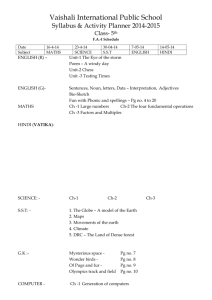
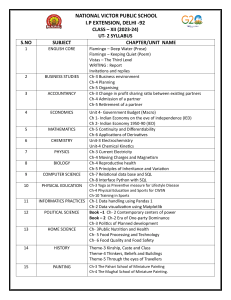
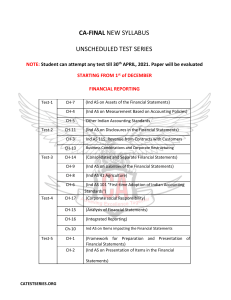
Course Outline
advertisement

Statics, ECIV 2311 STATICS HW: CH-2 TO CH-5 : Instructor : Statics-HW2-5 Dr. Bassam A. Tayeh , Phone: 2644400 Ext. 2889, Email: btayeh@iugaza.edu.ps Text Book & References: Engineering Mechanics: Statics, R.C. Hibbeler, 12th edition, SI Units , Prentice Hall, 2001. Several textbooks and references are available in the IUG Central Library. Course Description: Statics is the branch of engineering mechanics that studies the effects of forces and moments acting on rigid bodies that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity along a straight path. Course Objectives: This course is furnished to provide civil engineering students with the basic skills in engineering mechanics. Such skills are considered as pre-requisites for many other courses in the civil engineering curriculum. Among the main concepts that are covered in this course are vectors, equilibrium of a particle, equilibrium of rigid bodies, trusses and frames, shear and moment diagrams, centroids, and moment of inertia. Student Performance Evaluation / Grading The course consists of a three-hour lecture per week. Homework will be assigned each week. Explanations or solutions will be given in a separate helping session. Students are expected to do the homework and submit it weekly on time. Late submission will not be accepted. Class participation, quizzes and the final examination will evaluate student progress. Participation: Active participation in this course by all students is expected. Attendance for all lectures is strongly advised. Any student whose performance/attendance is unsatisfactory or not up to date will be notified by the College and may be dropped from the course for insufficient progress or participation. Exams and Grading Policy: Homework, Quizzes and Class Participation 10 points Midterm Exam 30 points Final Exam 60 points Total 100 Points ================================================================ Statics, ECIV 2311 - Course Outline Topic 1- General Principles ………………………………………. 0.5 week 1.2 Mechanics Lect. Notes CH1Introdcution 1.3 Fundamental concepts 1.4 Units of Measurement 1.5 The International system 1.6 Numerical Calculations 2- Force Vectors …………………………………….. 1.5 week 2.1 Scalars and vectors Ch-2.1 Ch-2.2 Ch-2.3 2.2 Vector operations Ch-2.4 2.3 Vector addition of forces . 2.4 Addition of a system of coplanar forces 2.5 Cartesian vectors (3-D) 2.6 Addition and subtraction of Cartesian Vectors (3-D) 2.7 Position Vectors 2.8 Force Vector directed along a line 2.9 Dot product 3- Equilibrium of a Ch-3.1 particle ………………………………. 1 week 3.1 Condition of the equilibrium of a particle Ch-3.2 Ch-3.3 3.2 The free- body diagram 3.3 Coplanar forces system (2-D equilibrium) 3.4 Three dimensional force systems 4- Force System Resultants …………………………… 4.1 Cross Product 2 week Ch 4.1 Ch 4.2 4.2 Moment of a force – scalar formulation Ch 4.3 4.3 Moment of a force – vector formulation Ch 4.4 4.4 Transmissibility of a force and principle of moments Ch 4.5 4.5 moment of a force about a specified axis 4.6 Moment of a couple 4.7 Movement of a force on a rigid body 4.8 Resultants of a force and couple system 4.9 Further reduction of a force and couple system 4.10 Reduction of a simple distributed loading 5- Equilibrium of a Rigid Body ………………………… 1.5 week 5.1 Conditions for rigid- body equilibrium Ch 5.1 Ch 5.2 5.2 Free- body diagram (2-D) Ch-5.3 5.3 Equations of equilibrium (2-D) Ch-5.1-H 5.4 Two and three force members Ch-5.2-H 5.5 Free body diagrams (3-D) Ch-5.3-H 5.6 Equations of equilibrium (3-D) 5.7 Constraints for rigid body 6- Structural Analysis week …………………………… 2 Ch-6.1 Ch-6.2 6.1 Simple trusses Ch-6-3 6.2 The methods of joints Ch-6-1-H 6.3 Zero- force members Ch-6.2-H 6.4 The method of sections Ch-6-3-H 6.5 Frames and machines 7- Internal Forces ……………………………. 1 week 7.1 Internal forces developed in structural members Ch-7.1 Ch-7.1-H 7.2 Shear and moment equations and diagrams 7.3 Relations between distributed load, shear, and moment 9- Center of Gravity and Centroid ……………. 1.5 week 8.1 Center of gravity and center of mass for a system of particles Ch-9.1 Ch-9.2 8.2 Center of gravity, center of mass, and centroid of a body Ch-9.1-H 8.3 Composite bodies Ch-9.2-H 8.4 Resultant of a general distributed force system 10- Moment of Inertia ……………………………………….. 2 weeks 9.1 Definition of moments of inertia for areas 9.2 Parallel axis theorem for an area 9.3 Radius of gyration of an area 9.4 Moments of inertia for composite areas 9.5 Moment of inertia for an area by integration 9.6 Products of inertia for an area 9.7 Moments of inertia for an area about inclined axes 9.8 Mohr’s circle for moments of inertia Ch-10.1 Ch-10.2 Ch-10.3 Ch-10.1H Ch-10-2H Ch-10.3H