virginia and Texas died from choking on the toy’s large plastic nails. The Team Talkin’ Tool Bench comes with a toy hammer, screwdriver, two 2 ¼-inch plastic screws and two 3inch plastic nails. Toys “R” Us, Wal-Mart, Target, and KB Toys sold the workbench nationwide from October 2005 through September 2006 for about $35. The toy recall allowed consumers with the workbench to exchange the plastic nails for a $50 certificate for another Hasbro product. The Consumer Product Safety Commission concluded that the oversize plastic nail met federal regulations for small parts and that the company had complied with federal labeling standards. The toy was recommended for use by children age 3 and older. Get the Lead Out Now the toy industry is actively involved with recalls associated with toys manufactured in China. The Fisher Price lead paint toy recall was the largest toy recall for Mattel since 1998. Fisher Price recalled almost 1 million toys due to high lead levels in the toys’ paint. The recall involved all plastic preschool toys manufactured by a Chinese vendor for Fisher Price from May to August of 2007. Some of the most popular toys recalled included Elmo Light Up, Ernie Light Up, Big Bird Light Up, Elmo Stacking Rings, Dora’s Talking House, and the Dora backpack. China manufactures 80 percent of the toys sold in the United States. During the fall of 2007, many consumers vowed that they would not purchase toys made in China due to the lead paint recalls. Some leaders in the industry predicted toy company sales would plummet; however, the recalls had little effect on toy sales. The “anti-China Christmas” did not come to pass. Many parents continue to give in to children who are yelling for the hottest toys in the market. Sales of traditional toys were flat in 2007, while video game sales grew $12.5 billion in 2006. Many children want DVDs, video games, and consumer electronics. Sales for U.S. manufactured toys rose following the recall of toys manufactured in China. U.S. companies represent only 5–10 percent of the toy market. A survey about the toy recalls indicated that 25 percent of consumers were concerned about toy recalls, but 31 percent said the recalls did not matter to them. Toy sales seem to be resilient to higher Chapter 6 Page 1 gas prices and a possible recession. Parents continue to buy toys for their children in good and bad times. Toys “R” Us has incorporated electronics into its product line and the Internet provides social-networking with sites that include Barbiegirls.com or BeBratz.com. Video games and game systems have allowed Toys “R” Us to maintain high sales. Think Critically 1. Why is it important for a major company such as Mattel to recall a popular toy? 2. What can toy manufacturers do to regain consumer confidence? 3. Why must toy manufacturers carry liability insurance? Chapter 6 Page 2