Conceptual Forces Worksheet
advertisement

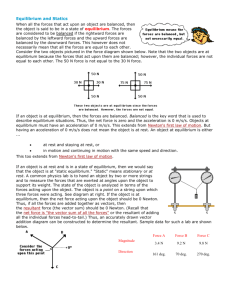
KEY_____________ Conceptual Forces Worksheet Name:______________ Mod:__________ Date:__________ Directions: Answer the following problems below using complete sentences to earn full credit. 1. Compare and contrast contact vs. field forces. Give examples of each. A field force and contact force both apply forces to objects. A contact force requires two objects to be in contact with one another to exist. A field force interacts with objects without contact through some force field. Examples of contact forces would be push and pull. Examples of field forces are gravity and electromagnetic. 2. How do we calculate the weight of an object? 𝑤 = 𝑚𝑔 𝑚 𝑤𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 (𝑁) = 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 (𝑘𝑔)𝑥 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝐷𝑢𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝐺𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 (9.8𝑠2 ) 3. What is the weight of a 40kg object? 𝑤 = 𝑚𝑔 𝑚 𝑤 = (40𝑘𝑔) (9.8𝑠2 ) 𝑤 = 392𝑁 4. What would be the mass of an object that weighted 200N? 𝑤 = 𝑚𝑔 𝑤 𝑚= 𝑔 200𝑁 𝑚= = 20.41𝑘𝑔 9.8𝑠𝑚2 5. What changes depending on location in the universe, weight or mass? Explain… Mass is the measure of matter in an object. Weight is the force of gravity pulling on an object. Mass stays constant regardless of location. Weight depends on the gravitational field produced by near by large masses. 6. State Newton’s First Law of Motion. Also known as the law of inertia. An object as rest remains at rest. An object in motion remains at a constant velocity, unless acted on by an unbalance net force. 7. State Inertia. The tendency for an object to resist change in motion. Directly proportional to mass. 8. Why is the normal force called a support force? It is the force created by an object supporting another object. Conceptual Forces Worksheet Methacton High School Physics Department 9. What is the difference between a tension force and a compression force? Tension is a pulling force and compression is a pushing force. 10. Define normal force. A contact force exerted by an object on another object in a direction perpendicular to the surface of contact. It is also known as a support force. 11. In what direction is the normal force drawn? The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface that the object is resting on. 12. Express Newton’s Second Law of Motion equation. The sum of the forces acting on object = Mass of object x Acceleration of object 13. Why do we write Fnet = ma and not F = ma? A single force does not cause an object to accelerate. It is the sum of all the forces acting on a single object that causes an object to acceleration as long as the sum of the forces do not equal zero. 14. In terms of forces, what does it mean for an object to be in equilibrium? An object is in equilibrium when the sum of the forces equal zero. This means that the object is in static equilibrium (rest) or dynamic equilibrium (constant speed). 15. What type(s) of motion does an object in equilibrium have? Static equilibrium (rest) or dynamic equilibrium (constant speed). 16. How does that motion change for the object if the force on the object is unbalanced? If an unbalanced force is applied to an object in equilibrium, the object will change its state of motion and accelerate. 17. Define Newton’s Third Law of Motion. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Forces always exist in pairs. Conceptual Forces Worksheet Methacton High School Physics Department