Topic: Formation of Fossil Fuels
advertisement

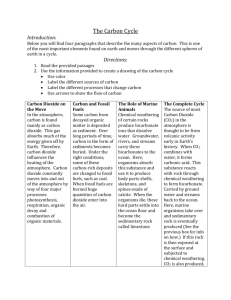
Topic: Fossil Fuels Topic: Changes to Land *The student is expected to explore the processes that led to the formation of sedimentary rocks and fossil fuels. (5.7A) *The student is expected to recognize how landforms, such as deltas, canyons, moraines, and sand dunes are the result of changes to Earth's surface by wind, water, and ice. (5.7B) 1. Fossil Fuels - can be burned to release large amounts of energy 2. Coal - formed from plants in forests and swamps some 400 million years ago. *Identify and observe actions that require time for changes to be measurable, including growth, erosion, dissolving, weathering, and flow AND interpret how land forms are the result of a combination of constructive and destructive forces such as deposition of sediment and weathering. (5.11A, 5.12A) 1. Process - series of events that lead to change 3. Oil and Natural Gas - formed by very tiny one-celled plants and animals in the ocean. 4. Formation of Fossil Fuels when plants and animals die they get covered by sediments, over millions of years, heat and pressure changed their bodies into oil, natural gas, or coal 2. Destructive Forces - processes that wear down the Earth’s landforms (weathering, erosion, glaciers, earthquakes) 3. Constructive Forces - processes that build up the Earth’s landforms (folding to build mountains, volcanoes and lava flows, sedimentation) 4. Earth’s Materials- rock, soil, water, gases Topic: Alternative Energy Topic: What Happened Before *The student is expected to identify alternative energy resources, such as wind, solar, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biofuels. (5.7C) *The student is expected to identify fossils as evidence of past living organisms and the nature of the environments at the time using models. (5.7D) 1. wind energy - energy produced by the wind *Draw conclusions about "what happened before" using data such as from tree-growth rings and sedimentary rock sequences (5.11B) 2. Solar Power - energy produced by the sun 3. Geothermal Energy - energy produced by the Earth 4. Hydroelectric Energy - Water is allowed to flow through tunnels in the dam, to turn turbines and thus drive generators. 5. Biofuels - produced from living organisms or from metabolic by-products (organic or food waste products). 1. Tree Growth Rings - tell the age of a tree, tell about an area’s past such as weather conditions 2. Sedimentary Rocks - formed by the sand, mud, and other particles falling to the ground or to the floor of a lake or ocean. Bottom layer is the oldest and top layer is the most recent. Topic: Weather and Climate Topic: The Sun and Water Cycle *The student is expected to differentiate between weather and climate. (5.8A) *The student is expected to explain how the Sun and ocean interact in the water cycle. (5.8B) 1. Climate - average weather conditions in an area; typical weather in a place over a long period of time 1. Evaporation - water evaporates from the oceans and freshwater sources into the atmosphere 2. Weather - describes whatever is happening outdoors in a given 2. Condensation - water vapor place at a given time. Weather is condenses into clouds what happens from minute to minute. The weather can change a lot within a very short time. 3. Precipitation - water returns to the oceans and land as rain, hail, sleet, or snow 4. Run-off – water on the land and in the ground runs off into the oceans. Topic: Systems, Structures, and Processes: Earth Systems *Describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system AND describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. (5.5AB) 1. Ocean currents - carry some of the sediment to coastlines, where it forms sandy beaches 2. Rivers – carry sediments from the land into the oceans 3. Tides - two a day, can erode shorelines wearing away at rock and dissolving minerals. 4. Weather Patterns - results from the interaction of several systems—land features, energy from the sun heating the Earth’s atmosphere, the spinning of the Earth creating winds, tornadoes, tropical hurricanes. Topic: The Earth, Sun, and the Moon *The student is expected to identify and compare the physical characteristics of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. (5.8D) *Identify the physical characteristics of the Earth and compare them to the physical characteristics of the moon (5.12C) 1. sun – star, major source of energy for the Earth 2. Solar System - sun and nine planets 3. rotation - Earth spins on its axis once approximately every 24 hours, day and night (5.8C) 4. revolution-Earth revolves around the sun, year 5. tilt-Earth is tilted on its axis as it revolves around the sun, explains seasons 6. axis - imaginary line running through the center of the Earth from North Pole to South Pole 7. Order of planets (My Very Excellent Mother Just Sent Us Nine Pizzas) (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto) 8. Lunar Cycle - every 30 days 9. Moon Phases - 8 phases (5.6A) 10. Moon - has no water, air, soil, or living things; made of molten lava (hard rock) with craters Topic: Water Carbon, and Topic: Natural Resources Nitrogen Cycle *Identify the significance of the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles. (5.6B) *Identify past events that led to the formation of the Earth's renewable, nonrenewable, or inexhaustible resources. (5.11C) 1. Water Cycle - process by which Earth’s water moves into and out of the atmosphere. 1. Renewable Resource – something that can be replaced such as wood from trees. 2. Carbon Cycle - carbon is continuously recycled among the atmosphere, plants and animals as carbon dioxide. 2. Nonrenewable Resource – is formed over a very, long period of time and cannot be replaced or renewed. (coal, oil, copper, and other minerals) 3. Nitrogen Cycle - the waste products and remains of dead animals and plants are broken down by bacteria, leaving nitrates in the soil. 3. Inexhaustible Resources – cannot be used up by human activity (energy from the sun, wind energy