chapt37
advertisement

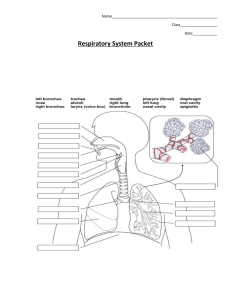
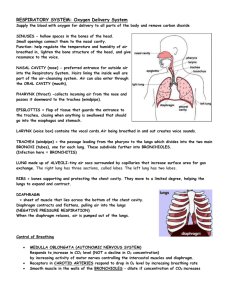
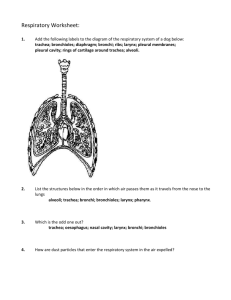
Chapter 37 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the following increases the surface area available for gas exchange? A. finely divided inner lung surface B. tubular body shape, as in annelids C. finely divided gills D. all of these choices increase surface area 2. Which of these organisms is able to use several body surfaces, such as gills, skin, and lungs, for respiration? A. humans B. birds C. amphibians D. reptiles 3. Which of the following steps is/are needed for mammalian inhalation? A. contraction of the diaphragm B. decrease in thoracic pressure C. rib cage is lifted D. expansion of thoracic cavity E. all of the steps are necessary 4. The entrance and exit of air into and out of the lungs is called A. breathing. B. external respiration. C. internal respiration. D. cellular respiration. E. air conditioning. 5. The type of respiration in which gases are exchanged between the blood and the tissue fluid is termed A. breathing. B. external respiration. C. internal respiration. D. cellular respiration. E. fermentation. 6. Which of the following statements is NOT true about obtaining oxygen from an aquatic environment? A. Water is more dense than air, so animals use more energy to gain oxygen in water. B. Water contains only about half as much oxygen as air. C. Gases pass more easily across a moist, thin surface. D. Fishes use about 25% of their energy on breathing. E. Fishes use highly vascularized tissues and the respiratory pigment hemoglobin to aid in obtaining oxygen from the water. 7. In small aquatic animals such as hydra and planarians, the most common structure used for gas exchange is A. lungs. B. body surface. C. gills. D. cardiovascular system. 8. Parapodia are A. gills on a lobster. B. gill covers on a fish. C. extensions of the body wall in polychaete worms. D. internal spaces in a planarian used in digestion and respiration. E. tentacles on a hydra. 9. Opercula are A. gills on a lobster. B. gill covers on a fish. C. extensions of the body wall in polychaete worms. D. internal spaces in a planarian used in digestion and respiration. E. tentacles on a hydra. 10. Gills are used in respiration by all of the following aquatic animals EXCEPT A. clams. B. fishes. C. lobsters. D. polychaete worms. 11. Oxygen rich water flowing in the opposite direction to oxygen poor blood in order to maximize the diffusion across the surfaces of a gill is a concept called A. reverse expiration. B. pneumonectomy. C. countercurrent flow. D. partial pressure saturation. E. hemoglobin saturation shift. 12. Air that moves out during expiration has ____ compared to air breathed in. A. warmed and gained moisture B. warmed and lost moisture C. cooled and gained moisture D. cooled and lost moisture E. neither cooled nor warmed 13. Which is NOT a major function of the respiratory tract? A. warming incoming air before it reaches the lungs B. moistening incoming air C. filtering out dust and water particles D. conducting air with higher O2 to lungs and conducting air with higher CO2 back out E. transferring and extracting nutrients 14. The earthworm is a terrestrial animal that uses its ________ in respiration. A. parapodia B. tracheoles C. body surface D. gills E. lungs 15. The grasshopper is a terrestrial animal that uses its ________ in respiration. A. parapodia B. tracheae C. body surface D. gills E. lungs 16. During hibernation, an amphibian uses its ________ in respiration. A. parapodia B. tracheoles C. body surface D. gills E. lungs 17. Vascularized outgrowths of the digestive system used in respiration in terrestrial vertebrates are A. parapodia B. tracheoles C. gills D. lungs 18. Which of these organisms uses positive pressure in ventilating the lungs? A. turtle B. cat C. frog D. crow 19. The Greek root word meaning "partition wall" is the basis for the term A. glottis. B. trachea. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharynx. 20. Which of these organisms has a method of complete ventilation not found in the others? A. turtle B. cat C. frog D. crow 21. There is unidirectional flow of air for greater absorption of oxygen in A. birds. B. amphibians. C. reptiles. D. mammals. 22. The Greek root word meaning "tongue" is the basis for the term A. glottis. B. trachea. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharynx. 23. Which statement is NOT true about the human respiratory system? A. The glottis is closed by the forward movement of the soft palate during swallowing. B. The glottis is the passageway through the larynx by which air enters the trachea. C. Food and air both enter the pharynx, presenting a potential danger to respiration. D. Air reaching the lungs has been warmed to body temperature by passage through the nose and upper respiratory passageways. E. Cilia and hairs in the nose help to screen out foreign materials in the air. 24. The Latin root word meaning "windpipe" is the basis for the term A. glottis. B. trachea. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharynx. 25. From the trachea, air next passes into the _______ during inhalation in a human. A. nose B. larynx C. alveoli D. bronchioles E. bronchi 26. The Greek root word meaning "throat" is the basis for the term A. glottis. B. trachea. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharynx 27. Trace the path of an inhaled air molecule. A. nasal cavity–glottis–larynx–trachea–pharynx–bronchi–bronchioles–alveoli B. nasal cavity–pharynx–larynx–glottis–trachea–bronchi–bronchioles–alveoli C. nasal cavity–pharynx–glottis–larynx–trachea–bronchi–bronchioles–alveoli D. nasal cavity–pharynx–glottis–larynx–trachea–bronchioles–bronchi–alveoli E. nasal cavity–pharynx–glottis–trachea–larynx–bronchi–bronchioles–alveoli 28. The Greek root word meaning "gullet" is the basis for the term A. glottis. B. trachea. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharynx. 29. Air in the bronchioles next enters the ______ during inhalation in a human. A. nose B. larynx C. alveoli D. bronchioles E. bronchi cavity--pharynx--glottis--trachea--larynx--bronchi--bronchioles--alveoli 30. The Greek root words meaning "over" and "tongue" are the basis for the term A. epiglottis. B. alveoli. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharyngeal. 31. Which respiratory organ normally allows both air and food passage? A. bronchi B. trachea C. larynx D. pharynx E. nasal cavity 32. The vocal cords are found in the A. bronchi. B. nose. C. larynx. D. lungs. E. pharynx. 33. The Adam's apple is actually a part of the A. pharynx. B. larynx. C. glottis. D. vocal cords. E. trachea. 34. Food is prevented from entering the trachea by the A. pharynx. B. larynx. C. bronchioles. D. saliva. E. epiglottis. 35. Which part of the respiratory system is composed of C-shaped cartilaginous rings and cilia? A. pharynx B. larynx C. trachea D. bronchioles E. alveoli cavity–pharynx–glottis–trachea–larynx–bronchi–bronchioles–alveoli 36. The Latin root word meaning "cavity" is the basis for the term A. epiglottis. B. alveoli. C. larynx. D. diaphragm. E. pharyngeal. 37. The greatest surface area for gas exchange occurs within the A. trachea. B. bronchi. C. bronchioles. D. alveoli. 38. Which part of the respiratory system will have the least amount of cartilage and the thinnest walls? A. larynx B. trachea C. bronchi D. bronchioles E. pharynx 39. Expired air will contain ____ than inspired air. A. less oxygen but more carbon dioxide B. less oxygen and less carbon dioxide C. more oxygen and more carbon dioxide D. more oxygen but less carbon dioxide E. the same amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide 40. Oxygen-poor blood becomes oxygen-rich blood in the capillary beds of the A. trachea. B. bronchi. C. bronchioles. D. alveoli. E. larynx. 41. With negative pressure breathing, the muscles that move the ribs and diaphragm are distant from the absorptive alveolar surfaces. What difficulty(ies) would occur if the muscles were around each alveolus and had to expand each alveolus to suck in air? A. Muscle tissue would get in the way of absorption of gases across the air-to-capillary border. B. Interspersed muscle tissue would take up much space and the lung-muscle volume would have to be much larger. C. Since muscle cells only contract and relax, it would be difficult for a few cells to cause alveolar expansion. D. Adding a third tissue to the intimate alveolar-capillary complex would increase the problems with disorders and diseases. E. All of the choices are correct. 42. Which association is NOT correct? A. larynx--voice box B. trachea--windpipe C. alveoli--gas exchange D. pharynx--vocal cords E. hair and mucus--nasal passages 43. In humans, the lungs are caused to inflate when the A. rib muscles contract. B. diaphragm muscle contracts. C. rib muscles and diaphragm contract. D. diaphragm relaxes. E. rib muscles and diaphragm relax. 44. As exhalation occurs in a human, all of the following occur EXCEPT A. Air moves from the trachea through the larynx and can cause the vocal cords to vibrate. B. The diaphragm moves upward in the chest. C. The diaphragm moves by relaxation of its muscle. D. Air is exhaled as a result of decreased pressure within the lungs. E. The alveoli are compressed and air is forced out of them. 45. Oxygen is transported in blood most efficiently by A. being dissolved in the plasma. B. chemical conversion to water. C. combining with hemoglobin. D. combining with carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate ions. E. as a free oxygen ion or radical. 46. How is most carbon dioxide transported in the blood? A. as gas bubbles of CO2, just as in carbonated soft drinks B. as bicarbonate ions (HCO3) C. on the free hemoglobins since they have lost their oxygen in the tissues D. as carbon monoxide E. as carbon compounds and oxygen radicals 47. The highest carbon dioxide concentration will be found in (or at) the A. atmosphere. B. trachea. C. alveoli. D. tissue cells. E. blood. 48. Most of the oxygen picked up by the blood in the lungs A. dissolves in the plasma. B. unites with hemoglobin. C. forms microscopic bubbles. D. diffuses back across the alveoli. E. combines with bicarbonate ions. 49. Transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and tissues occurs A. in the alveoli of the lungs. B. in the bronchioles of the lungs. C. in the blood capillary beds in the tissues. D. in the lymph capillary beds in the tissues. E. directly between red blood cells and tissue cells. 50. The exchange of gases between the lungs and the blood occurs by the process of A. diffusion. B. osmosis. C. filtration. D. active transport. E. ionic bonding. 51. By what route does CO2 leave the body? A. pulmonary artery -> alveolus -> bronchus -> bronchiole -> trachea -> pharynx -> larynx B. pulmonary vein -> bronchiole -> alveolus -> bronchus -> trachea -> pharynx -> larynx C. pulmonary artery -> alveolus -> bronchiole -> bronchus -> trachea -> larynx -> pharynx D. pulmonary vein -> alveolus -> bronchus -> bronchiole -> trachea -> larynx -> pharynx E. pulmonary artery -> alveolus -> bronchiole -> bronchus -> trachea -> pharynx -> larynx 52. Carbonic anhydrase A. is a digestive enzyme. B. is dissolved in plasma. C. speeds up the conversion of carbonic acid to carbon dioxide and water. D. speeds up the conversion of carbon dioxide to oxygen. E. speeds up the conversion of oxyhemoglobin. 53. Blood richest in oxygen is found in the A. inferior vena cava. B. superior vena cava. C. pulmonary arteries. D. pulmonary veins. E. systemic capillaries. 54. The breathing rate is controlled by chemoreceptors that mainly detect A. levels of oxygen in the alveolar air space. B. levels of oxygen in the blood. C. levels of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air space. D. levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. E. conscious control of our brain. 55. The rate of breathing is chiefly dependent on chemical factors in the blood, of which the most important is A. oxygen concentration. B. carbon dioxide concentration. C. hemoglobin concentration. D. nitrogen concentration. E. acidity. 56. Aortic and carotid bodies are A. the same as the SA and AV nodes. B. types of valves in the heart. C. present in the lungs. D. sensitive to changes in CO2 and H+ in the blood. E. sensitive to oxygen changes. 57. When trying to stimulate breathing, it is better to give a mixture of carbon dioxide and oxygen than only oxygen because A. pure oxygen causes you to breathe too rapidly. B. carbon dioxide and oxygen together exert a greater pressure than an equal amount of oxygen. C. carbon dioxide buildup in the blood stimulates the respiratory center in the brain. D. oxygen causes lactic acid buildup, and the change in pH prevents breathing. E. oxygen alone could lead to spontaneous human combustion. 58. Hemoglobin is useful because it A. transports oxygen with a higher efficiency. B. transports carbon dioxide with high efficiency. C. transports food molecules and releases them to cells in need of nutrients. D. acts as a carrier for hormones. E. All of the choices are correct. 59. As the temperature increases, the amount of oxygen carried by hemoglobin will A. increase gradually to carry off the additional heat. B. decrease. C. remain the same since temperature is unrelated to oxygen demand. D. increase immediately to 100 % of the hemoglobin capacity. E. increase for active individuals but remain constant for inactive people. 60. The highest oxygen concentration will be found in (or at) the A. atmosphere. B. trachea. C. alveoli. D. tissue cells. E. blood. 61. Comparing the graphs of saturation of hemoglobin in the lungs and in the tissues [textbook page 677], it is apparent that A. hemoglobin becomes nearly completely saturated in the lungs and then loses all oxygen as it passes through tissues. B. cooler tissues allow more saturation of hemoglobin. C. higher pH of tissues allows more saturation of hemoglobin. D. lower pH and higher temperature of tissue promotes the release of oxygen by hemoglobin. E. All of the choices are correct. 62. A pressurized airplane cabin and an oxygen tent over a patient in a hospital both address the need of a person for oxygen. How do these compare? A. The oxygen tent increases the air pressure to increase the PO2. B. Airplane cabin pressure lowers the partial pressures for normal breathing. C. Both use the same mechanism to force hemoglobin to increase affinity for oxygen. D. The oxygen tent increases concentration of O2 while the airplane maintains total air pressure without changing concentrations. 63. Which is NOT a correct association of respiratory problems and symptoms? A. laryngitis–upper respiratory infection that causes hoarseness or loss of voice B. tonsillitis–inflammation of the uvula often cured by removal of the useless tissue C. cancer–persistent hoarseness without the presence of upper respiratory infection. D. sinusitis–pain and tenderness in lower forehead and over the cheeks E. pneumonia–lungs fill with fluid 64. Which is NOT a correct association of lower respiratory problems and causes or symptoms? A. chronic bronchitis–ongoing inflammation and possible infection of bronchi with loss of cilia B. pulmonary fibrosis–loss of lung elasticity due to breathing silica, coal dust, asbestos, etc. C. emphysema–reduced lung and chest volume due to collapsed alveoli and over-ventilation D. pulmonary tuberculosis–a bacterial infection that the body tries to isolate and seal off system 65. Many lung ailments are "not curable but treatable." Which is more curable? A. advanced lung cancer with metastases B. standard tuberculosis C. asthma D. emphysema 66. A lung disease caused by bacteria which become encapsulated is called A. emphysema. B. pneumonia. C. rheumatic fever. D. tuberculosis. E. pulmonary fibrosis. 67. Which of the following diseases is caused by exposure to particles inhaled primarily in the workplace (silica, coal dust, etc.)? A. emphysema B. pneumonia C. rheumatic fever D. tuberculosis E. pulmonary fibrosis. 68. The removal of the lung is called A. tracheotomy. B. respiratory distress syndrome. C. bronchitis. D. pneumonectomy. E. emphysema. 69. Respiration involves which of the following? A. breathing B. external gas exchange between air and blood in the lungs C. internal gas exchange between the blood and tissue fluid D. All of the choices are involved in respiration. 70. Aquatic organisms A. have to work harder to obtain oxygen than do land organisms B. have to expand more energy in respiration because water is more dense than air C. work harder to obtain oxygen because water saturated with oxygen has only a fraction of the oxygen found in air D. All of the choices are true with respect to aquatic organisms. 71. Which of the following structures is/are miss-matched with its function? A. alveoli–gas exchange B. glottis–passage of air C. epiglottis–speech D. nasal cavities–filter, war, and moisten air 72. Chemical content of the blood is monitored by which of the following? A. chemoreceptors in the aortic body of the aorta B. chemoreceptors in the carotid body of the carotid areteries C. the medulla oblongata D. All of the choices monitor chemical content of the blood. 73. The highest concentration of oxygen in the human blood is found in the A. aorta. B. pulmonary artery. C. pulmonary vein. D. alveoli. 74. Of the following conditions, which is NOT a disease of the upper respiratory tract? A. sinusitis B. tonsillitis C. laryngitis D. pneumonia 75. A disease in which the alveoli are distended and their walls damaged so that surface areas for gas exchange is reduced is A. bronchitis. B. emphysema. C. pulmonary tuberculosis. D. pneumonia. 76. The circulatory system of an insect plays no role in the transport of respiratory gases. True False 77. The iron in a hemoglobin molecule is actually what binds the oxygen. True False 78. Animals must continually acquire oxygen and release carbon dioxide because they do not have a storage area for gases. True False 79. While air carries more oxygen in a given volume than does water, air presents a problem in respiration since it dries out the respiratory tissues unless treated before reaching them. True False 80. In insects, the circulatory system picks up oxygen from the tiny air sacs at the end of the tracheoles and carries the oxygen through the blood to all tissues. True False 81. The body surface of an earthworm is kept moist by mucus and excretory fluid so that gas exchange can occur across it. True False 82. Spiracles are the valve-like openings on the sides of an insect's body, through which air enters the trachea. True False 83. Fish gills are less efficient at removing oxygen from water than human lungs at removing oxygen from air. True False 84. Hemoglobin carries most of the oxygen and most of the carbon dioxide transported in the blood in humans. True False 85. During inspiration, air pressure in the lungs decreases and air comes rushing in. True False 86. When nerve impulses pass to the diaphragm, the diaphragm relaxes and exhalation occurs. True False 87. The movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the blood depends on diffusion gradients. True False 88. The respiratory center of higher animals is located in the medulla of the brain. True False 89. As carbon dioxide reacts with water in blood, hydrogen ions are produced. True False 90. Hemoglobin is a molecule that has a remarkable ability to form an irreversible and permanent combination with oxygen. True False 91. All blood carried away from the heart is high in oxygen concentration and low in carbon dioxide concentration. True False 92. Chemoreceptors monitor the chemical composition of the blood, sending information to brain centers that are able to increase or decrease the rate of respiration to correct the blood chemistry. True False 93. Lung disorders such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or emphysema can be controlled by antibiotic treatment. True False 94. Pulmonary tuberculosis in an otherwise healthy individual may indicate a compromised immune system or HIV infection. True False 95. The muscular diaphragm is responsible for creating the thoracic muscular changes associated with human respiration. True False 96. Gas exchange in the lungs and tissues is due to active transport. True False 97. Describe the system by which fish move water over their gills to transfer oxygen from water to blood. 98. Compare the movement of air into and out of the lungs in a human and in a bird. 99. Compare the gas exchange structures and mechanisms used in a planarian, a grasshopper, and an earthworm. 100. List, in correct sequence, and describe the structures through which air passes in the human respiratory system during inhalation. 101. Describe the process by which oxygen enters the blood in the lung and leaves it in the body tissues. 102. Describe the process by which carbon dioxide enters the blood in the body tissues and leaves it in the lung. Chapter 37 KEY 1. D 2. C 3. E 4. A 5. C 6. B 7. B 8. C 9. B 10. D 11. C 12. A 13. E 14. C 15. B 16. C 17. D 18. C 19. D 20. D 21. A 22. A 23. A 24. B 25. E 26. E 27. C 28. C 29. C 30. A 31. D 32. C 33. B 34. E 35. C 36. B 37. D 38. D 39. A 40. D 41. E 42. D 43. C 44. D 45. C 46. B 47. D 48. B 49. C 50. A 51. C 52. C 53. D 54. D 55. B 56. D 57. C 58. A 59. B 60. A 61. D 62. D 63. B 64. C 65. B 66. D 67. E 68. D 69. D 70. D 71. C 72. D 73. C 74. D 75. B 76. TRUE 77. TRUE 78. TRUE 79. TRUE 80. FALSE 81. TRUE 82. TRUE 83. FALSE 84. FALSE 85. TRUE 86. FALSE 87. TRUE 88. TRUE 89. TRUE 90. FALSE 91. FALSE 92. TRUE 93. FALSE 94. TRUE 95. TRUE 96. FALSE 97. Answers will vary. 98. Answers will vary. 99. Answers will vary. 100. Answers will vary. 101. Answers will vary. 102. Answers will vary.