Notes – Cells & Energy (Chapter 1, Lesson 3)
advertisement
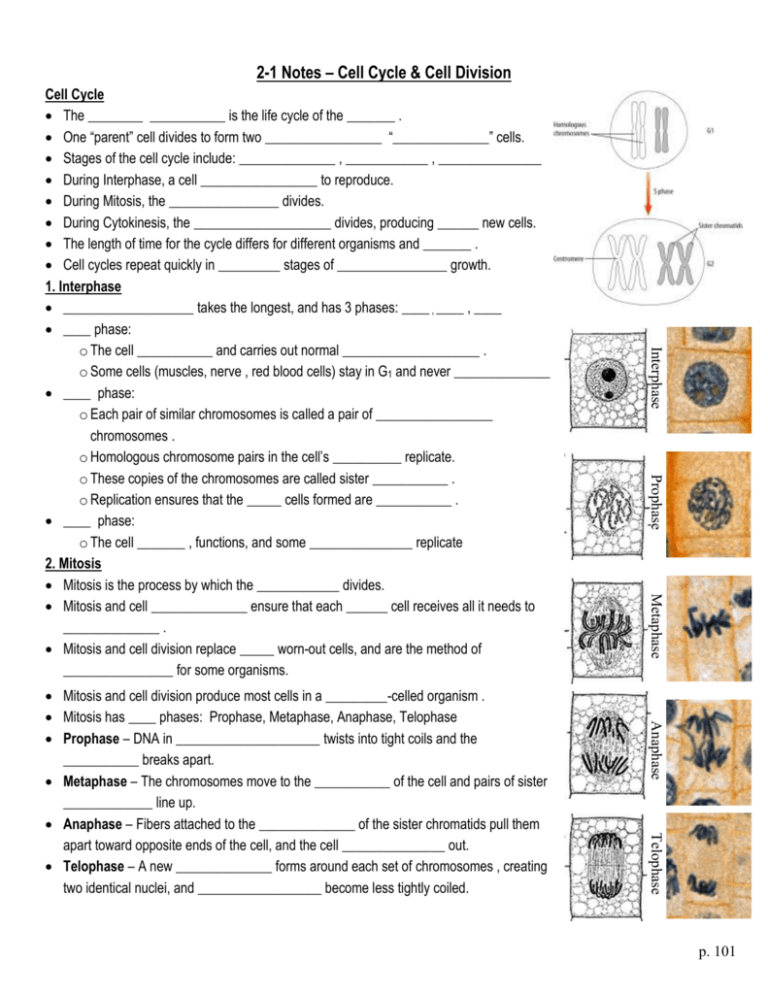
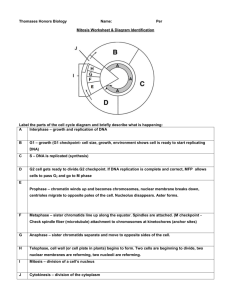
2-1 Notes – Cell Cycle & Cell Division Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitosis and cell division produce most cells in a _________-celled organism . Mitosis has ____ phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Prophase – DNA in _____________________ twists into tight coils and the ___________ breaks apart. Metaphase – The chromosomes move to the ___________ of the cell and pairs of sister _____________ line up. Anaphase – Fibers attached to the ______________ of the sister chromatids pull them apart toward opposite ends of the cell, and the cell _______________ out. Telophase – A new ______________ forms around each set of chromosomes , creating two identical nuclei, and __________________ become less tightly coiled. Interphase Cell Cycle The ________ ___________ is the life cycle of the _______ . One “parent” cell divides to form two _________________ “______________” cells. Stages of the cell cycle include: ______________ , ____________ , _______________ During Interphase, a cell _________________ to reproduce. During Mitosis, the ________________ divides. During Cytokinesis, the ____________________ divides, producing ______ new cells. The length of time for the cycle differs for different organisms and _______ . Cell cycles repeat quickly in _________ stages of ________________ growth. 1. Interphase ___________________ takes the longest, and has 3 phases: ____ , ____ , ____ ____ phase: o The cell ___________ and carries out normal ____________________ . o Some cells (muscles, nerve , red blood cells) stay in G1 and never ______________ ____ phase: o Each pair of similar chromosomes is called a pair of _________________ chromosomes . o Homologous chromosome pairs in the cell’s __________ replicate. o These copies of the chromosomes are called sister ___________ . o Replication ensures that the _____ cells formed are ___________ . ____ phase: o The cell _______ , functions, and some _______________ replicate 2. Mitosis Mitosis is the process by which the ____________ divides. Mitosis and cell ______________ ensure that each ______ cell receives all it needs to ______________ . Mitosis and cell division replace _____ worn-out cells, and are the method of ________________ for some organisms. p. 101 Cytokinesis 3. Cytokinesis The _____________ and its contents divide to form two identical _____________ cells. At the start, the cell ______________ pinches inward. In a cell with a _____ _______ , a _______ ________ forms between the two nuclei. The cell plate later becomes the cell _______________ , which builds the new cell walls. Cell Division • Results in two new ______________ cells to replace the original ____________ cell. • Each ________________ cell has the exact same _______________ and ________ of ____________________ as the _____________ cell. • All the cells in your body (except _____ and _______ ) have ___________ chromosomes. Cell Cycle Phase Stages Description Growth and cellular functions Interphase Growth and chromosome replication Growth and cellular functions; organelle replication Mitotic Phase Nucleus divides Cytoplasm divides Review ____ 1. When a cell is preparing to reproduce, what phase of the cell cycle is it in? A. S phase C. interphase B. prophase D. mitosis ____ 2. In which phase does the nucleus divide? A. G2 C. cytokinesis B. mitosis D. cell division ____ 3. In which type of cell would you expect to see a cell plate form? A. plant cell C. stomach cell B. animal cell D. parent cell ____ 4. Each chromosome in one set of chromosomes has a similar chromosome in the other set of chromosomes. What is a pair of similar chromosomes called? A. sister chromosomes C. daughter chromosomes B. homologous chromosomes D. parent chromosomes ____ 5. Sister chromatids are held together at what region of the chromatids? A. the ends C. the cell plate B. the centromere D. G1 ____ 6. When do the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to separate? A. prophase C. anaphase B. metaphase D. telophase ____ 7. What happens during cytokinesis? A. the nucleus divides C. chromosomes are replicated B. the cytoplasm divides D. growth and cellular functions ____ 8. What is the first phase of mitosis? A. interphase C. prophase B. G1 D. cell division 2-1 Notes – Cell Cycle & Cell Division Cell Cycle • • • • • • • • The cell cycle is the life cycle of the cell. One “parent” cell divides to form two identical “daughter” cells. Stages of the cell cycle include: Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis During Interphase, a cell prepares to reproduce. During Mitosis, the nucleus divides. During Cytokinesis, the cytoplasm divides, producing two new cells. The length of time for the cycle differs for different organisms and cells. Cell cycles repeat quickly in early stages of animal growth. 1. Interphase • Interphase takes the longest, and has 3 phases: G1 , S , G2 • G1 phase: • • Telophase – A new membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two identical nuclei, and chromosomes become less tightly coiled. Telophase • apart. Metaphase – The chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and pairs of sister chromatids line up. Anaphase – Fibers attached to the centromere of the sister chromatids pull them apart toward opposite ends of the cell, and the cell stretches out. Anaphase • Metaphase the cell grows, functions, and some organelles replicate 2. Mitosis • Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus divides. • Mitosis and cell division ensure that each new cell receives all it needs to function. • Mitosis and cell division replace old worn-out cells, and are the method of reproduction for some organisms. • Mitosis and cell division produce most cells in a many-celled organism. • Mitosis has 4 phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase • Prophase – DNA in chromosomes twists into tight coils and the nucleus breaks • Prophase • The cell grows and carries out normal functions. Some cells (muscle, nerve, red blood cells) stay in G1 and never reproduce. S phase: • Each pair of similar chromosomes is called a pair of homologous chromosomes. • Homologous chromosome pairs in the cell’s nucleus replicate. • These copies of the chromosomes are called sister chromatids. • Replication ensures that the new cells formed are identical. G2 phase: Interphase • • • • • At the start, the cell membrane pinches inward. In a cell with a cell wall, a cell plate forms between the two nuclei. The cell plate later becomes the cell membrane, which builds the new cell walls. Cell Division • Results in two new daughter cells to replace the original parent cell. • Each daughter cell has the exact same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell. • All the cells in your body (except egg and sperm) have identical chromosomes. Cell Cycle Phase Interphase Mitotic Phase Stages G1 S G2 Mitosis Cytokinesis Cytokinesis 3. Cytokinesis • The cytoplasm and its contents divide to form two identical daughter cells. Description Growth and cellular functions Growth and chromosome replication Growth and cellular functions; organelle replication Nucleus divides Cytoplasm divides Review (Answers: 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-B, 5-B, 6-C, 7-B, 8-C) ____ 1. When a cell is preparing to reproduce, what phase of the cell cycle is it in? A. S phase C. interphase B. prophase D. mitosis ____ 2. In which phase does the nucleus divide? A. G2 B. mitosis C. D. cytokinesis cell division ____ 3. In which type of cell would you expect to see a cell plate form? A. plant cell B. animal cell C. D. stomach cell parent cell ____ 4. Each chromosome in one set of chromosomes has a similar chromosome in the other set of chromosomes. What is a pair of similar chromosomes called? A. sister chromosomes C. daughter chromosomes B. homologous chromosomes D. parent chromosomes ____ 5. Sister chromatids are held together at what region of the chromatids? A. the ends C. B. the centromere D. the cell plate G1 ____ 6. When do the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to separate? A. prophase C. anaphase B. metaphase D. telophase ____ 7. What happens during cytokinesis? A. the nucleus divides B. the cytoplasm divides C. D. chromosomes are replicated growth and cellular functions ____ 8. What is the first phase of mitosis? A. interphase B. G1 C. D. prophase cell division