Writing Learning Outcomes
advertisement

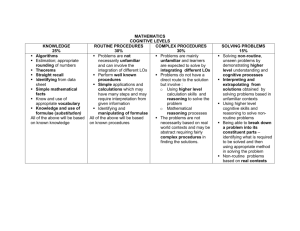
Writing Assessable Learning Outcomes Learning outcomes refer to what a student will be able to know or do at the end of a learning unit. Learning outcomes are written for 4 areas of learning: Knowledge This refers to the content, topics, what we know of as the syllabus. You may start these learning outcomes by saying: Having successfully completed this unit, you will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:…. Cognitive Skills This is what you expect students to do with the content: describe, compare, evaluate, apply etc. These always start with a verb that will guide how you assess – see table with a list of verbs below. Subject Specific Skills Not all units will have this set of learning outcomes, and relates to manipulation skills and professional skills that a graduate of such a programme needs. For motor skills you may use verbs like: co-ordinates, balances, operates, handles (with confidence/skilfully), expresses, performs, calibrates, rotates etc. Key Skills The University have a guided list of key skills (see QAU Handbook, section 2.3.1.4 – scroll to near bottom) which are: communicate orally work in a team work independently appropriately use ICT research & critically evaluate information apply techniques, theories in a new context In assessing key skills you may want to add a particular group of key skills to a set of core assignments and include in the marking. Or, you may ask students to evidence their key skills work through, for example, Progress Files. You may have a mix of techniques. For example assessing attitudes or group work/seminar work you could use verbs like: supports, shares, responds, judges, joins, questions, praises, listens, argues, responds, challenges, integrates, enjoys, volunteers, attempts, listens, receives, decides. Cognitive Skills for Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain Selection of active verbs for learning outcomes Answers the questions 1. knowledge – ability to recall previously learned material, know specific facts/methods/procedures, know basic concepts/principles. define, label, recall, order, list, quote, match, state, recognise, identify, recite Who, what, when, where, how? How do you define? 2. Comprehension – ability to understand the meaning of material, interpret charts/graphs, estimate future consequences implied in the data. describe, discuss, summarise, paraphrase, report, review, understands, explain How would you paraphrase? What are the main ideas? How would summarise? Give examples of…… 3. Application –ability to use learned information in new situations/problem solving/solutions that have ‘best answers’, demonstrate correct usage of procedures, apply laws/theories to practical situations. assess, demonstrate, examine, distinguish, establish, show, report, implement, determine, produce, solve, draw, interpret, provide, use, utilise, write How is xxx an example of yyy ? How is xx related to yy? Why is xx significant? 4. Analysis – ability to identify component parts of knowledge, to understand its structure and composition, recognise logical fallacies in reasoning, make distinctions between facts and inferences. analyse, illustrate, discriminate, differentiate, distinguish, examine, question, infer, support, prove, test, experiment, categorise, write What are the parts/features of xx? Classify acccording to …..? Outline/diagram How does xx compare/contrast with ? What evidence is there for …? 5. Synthesis- ability to creatively apply knowledge to new areas, integrate new knowledge, write well argued paper/speech, propose research design to test hypothesis. What would you infer/predict from ..? What ideas can you add to ? How would you create/design …? What might happen if you ? What solutions would you suggest..? 6. Evaluation – ability to judge the value of evidence/ material for a given purpose. Compile, categorise, generate, negotiate, reconstruct, reorganise, revise, validate, organise, plan, propose, set up, write, substitute, initiate, express, compare, modify, design, create, build, devise, integrate Appraise, criticise, assess, argue, justify, defend, interpret, support, estimate, evaluate, critique, review, write Do you agree that…? What do you think about..? What is the most important…? Prioritise & give rationale Decision making – rationale Criteria for assessing …. As can be seen the cognitive complexity increases with ‘evaluation’ being a more complex cognitive activity than ‘knowledge’. Writing Learning Outcomes Select likely learning outcomes from the subject’s benchmark statement, from your unit aims and from your professional body (if appropriate). Learning outcomes should be written at both Programme and Unit level. You can start at either level. Your learning outcomes will need to range: knowledge, key skills, cognitive skills and subject specific skills although you may find your benchmark statement uses slightly different headings. Start your learning outcome with an active verb – use verbs above as a guide. Check you cognitive learning outcomes span the range of cognitive skills, ensuring that a balance of skills at the various levels of the programme. Map learning outcomes to teaching method/activity/assignment. Map learning outcomes to a type of assessment – you may find several learning outcomes are assessed in one assignment. Ensure that the learning outcomes can be identified in that assignment for assessment. The verb will help you devise the assessment strategy. Mapping Learning Outcomes to Assessment You may want to map your core learning outcomes with a type of assessment. This will give you an overview of what you are doing and you may see that you are assessing a learning outcome across several types of assessment. You could get your core learning outcomes from your Programme Specification, but ensure you consider how you deal with the various levels. To do this you could take some information from units across the various levels. Programme_______________________- Learning outcomes (include: knowledge, cognitive, key & subject specific skills) – select core learning outcomes that appear across units – it is not necessary to list all learning outcomes. Learningteaching activity You will need this for the learningteachingassessment cycle part – just give idea of different teaching& learning used to accommodate a learning outcome. Type of assessment Eg. essay, group work, presentation, work-based, extended project etc. Unit Code