Acids and Bases Study Guide: Definitions & Calculations
advertisement

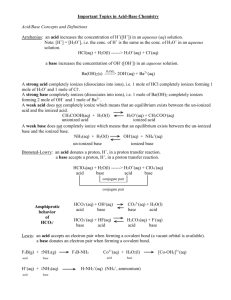
Chapter 19 Study Guide ANS 1. List the properties of acids and bases. Acids – taste sour, release hydrogen gas when reacted with active metals, react with bases to produce salts and water, turn litmus red, are electrolytes (conduct electricity) Bases – taste bitter, feel slippery, react with acids producing salt and water, turn litmus blue, are electrolytes (conduct electricity) 2. Define monoprotic, diprotic, and triprotic acids. Give an example of each. Monoprotic – contains one acidic H (HCl, CH3COOH, HI) Diprotic – contains two acidic Hs (H2SO4) 3. Define a strong acid. A substance that is a strong electrolyte and that nearly completely ionizes and produces H3O+. 4. Define a strong base. A substance that is a strong electrolyte and that nearly completely ionizes and produces OH-. 6. Define a Bronsted-Lowry acid and base. Acid – proton donor Base – proton acceptor 7. In the equation HCl(g) + H2O(l) ↔ H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq), identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base. Acid, base, conjugate acid, conjugate base 8. In the reaction NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH–, identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base. Base, acid, conjugate acid, conjugate base 9. Define a conjugate acid. Compound formed after the addition of a proton to a base 10. Define a conjugate base Compound that remains after the acid has given up a proton 11. Define a conjugate acid-base pair. Species that appear on opposite sides of an equation and differ by a proton 12. In the reaction HF + H2O H3O+ + F–, identify the conjugate acid-base pairs HF and F- H2O and H3O+ 13. In the reaction HClO3 + NH3 NH4+ + ClO3–, identify the conjugate acid-base pairs HClO3 and ClO3- NH3 and NH4+ 14. In the reaction CH3COOH + H2O H3O+ + CH3COO–, identify the conjugate acid – base pairs. CH3COOH and CH3COO- H2O and H3O+ 15. Define amphoteric Species that reacts as acid or a base 16. What is the pH, pOH, [H3O+], and [OH-] for pure water? pH = 7 pOH = 7 [H3O+] = 1.0 x 10-7 M [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7 M 17. How do you know if a solution is acidic or basic? Acid – pH < 7 pOH > 7 [H3O+] > [OH-] [H3O+] > 1.0 x 10-7M [OH-] < 1.0 x 10-7 M Base – pH >7 pOH < 7 [H3O+] < [OH-] [H3O+] < 1.0 x 10-7M [OH-] > 1.0 x 10-7 M 18. What is the pH of a 10-3 M HCl solution? HCl is a strong acid, dissociates completely so HCl conc=H+ conc pH = -log(10-3) = 3 19. What is the pH of a 10-4 M KOH solution? Strong base, pOH = -log(10-4) =4 pH = 14-4 = 10 20. If [H3O+] = 1.7 x 10-5 M, what is the pH of the solution? pH = -log(1.7 x 10-5) 21. If [H3O+] = 8.26 x 10-3 M, what is the pH of the solution? pH = -log(8.26 x 10-3) 22. What is the pH of a solution whose hydronium ion concentration is 5.03 x 10-2 M? pH = -log(5.03 x 10-2) 23. What is the pH of a 0.0056 M KOH solution? pOH = -log (0.0056) = 2.25 pH = 14 – 2.25 = 11.75 24. What is the pH of a 0.000066 NaOH solution? pOH = -log (0.000066) = 3.18 pH = 14 – 3.18 = 10.81 25. What is the hydronium ion concentration of a solution whose pH is 8.97? [H+] = 10^-pH = 10^-8.97 = 1.07 x 10-9 M 26. What is the hydronium ion concentration of a solution whose pH is 3.55? [H+] = 10^-pH = 10^-3.55 27. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of a solution whose pH is 9.43? [H+] = 10^-pH = 10^-9.43 = 3.72 x 10-10 M [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14/3.72 x 10-10 = 28. Write and balance the neutralization equation for nitric acid and potassium hydroxide. Is the resulting solution acidic, basic, or neutral? HNO3 + KOH KNO3 + H2O 29. When a strong acid and weak base are neutralized the resulting solution is _acidic___. 30. When a strong base and weak acid are neutralized the resulting solution is __basic__. 31. Write all of the ionization equations for phosphoric acid, H3PO4. Write the 3 equilibrium constant expressions. 32. Write the dissociation equation for barium hydroxide. Ba(OH)2 Ba+2 + 2OHRemember aqueous symbols 33. Write the dissociation equation for the base methyl amine, CH3NH2. Write the Kb expression. CH3NH2 + H2O CH3NH3+ + OHAll are aqueous except liquid water 34. How many acidic hydrogens does acetic acid, HC2H3O2 have? 1, hydrogens bonded to C are not acidic 35. How many acidic hydrogens does sulfurous acid, H2SO3 have? 2 36. Na2CO3 = basic, NH4Cl = acidic, KBr = neutral