CHE 263 Sample course syllabus (click here)
advertisement

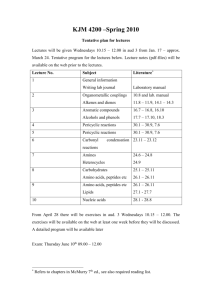
1 Chemistry 261/263 Sections 1-2 CHE 261/263 - Organic Chemistry II Summer 2010 Lectures: M-Th (10:00 – 11:45 am), JE114 Laboratory: M, W (5:45 – 9:35 pm) and T, Th (1:10-500 pm), JE325 Lecturer: Adiel Coca, Ph.D. Office: 304 Jennings Hall Phone: 203 – 392 - 6982 E-mail: cocaa2@southernct.edu Office Hours: M-Th (11:45 am – 12:45 pm) or by appointment Required Texts: McMurray, J. Organic Chemistry, 7th ed. with NOW, 2008, Brooks/Cole Publisher. Molecular Model Kit (two options available in the bookstore). Goggles (available from chemistry club). Hardcover Lab Notebook Optional Material: Traynham, J. G. Organic Nomenclature: A programmed Introduction, 5th ed., 1997, Prentice Hall Publisher. McMurray, S. Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry, 7th ed., 2008, Brooks/Cole Publisher. Weeks, D. Pushing electrons. Your course grade is based on the following criteria CHE 261: class participation, 3% Three exams, 24% each Laboratory grade, 25%. All projects must be completed and a passing grade (≥60%) must be received in the laboratory component of the course in order to receive a passing grade in the course!!! CHE 263: class participation, 3% Three exams, 32.3% each The course grade will be based on the grading scale below with possible adjustments at the instructor's discretion: A+ (100-96) A (95-91) A- (90-86) B+ (85-82) B (81-78) B- (77-74) C+ (73-70) C (69-66) C- (65-62) D+ (61-58) D (57-54) D- (53-50) F <50 2 Your grade will not be based upon any claimed “need” which you may have. It is incumbent upon you, the student, to perform at the level that will fulfill the specific “need.” In addition, there is no provision in this course to do work for “extra credit.” Exams (Target dates): 1st exam: Thursday, 7/15/10 – Covering chapters 11, 17, 18, 19 (first half) 2nd exam: Tuesday, 7/27/10 – Covering chapters 19 (second half), 20, 21, 22 3rd exam: Thursday, 8/5/10 – Covering chapters 23, 15, 16, 24. The exams will be taken during regular class time. Students who arrive late will not be allotted extra time. Any changes will be announced in class. Only students with valid excuses will be permitted to take the make-up exam. Conflicts in scheduling should be resolved in advance (at least one week before the exam). All exams will be comprehensive written tests (but they will concentrate on the material covered since the previous test). They will be constructed in such a way as to emphasize active understanding of the material. Books, scratch paper (other than furnished), cell phones (and similar electric devices), and calculators will not be allowed. The use of a molecular model kit is limited to only one carbon with four bonds during examination. Helpful Hints. Organic Chemistry is a difficult course. It covers a lot of demanding material. Here are some tips to do well in this course: study everyday, do reviews weekly read the material before the lecture. solve as many end-of-chapter problems as possible (resort to answer book only after you have attempted the problem). study with a friend; if you can explain a concept to your study mate, you understand it just reading and understanding the material (passive understanding) is insufficient; you should be able to use the just learned concepts in situations not previously encountered, and make logical connections with concepts learned previously (active understanding) constantly probe your understanding by asking (and answering) question "why?" in relation to all statements and logical constructions do not fall behind in your study; it is virtually impossible to prepare well for the exam in just a few days before it. Cramming for this course will not work! Attendance: Optional but highly recommended. Academic Integrity: All forms of academic dishonesty will not be tolerated. Such infractions are considered cause, at the least, for awarding a grade of "0" on the assignment or exam in question. For more details, see the student handbook on the subject. This policy will be strictly enforced. 3 Student Disabilities: I believe in providing reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities on an individualized and flexible basis. If you are a student with a documented disability, the university’s Disability Resource Center (DRC) determines appropriate accommodations through consultation with the student. Before you may receive accommodations in this class, you will need to make an appointment with the Disability Resource Center, located in EN C-105A. To speak with me about other concerns, such as medical emergencies or arrangements in case the building must be evacuated, please make an appointment as soon as possible. CengageNOW: It is strongly recommended that student routinely log-on to CengageNOW at http://www.cengage.com/sso/ and work on the problems provided. Register by clicking first on create my account, then register as a student, then enter the access code that comes with your textbook, then provide the required information, and finally choose SCSU as your institution. The “section key” is E-5WMMRF2CDBWJ8. These assignments will not be graded, but will provide another resource for doing well in the course. Outline of Lectures: Tentative Schedule 1. Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations (4 lectures) SN1 and SN2 E1 and E2 Effects of solvent, substrate structure, and nucleophile (base) on reactivity Sections covered: All Chapter 11 Assigned problems: 1-13, 15-20, 25-27, 29-31, 34-44, 47-52, 56-57, 61, 62, 65. 2. Alcohols and Phenols (3 lectures) Naming Preparation Reactions Protection Phenols Sections covered: All of Chapter 17, Read 15.1 Assigned problems: Chapter 15: 1: 1-3, 13, 18-19. Chapter 17: 1, 2, 4-16, 21, 22 (except e), 23-25, 29-30, 31, 32 a, d, 33-38, 40a-c, 41, 44, 46-49, 51, 57, 68, 69. 3. Ethers and Epoxides; Thiols and Sulfides (2 lectures) Naming Preparation of ethers Reactions of ethers Ring-opening of epoxides Thiols and sulfides 4 Sections covered: All of Chapter 18 except 18.4. Assigned problems: Chapter 17: 39. Chapter 18: 1-9, 11-17, 19-27, 28 a,d, 29, 30, 32-34, 39-41, 43, 44, 50-52. 4. A preview of Carbonyls (0.5 lectures) Sections covered: pg. 686-694. Assigned problems: 1-3. 5. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition (4.5 lectures) Naming Preparation Reactions: Oxidation Reactions: Nucleophilic addition. Reactions: Conjugate nucleophilic additions Sections covered: All of Chapter 19. Assigned problems: 1-3, 4a, d, 5-17, 19-23, 27-30, 32-37, 39-45, 48-51, 56-57, 59, 62, 72, 73. 6. Caboxylic acids and Nitriles (2 lectures) Nomenclature Acidity Preparation Reactions Overview Nitriles Sections covered: All of Chapter 20. Assigned problems: 1-3, 6-7, 9-14, 17-19, 21-22, 24-29, 31-32, 35-41, 43, 45, 49b, 50-52. 7. Caboxylic acids derivatives (3 lectures) Naming Reactions: Carboxylic acids Reactions: Acyl Halides Reactions: Acid Anhydrides Reactions: Esters Reactions: Amides Sections covered: All of Chapter 21. Assigned problems: 1-21, 23-25, 28-30, 32-33, 35-41, 43-45, 47-49, 51-53, 56, 63-66, 71. 8. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions (3 lectures) Keto-Enol Mechanism of Alpha-Substitution Alpha Substitution: Ketones and Aldehydes Alpha Substitution: Carboxylic Acids Enolate Preparation Enolate Reactions 5 Sections covered: All of Chapter 22. Assigned problems: 1-39, 42-47, 52, 54-56. 9. Carbonyl Condensation (5 lectures) Aldol Reaction Formation of Enones Mixed Aldol Reactions Intramolecular Aldol Claisen Condensation Mixed Claisen Intramolecular Claisen: Dieckmann Reaction Michael Addition Condensation with Enamines: Stork Reaction Robinson Annulation Sections covered: All of Chapter 23. Assigned problems: 1-46, 50-51, 53-54, 56, 58-63. 10. Benzene and Aromaticity (3 lectures) Naming Stability of Aromatic Compounds Huckel Rule Aromatic Compounds: Ions, Heterocycles, Polycycles Sections covered: All of Chapter 15 Assigned problems: 4-12, 14-17, 24-40, 42. 11. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (4 lectures) Reactions: Halogenation, Nitration, Sulfonation, Hydroxylation Friedel-Crafts Reactions: Alkylation and Acylation Substituent effects Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzyne Oxidation and Reductions of Aromatic Compounds Sections covered: All Chapter 16 Assigned problems: 17.31d, f, 17.32, 17.52, 18.31, 18.38, 18.53, 18.55, 18.56, 19.4b, c, 19.53, 20.30, 20.42, 20.46-48, 20.49a, 21.42, 21.54, 21.55, 21.57. Chapter 16: 1-37, 39-56, 60-63, 65, 69-70, 72-75. 12. Amines and Heterocycles (3 lectures) Naming Basicity Preparation Reactions Heterocycles Sections covered: All Chapter 24. Assigned problems: 1-6, 8-20, 22-53, 55-57, 59, 63-64, 66, 68-70, 72. 6 13. Pericyclic Reactions (If time allows, 5 lectures) Molecular Orbitals Electrocyclic reactions Cycloaditions Sigmatropic Rearrangements Sections covered: All Chapter 30, sections 14.4, 14.5, 18.4. Assigned problems: 17.43, 18.10, 18.49. Chapter 14: 7-10, 17, 18, 21e, 27, 32-41, 43-45, 55-57. Chapter 30: 1-30, 32, 34-38, 40. All information on this syllabus is subject to change at the discretion of the instructor.