Track Back Block D - The Dudley Grid For Learning
advertisement
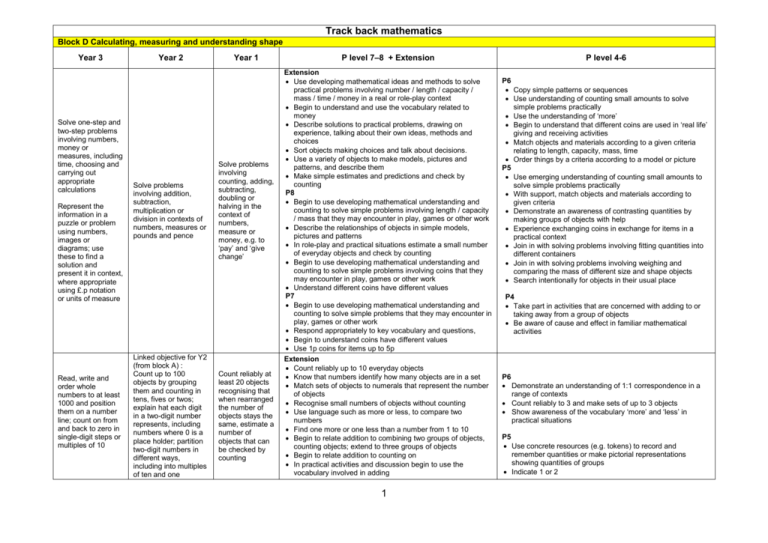
Track back mathematics Block D Calculating, measuring and understanding shape Year 3 Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time, choosing and carrying out appropriate calculations Represent the information in a puzzle or problem using numbers, images or diagrams; use these to find a solution and present it in context, where appropriate using £.p notation or units of measure Read, write and order whole numbers to at least 1000 and position them on a number line; count on from and back to zero in single-digit steps or multiples of 10 Year 2 Solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication or division in contexts of numbers, measures or pounds and pence Linked objective for Y2 (from block A) : Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain hat each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition two-digit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of ten and one Year 1 Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measure or money, e.g. to ‘pay’ and ‘give change’ Count reliably at least 20 objects recognising that when rearranged the number of objects stays the same, estimate a number of objects that can be checked by counting P level 7–8 + Extension Extension Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems involving number / length / capacity / mass / time / money in a real or role-play context Begin to understand and use the vocabulary related to money Describe solutions to practical problems, drawing on experience, talking about their own ideas, methods and choices Sort objects making choices and talk about decisions. Use a variety of objects to make models, pictures and patterns, and describe them Make simple estimates and predictions and check by counting P8 Begin to use developing mathematical understanding and counting to solve simple problems involving length / capacity / mass that they may encounter in play, games or other work Describe the relationships of objects in simple models, pictures and patterns In role-play and practical situations estimate a small number of everyday objects and check by counting Begin to use developing mathematical understanding and counting to solve simple problems involving coins that they may encounter in play, games or other work Understand different coins have different values P7 Begin to use developing mathematical understanding and counting to solve simple problems that they may encounter in play, games or other work Respond appropriately to key vocabulary and questions, Begin to understand coins have different values Use 1p coins for items up to 5p Extension Count reliably up to 10 everyday objects Know that numbers identify how many objects are in a set Match sets of objects to numerals that represent the number of objects Recognise small numbers of objects without counting Use language such as more or less, to compare two numbers Find one more or one less than a number from 1 to 10 Begin to relate addition to combining two groups of objects, counting objects; extend to three groups of objects Begin to relate addition to counting on In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding 1 P level 4-6 P6 Copy simple patterns or sequences Use understanding of counting small amounts to solve simple problems practically Use the understanding of ‘more’ Begin to understand that different coins are used in ‘real life’ giving and receiving activities Match objects and materials according to a given criteria relating to length, capacity, mass, time Order things by a criteria according to a model or picture P5 Use emerging understanding of counting small amounts to solve simple problems practically With support, match objects and materials according to given criteria Demonstrate an awareness of contrasting quantities by making groups of objects with help Experience exchanging coins in exchange for items in a practical context Join in with solving problems involving fitting quantities into different containers Join in with solving problems involving weighing and comparing the mass of different size and shape objects Search intentionally for objects in their usual place P4 Take part in activities that are concerned with adding to or taking away from a group of objects Be aware of cause and effect in familiar mathematical activities P6 Demonstrate an understanding of 1:1 correspondence in a range of contexts Count reliably to 3 and make sets of up to 3 objects Show awareness of the vocabulary ‘more’ and ‘less’ in practical situations P5 Use concrete resources (e.g. tokens) to record and remember quantities or make pictorial representations showing quantities of groups Indicate 1 or 2 Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and twodigit numbers Use knowledge of number operations and corresponding inverses, including doubling and halving, to estimate and check calculations Develop and use written methods to record, support or explain addition and subtraction of twodigit and three-digit numbers Begin to relate subtraction to taking away In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in subtraction Estimate a number of objects and round twodigit numbers to the nearest 10 Add or subtract mentally a single-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any twodigit number; use practical and informal methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers Linked objective for Y2 (from Block A) Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition and vice versa and use this to derive and record related addition and subtraction number sentences Relate addition to counting on; recognise that addition can be done in any order; use practical and informal written methods to support the addition of a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to a one-digit or two-digit number P8 Count reliably to at least 5; begin to count up to 10 objects In role play and practical situations estimate a small number and check by counting Begin to recognise numerals 0–9 and relate them to sets of objects Compare two given numbers of objects saying which is more and which is less P7 Recognise numerals 0–5 and to understand that each represents a constant number or amount Count reliably at least 5 objects Show a count up to 5 by a simple tally Begin to recognise difference in quantities P4 Show an interest in number activities Respond to the word ‘more’ and ‘gone’ Linked objective for Y1 (from Block A) Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition and vice versa and use this to derive and record related addition and subtraction number sentences Use practical and informal written methods to multiply and divide two-digit numbers (e.g. 13 × 3, 50 ÷4); round remainders up or down, depending on the context Understand that division is the inverse of multiplication and Multiplication and division prior to Y3 is covered and exemplified is block E 2 vice versa; use this to derive and record related multiplication and division number sentences Find unit fractions of numbers and quantities (e.g. ½, 1/3, ¼, 1/6 of 12 litres) Use a set-square to draw right angles and to identify right angles in 2-D shapes; compare angles with a right angle; recognise that a straight line is equivalent to two right angles Read and record the vocabulary of position, direction and movement, using the four compass directions to describe movement about a grid Recognise and use whole, half and quarter turns, both clockwise and anti-clockwise; know that a right angle represents a quarter turn Identify objects that turn about a point (e.g. scissors) or about a line (e.g. a door); recognise and make whole, half and quarter turns Extension Use everyday vocabulary to describe turn P8 Gain experience of instructions involving the idea of turn P7 Experience the notion of turn Follow and give instructions involving position, direction and movement Visualise and use everyday language to describe the position of objects and direction and distance when moving them, e.g. when placing or moving objects on a games board Extension Use everyday vocabulary words to describe position, direction and movement P8 Encounter a wider variety of everyday words to describe position, direction and movement P7 Respond to instructions that contain familiar words to describe position Draw and complete shapes with reflective symmetry; draw the reflection of a shape in a mirror line along one side’ Know the relationships between kilometres and metres, metres and centimetres, kilograms and grams, litres and millilitres; choose and use appropriate units to estimate, P6 Encounter and explore changes of position of themselves and objects Show understanding of words, signs and symbols which describe positions P5 Encounter and notice changes of position of themselves and objects P4 Encounter and notice changes of orientation of themselves and objects Symmetry prior to Y3 is covered and exemplified is block B Estimate, compare and measure lengths, weights and capacities, choosing and using standard units (m, cm, kg, litre) and suitable measuring instruments Extension Begin to understand and use the language of measures in practical contexts Use the language of measures to compare the length / capacity / mass of 2 or more objects in practical contexts Estimate, measure, weigh and compare P8 Use familiar words to describe measures in practical contexts Order 2 items by their length / capacity / mass 3 P6 Show awareness of the vocabulary ‘more’ and ‘less’ in practical situations Compare the overall length / capacity / mass of one object with another when the difference is not great P5 Find ‘big’ and ‘small’ objects on request Compare the overall length / capacity / mass of one object with another when there is a marked difference in size measure and record measurements Read, to the nearest division and half-division, scales that are numbered or partially numbered; use the information to measure and draw to a suitable degree of accuracy Read the time on a 12-hour digital clock and to the nearest 5 minutes on an analogue clock; calculate time intervals and find start or end times for a given time interval objects choosing and using suitable uniform non-standard or standard units and measuring instruments, e.g. a lever balance, metre stick or measuring jug Compare directly two objects P7 Use familiar words to compare sizes and quantities Order things by a criteria – using trial and improvement – with assistance, draw what they have done and know this is a record P4 Through exploration, gain awareness of differences in length / capacity / mass Join in with solving problems involving comparing different sized objects Read the numbered divisions on a scale, and interpret the divisions between them, e.g. on a scale from 0 to 25 with intervals of 1 shown but only the divisions 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 numbered; use a ruler to draw and measure lines to the nearest centimetre Use units of time (seconds, minutes, hours, days) and know the relationships between them; read the time to the quarter hour; identify time intervals, including those that cross the hour Use vocabulary related to time; order days of the week and months; read time to the hour and half hour. Extension Understand and use the language of time Begin to recognise o’clock on a clock face Sequence familiar events in their day Match key personal events, e.g. Christmas and swimming in the sea, to the named seasons Compare how long it takes to do things using a simple timer P8 Begin to be aware of and repeat the language of time Recognise order in the day through ordering of significant events Links significant personal events to the passing of time Associate familiar activities and experiences to seasonal changes P7 Develop awareness of time through discussion about daily events and when they happen 4 P6 Respond to some words, signs or symbols related to time Participate in the sequencing of pictures of two daily events Begin to be aware of the language of time used in everyday routines P5 Encounter the vocabulary of time through daily discussions of days of the week and timetabled events for the day P4 Through exploration, gain awareness of differences in time