Unit #3 Study Guide
advertisement

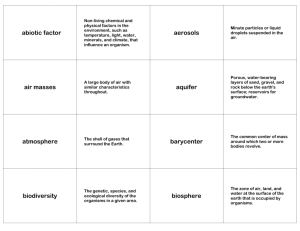
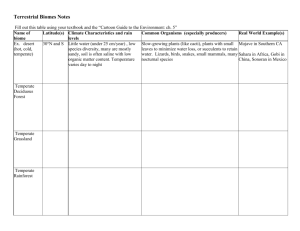
Unit #3 Study Guide, test is on 1/11/11 Study the Biome notes and map (green sheets) Be able to identify where each biome is on the map. Be able to describe the plant life, climate and location of each biome. Taiga is a vast Coniferous forest in the northern areas of Canada, Russia and Scandinavia. Tropical rain forests occur along the equator, are very hot, substantial rain, and have no seasonal changes of temperature or precipitation. Grasslands are determined by precipitation- more rain and they would be forests; less rain they would become deserts. They are usually found as a transition between deserts and forests A desert is an ecosystem in which productivity is limited by water. The world’s great deserts occur about 30 degrees north and south of the equator, At the “horse latitudes”. The biggest threat to rain forests, deciduous forests and taiga forests is deforestation. This is also a major cause of global warming. LOS Terms Abiotic- Non-living Biodiversity-1. number and variety of organisms found within a specified geographic region 2.variability among organisms, including the variability within and between species and within and between ecosystems Biome- broad area of the Earth's surface characterized by distinctive vegetation and associated animal life; e.g., broad-leaf forest biome, grassland biome, desert biome. Biotic- relating to life or living organisms Carrying Capacity- Maximum number of individuals that a given environment can support for a sustained period of time. Community- group of plants and animals living and interacting with one another in a specific region under relatively similar environmental conditions Conifer- any of various mostly needle-leaved or scale-leaved, chiefly evergreen, conebearing gymnosperm trees or shrubs such as pines, spruces, and firs Conservation-Life science: the protection, preservation, management, or restoration of wildlife and of natural resources such as forests, soil, and water, to prevent exploitation, destruction or neglect Consumer-organisms requiring complex organic compounds for food, which is obtained by preying on other organisms or by eating particles of organic matter Decomposer- organisms such as bacteria and fungi that feed and break down dead organisms, returning constituents of organic substances to the environment. Ecosystem- all the organisms in a given area and the abiotic factors with which they interact. Evapotranspiration- A process in plants which can be compared to breathing in people. Water is released from plants and then evaporates into the atmosphere. Example: Clouds that form over areas of forest or crops. Food Chain- arrangement of the organisms of an ecological community according to the order of predation in which each uses the next as a food source Food Web- totality of interacting food chains in an ecological community Limiting Factor- Conditions or resources that control the size of a population. Eco- This pre-fix means environment or house, (from Greek oikos, meaning house) Niche- The unique role an organism plays in its community or environment. Precipitation- Water that falls onto the earth from the atmosphere. Example: Includes rain, snow, sleet, hail Sublimation- The process of water changing from a solid to a gas Example: Water from glaciers or snow that does not melt, but goes up into the atmosphere Ecology- The study of how organisms live together in their environment. Symbiosis- Any close relationship between species. o Mutualism- both species benefit ++ o Commensalism- one organism benefits and the other is not affected. + ~ o Parasitism- one organism benefits but the other is harmed. + Runoff- Water that reaches the ground from precipitation, that then runs off into streams, lakes, or the ocean. Example: Running rivers or streams Infiltration- The process of water seeping into the soil and making its way to groundwater. Example: Runoff in streams that soaks into the ground, like in washes around Tucson. Vapor Transport- The movement of clouds from one place to another by wind currents. Example: Clouds being pushed by the wind from the equator to places North and South of the equator. Condensation- The process of water changing from a gas back to a liquid by cooling down Example: The formation of clouds from water that has evaporated from the Earth. Evaporation- The process of water changing from a liquid to a gas by the Sun’s energy .Example: Water from the ocean heated up and rising into the atmosphere. Population activity: Be able to evaluate data of populations by graphing data from a table, and telling “the story” of the data. Hydrologic Cycle Describe the Hydrologic cycle by drawing a cycle, which includes evapotranspiration and precipitation, and showing the direction the water is moving relative to the surface of the earth and atmosphere. Carbon Cycle Describe the Carbon Cycle by drawing the cycle, including the atmosphere, photosynthesis, producers, consumers, cellular respiration, decomposition and combustion. Know the last six “words of the week” from the agenda (from 11/2-1/7)