LONDON CANCER NEWS DRUGS GROUP Erlotinib re
advertisement

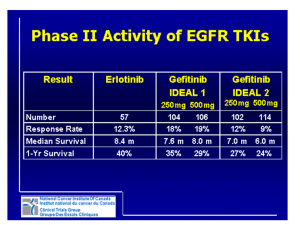
LONDON CANCER NEWS DRUGS GROUP Erlotinib re-challenge for the third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC London and South East Regional Medicines Information September 2012 Background A LCNDG rapid review was conducted in January 2012 for erlotinib third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC. Erlotinib is accepted for funding via the CDF in London for third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC. However, one of the LCNDG CDF criteria for erlotinib to be used in this setting is that the patient has not previously received erlotinib or EGFR-TKI therapy. This summary looks at the evidence surrounding re-challenging a patient with erlotinib for the third or fourth-line treatment of NSCLC when the patient has previously received erlotinib or EGFR-TKI therapy as an earlier line of treatment. Published data The original LCNDG review cited a phase III randomised control trial. Unfortunately, this study does not state whether patients who had been previously treated with an EGFR inhibitor were included in the trial. The American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update states that erlotinib may be used as third-line therapy in patients with NSCLC and a PS of 0 to 3 who have progressed on or following second-line chemotherapy and have not received prior erlotinib or gefitinib (6). Erlotinib after failure of gefitinib A search of the literature identified two phase II studies, a small prospective study with 8 patients, and some retrospective studies. Phase II studies Cho B.C. et al. conducted a study with 21 patients who had generally received gefitinib as a third-line therapy and showed progressive disease within 4 months of discontinuing gefitinib (1). Erlotinib was administered as a fourth-line therapy to 10 patients, and the remaining 11 patients received erlotinib as a fifth-line therapy after treatment with irinotecan as fourth-line chemotherapy. The median age of the patients was 56 years (range 36–70 years). 47.6% of patients had an ECOG performance status of 0–2. Patients received erlotinib 150mg daily. Responses in 21 assessable patients included 2 partial responses, 4 stable disease, and 15 progressive disease, which gave an overall response rate of 9.5% (95% CI 3–22%) and a disease control rate of 28.6% (95% CI 9.3–47.9%). Four of six gefitinib responders had progressive disease whilst on erlotinib. Ten out of the 21 patients (47.6%) were refractory to both tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The most common adverse event was grade 1/2 skin rash, which affected 28.5% of patients. Grade 3 skin rash occurred in one patient and grade 1 diarrhoea occurred in two patients. One patient (4.8%) discontinued erlotinib as a result of grade 3 vomiting. Dose reduction was required in one patient because of a grade 3 skin rash. Zhou ZT. et al. also conducted a phase II study of erlotinib 150mg daily in 21 patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC who showed disease progression on gefitinib treatment (2). The median age of the patients was 63 years (range 48–78). 66.7% of patients had an ECOG performance status of 0–2. 9.5% of patients had received 1 prior chemotherapy regimen, 61.9% of patients had received 2 prior chemotherapy regimens, and 28.6% had received 3 prior chemotherapy regimens. Out of the 21 patients, 2 (9.5%) had a partial response and 4 (19%) had stable disease, giving an overall response rate of 9.5% (95% CI 5.5–19.6%), and a disease control rate of 28.5% (95% CI 16.4–58.7%). The two patients with partial response to erlotinib had both obtained a partial response to gefitinib. In the four patients showing stable disease with erlotinib, three patients had stable disease following gefitinib treatment and one patient had progressive disease with gefitinib treatment. The most common adverse event was grade 1/2 skin rash, which affected 75% of patients. Grade 3 skin rash occurred in one patient and grade 1 diarrhoea occurred in 3 patients. Retrospective analysis Hata A. et al. conducted a retrospective analysis of 125 patients with relapsed NSCLC who had been treated with erlotinib 150mg daily after gefitinib failure (3). 70% of patients had a performance status of 0 or 1. 71 patients (57%) had previously responded to prior gefitinib therapy. Out of 125 patients, 11 had a partial response to erlotinib and 44 patients had stable disease, which gave an overall response rate of 9% (95% CI 5–15%) and a disease control rate of 44% (95% CI 35–53%). Patients who achieved a partial response had responded to prior gefitinib therapy. The median PFS was 2.0 months (95% CI 1.4–2.5 months) and the median overall survival time was 11.8 months (95% CI 6.4–16.0 months). The most common adverse event was skin rash, which was reported in 101 patients (81%). Interstitial lung disease was observed in four (3%) of the patients. No treatment-related death was observed. Dose reduction or interruption was performed in 61 (49%) of patients because of adverse events. The authors report that following multivariate analysis, insertion of cytotoxic chemotherapies between gefitinib and erlotinib treatment was associated with longer PFS. Re-challenge with erlotinib A search of the literature identified a retrospective study and a case report (5). Retrospective study Becker A. et al. conducted a retrospective study of 14 patients with stage IV NSCLC who had initially responded to tyrosine kinase inhibitors but stopped at disease progression and received platinum based chemotherapy. At renewed progression, patients were retreated with an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (4). The median age was 55 years (range 39–70 years). All except one patient were initially treated with erlotinib. In one patient this was combined with sorafenib. In all cases, the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor used after the platinum based chemotherapy was erlotinib. In three patients this was in combination with cetuximab. After a median follow-up of 9 months, 86% of patients had either partial response (n = 5) or stable disease (n = 7). Progressive disease was seen in 2 patients (14%). Two of the three patients who also received cetuximab had progressive disease and one patient had a partial response. Skin rash was commonly seen. Case report 2 Following 4 weeks of initial erlotinib 150mg daily, a 70 year-old female with stage IV NSCLC showed a complete response in her intracranial disease and a partial response in her lung disease. After 12 months of erlotinib therapy, the lung tumour progressed. She received two cycles of carboplatin and paclitaxel (which confirmed stable disease) but she refused further cytotoxic chemotherapy due to severe treatment-related diarrhoea. She was re-challenged with erlotinib and achieved a partial response after 4 weeks, although she also experienced a grade 3 skin rash which didn’t require dose modification. Summary The evidence is weak and the ASCO clinical practice guideline states that patients may be treated with erlotinib for third-line treatment of NSCLC if they have not received prior EGFR inhibitors. However, the evidence that is available suggests that re-challenge with erlotinib may result in some level of benefit for a minority of patients but it should also be noted that erlotinib rechallenge is associated with a high risk of skin rash. References 1) Cho B.C. et al. Phase II study of erlotinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of gefitinib. Journal of clinical oncology. 2007; 25(18):2528–2533 2) Zhou ZT. et al. Erlotinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after gefitinib failure. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2009; 64:1123–1127 3) Hata A. et al. Erlotinib after gefitinib failure in relapsed non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical benefit with optimal patient selection. Lung cancer. 2011; 74:268–273 4) Becker A. et al. Retreatment with erlotinib: Regain of TKI sensitivity following a drug holiday for patients with NSCLC who initially responded to EGFR-TKI treatment. European journal of cancer. 2011; 47:2603–2606 5) Guo R. et al. Subsequent chemotherapy reverses acquired tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance and restores response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor in advanced non-smallcell lung cancer. BMC cancer. 2011; 11:90 6) Azzoli C.G. et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Journal of clinical oncology. 2009; 27(36):6251-6266. Details of search strategy: 1. EMBASE; ERLOTINIB/; 11881 results. 2. EMBASE; LUNG NON SMALL CELL CANCER/; 46079 results. 3. EMBASE; 1 AND 2; 5038 results. 4. EMBASE; *ERLOTINIB/; 2217 results. 5. EMBASE; *LUNG NON SMALL CELL CANCER/; 30588 results. 6. EMBASE; 2 AND 4; 1225 results. 7. EMBASE; 4 AND 5; 970 results. 8. EMBASE; 7 [Limit to: Human and English Language and (Year Published Last 5 Years)]; 591 results. 9. MEDLINE; erlotinib.ti,ab; 2421 results. 10. MEDLINE; CARCINOMA, NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG/; 27182 results. 11. MEDLINE; 9 AND 10; 954 results. 12. MEDLINE; *CARCINOMA, NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG/; 23622 results. 13. MEDLINE; 9 AND 12; 857 results. 14. MEDLINE; 13 [Limit to: English Language and Humans and (Year Published Last 5 Years)]; 632 results. 15. EMBASE; exp DRUG RECHALLENGE/; 739 results. 16. EMBASE; 7 AND 15; 1 results. 17. MEDLINE; rechallenge.ti,ab [Limit to: English Language and Humans]; 1449 results. 3 18. MEDLINE; 13 AND 17 [Limit to: English Language and Humans]; 0 results. 19. EMBASE; 7 [Limit to: Human and English Language and (Clinical Trials Clinical Trial or Phase 1 Clinical Trial or Phase 2 Clinical Trial or Phase 3 Clinical Trial or Phase 4 Clinical Trial)]; 297 results. 20. MEDLINE; 13 [Limit to: English Language and Humans and (Age Groups All Adult 19 plus years)]; 351 results. 21. EMBASE; 19 [Limit to: Human and English Language and (Clinical Trials Phase 1 Clinical Trial or Phase 2 Clinical Trial or Phase 3 Clinical Trial or Phase 4 Clinical Trial) and (Year Published Last 5 Years)]; 128 results. 22. MEDLINE,EMBASE; Duplicate filtered: [13 [Limit to: English Language and Humans and (Age Groups All Adult 19 plus years)]], [19 [Limit to: Human and English Language and (Clinical Trials Phase 1 Clinical Trial or Phase 2 Clinical Trial or Phase 3 Clinical Trial or Phase 4 Clinical Trial) and (Year Published Last 5 Years)]]; 479 results. 4