SCREENING TEST type centers in box with 9 point indent
advertisement

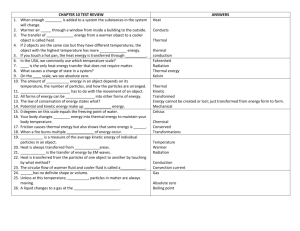
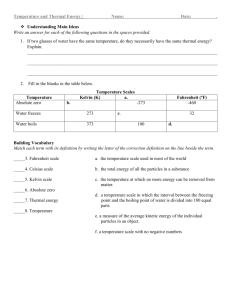
Answers Thermal Energy and Heat Unit 5 Study Guide 1. C 2. A 3. C 4. C 5. A 6. A 7. C 8. B 9. C 10. D 11. kinetic 12. Kelvin 13. thermal energy 14. silver 15. thermal expansion 16. F,100°C 17. T 18. F, convection 19. F, insulator 20. F, contract 21. Beaker C. The thermal energy of the water increases with temperature and with the number of molecules. Because beaker C has the highest temperature and as much water as any other beaker, it has the most thermal energy. 22. Beakers A and B. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Since the water temperature is the same in both beakers, the water molecules have the same average kinetic energy. 23. A change in temperature of 1 Celsius degree is greater than a temperature change of 1 Fahrenheit degree because a Celsius degree is larger than a Fahrenheit degree. The Celsius degree is larger because there are 100 Celsius degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, but there are 180 Fahrenheit degrees between the same points. 24. Thermal energy is the total energy of all of the particles of a substance. Heat is the movement of thermal energy from a substance at a higher temperature to another at a lower temperature. Thermal energy is a form of energy, while heat is the transfer of energy. 25. Air is a poor conductor of heat and thus acts as an insulator. The air space reduces the heat transfers by conduction. 26. Without an air layer, the single pane allows heat to escape easily by conduction. 27. As a fluid absorbs heat, it expands, which causes its density to decrease. If a fluid is heated from below, the warmer, less-dense fluid rises and the cooler, denser fluid sinks into its place. This cooler fluid is warmed, becomes less dense, and rises. The warmer, lessdense fluid transfers heat to the fluid around it as it rises. As it transfers heat, it cools, becomes denser, and sinks. The continuous rising of warmed fluid and the sinking of cooled fluid form convection currents. 28. Conduction transfers energy within an object or between objects when fastmoving particles collide with slowermoving particles and transfer kinetic energy, making the slower particles move faster. Thermal Energy and Heat Chapter Tests