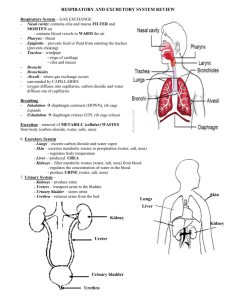
Urinary Incontinence- Involuntary loss of urine
advertisement

GI/GI Exam 2 10/18/2005 9:51:00 AM Urinary Tract Infection Second most common infection in the US Not much morbidity Divide into upper and lower UTI Lower is much more common Upper includes kidney Lower is bladder Most commonly an older person problem Over the age of 65 4-10% Below this age is 1-4% Mainly an adult problem Young group is pediatric females—diapers to toilet training This is a hygiene problem o Wearing diapers too long o Wiping front to back or back to front o Bubble baths—urethra has bacterostatic chemicals 80-90% have E. coli at the base of the problem UTI's are ascending infections Ratio of men to women is 1:10 Subcategories o Blockage of one ureter o Catheter 5%/day risk of getting a UTI of a hospital stay o Now at 1% o Coated w/tephalon o Less frequent changing of catheter 18-27 y/o women—sexually active o Honeymoon cystitis o Peri-urethral swelling o Increase urethral outlet pressure o Harder to urinate o Urinary stasis o Good medium for bacterial growth Pregnant women Diabetes Mellitus o Reduced immune status o Enhanced environment for bacteria—glucose in urine Obstruction of any type o Hypertrophy of prostate o Floor of pelvis tightened—women How to o Surgery o Stenosis of urethra Obstruction leads to stasis Hypertension o Upper urinary tract—kidneys o Form of renal failure Neurogenic bladder o Lost ability to contract bladder decide if Lower or Upper If common UTI, can be treated conservatively Have to be more cautious w/upper Upper UTI is sicker o 102 to 104 o Shaking chills o Unilateral flank pain (can be B/L) o Casts Historical—what happened wks ago Bloody casts o Epithelial cells (renal) o Pt looks ill o Urine labs are abnormal o Very unusual for Dysuria Lower o Change in urinary output o Burning pain w/urethritis o Females do not have strong urethritis (pain is not prominent) o Males are more likely to have pain and copious discharge Fever is present is low grade Cystitis—low grade ESR slightly elevated if bladder, none w/urethritis Urine labs abnormal Combination of bacterial and WBC Bacterial or WBC alone consider contamination o Double catch for women o Triple catch for men o Blood may be in urine o o o o Kidney and upper UTI Medullary portion affected first Can occur from ascension Build up of urine from stenosis of ureter Cortex affect primarily or only—can't talk about ascension o Look at vascular tree o Patchy infiltrate of infection o Septicemia—look at both kidneys o This is worse than medullary—environment is hostile due to osmolarity Investigate Pt. IVP and retro exam Include abdominal US Tx Only one's that look for spinal cause and susceptibility to infection Don't know why have UTI but do Hydrating the pt will help the pt—flush out the organisms Cranberry juice o Not b/c acidifier o A component that makes it difficult for the bacteria to grab onto the wall o Reduced bacterial adhesions We do not know for sure how much to drink Recommend 4-8oz glasses per day—Dr. Kuhn got results w/this If this is going to work, it will tend to work quickly If this does not work, look at the water that they are drinking Recommend steamed, distilled water Prostatitis Bacterial acute o Young men significantly o Instrumentation—catheter o Has more Sx that are more recognizable o May be the first time that they have difficulty urination o May see discharge which is reliable o Burning sensation o Rectal/digital exam—enlargement of gland o Typical that it hurts during the exam and noticeably enlarged o Positive cup 3 test (more so than chronic) o Fever, blood, WBC o Ascending UTI Bacterial chronic o Older men o Idiopathic o Recurrent UTI Misc.—non-bacterial o Viral o Meds that irritate gland o Less discharge o Less burning o Long standing Sx o More workup is required Rectal/digital exam o Size o Texture o Shape o DO NOT MASSAGE THE GLAND This introduces the bacteria deeper into the gland where the body can not deal w/it as well Urethritis E. coli origin Ascending route Anytime aggravate urethra 2 categories o Gonococcal Epidemic Sx for men are worse Burning urination Copious discharge Have urgency and frequency Women Some discharge Not a lot of burning Complications Endocarditis Meningitis Synovial inflammation—synovitis—arthralgia as complication Severity of the infection does not correlate to the complications Dx Tx Penicillin o Non-gonococcal Chlamydia Less discharge Same differences of Sx of men and women Penicillin does work Sulfa drugs Burning on urination Men have more prominent complaints More tissue to have aggravated Bacteria and WBC Urgency due to bladder outlet E. coli o Sx Exam 2 10/18/2005 9:51:00 AM Urinary Incontinence- Involuntary loss of urine Incidence: More than 12 million Americans In women (approx. 38%) 40% of hospitalized elderly persons 50% of nursing home residents a leading cause of nursing home admissions Cost $$: Over $1 billion in sales/year Psychological costs o Embarrassment and social inhibition o Depression, impaired nutrition in elderly Causes: Myth: normal and expected age-related change Age-related physiological changes in the lower urinary tract or chronic illness may predispose to urinary incontinence o Changes consist of: decrease bladder capacity, flow rate, ability to postpone voiding, nocturnal fluid excretion, and prostate size. Anatomy Detrusor muscle and two sphincters Detrusor muscle innervations o Pelvic nerve via PSNS (cholinergic receptor- Ach neurotransmitter) Bladder neck and proximal urethra o SNS (alpha-adrenergic receptor- nor-epinephrine neurotransmitter) Base of the urethra (skeletal muscle- voluntary) o Pudendal nerve (Ach neurotransmitter) Function Storing urine o Relaxation of detrusor muscle o Contraction of sphincters o Intravesicular pressure is less than urethral pressure Voiding urine: o Detrusor muscle contracts and sphincter relax o Intravesicular pressure is greater that urethral pressure Causes of Reversible Incontinence Acute illness with: o Confusion or disorientation o Immobility o Lethargy Urinary tract infection Fecal impaction Use of certain drugs Classification of Persistent Incontinence Persistent incontinence may result from untreated illness or arise insidiously 5 basic classifications o o o o o stress urge overflow functional mixed Stress Incontinence- loss of small amounts of urine during coughing, laughing, or other activities which increase intra-abdominal pressure Due to weak pelvic floor and urethral muscles Predominantly found in women Urge Incontinence- leakage of large amounts of urine precipitate by involuntary bladder contractions. Inability to delay voiding once a sensations of bladder fullness is perceived. Due to various GU and CNS conditions that cause hyper-reflexia of bladder contractions o Urethritis, cystitis, stones, stroke, spinal cord injury, MS, Parkinson’s Alzheimer’s, tumors *low volume voider, a patient that empties the bladder frequently, she decreases the amount being able to be held. Overflow Incontinence- constant dribbling of small amounts of urine also known as: paradoxical incontinence, Neurogenic incontinence. Due to over-distention of the bladder Causes include: o Anatomic obstruction o Hypocontractile bladder o Use of certain medications Functional Incontinence- involuntary loss of urine resulting from the inability to use a toilet Due to physical, psychological, or environmental factors Occurs despite normal urinary tract infection. Mixed Incontinence- combinations of the four previous categories Most common combination- stress and urge incontinence Identifying presence of greater than 1 type important for treatment options. Patient Evaluation Primary goal: identify reversible factors contributing to incontinence History: o Symptoms (frequency, volume, Dysuria, urgency) o Active and past medical conditions o Environmental factors and medications Urobehavioral diary o Self-monitoring and feedback Physical exam o Neurologic, abdominal, pelvic, rectal Lab o Serum electrolyte, BUN, glucose o Urinalysis (hematuria, Pyuria, bacteriuria, glycosuria) and culture Spinal exam Urodynamic evaluation (co-management) o Sonography, catheterization, cystography Treatment Goals in Elderly Maintain existing continence Improve socialization Decrease embarrassment Preserve renal function Avoid catheterization and the need for absorbent undergarments Conservative Treatment Options Biofeedback Methods o Monitoring pelvic floor muscle. And contraction of external urethral sphincter through reinforcement with visual and auditory signals o 25% success rate o requires expensive equipment Aggressive Treatment Collagen injections Nip and Tuck Exam 2 10/18/2005 9:51:00 AM 10/17/05 Nocturnal Enuresis- wetting the bed at night Common problem in children 4% of people have incontinence up until age 60 Causes: Psychosocial- divorce, terminal illness, Regression- regress into a younger mental state due to stress UTI- #1 on differential Breneman- study that followed children growing up with NE, they found that 66% of cases could be eliminated from food allergies Most common allergen is cow’s milk Esperanea & Gerard Dairy products are allergens that trigger enuresis, some citrus products and decrease threshold in sphincter muscles. Etiologies for Enuresis Children seem to be late walkers (possibly from skeletal muscle immaturity) Seem to be on the smaller side of the height and weight charts Are not good at school Are very deep sleepers, so if they don’t wake up, they just pee Most destructive aspect is punishment/reward from parents Exam 2 10/18/2005 9:51:00 AM Carcinoma to GU System #1 primary is prostate 70, 000/year and climbing 32,000 deaths/yr Lab studies—PSA Change in urinary habits can be prevented by surgical removal, and early detection (the more invasive, more expensive surgeries ten to have a better outcome) Patient History #2 Bladder is next 37,000/yr 3:2 males: females (females are increasing) Women are working in places that they did not use to Women are smoking more In males a triple catch urine specimen would be abnormal Tx. Options: Mets to bladder Melanoma—GIGU An increase in acidphosphatase is an indicator that the mets has left the prostate and moved elsewhere #3 Testicular Carcinoma (rare) earliest sign is a mass (part of male physical examination) pain, which is from the mass blocking the secretory duct Kidneys ¾ w/calcifications on lumbar films are malignant processes o This includes diabetes mellitus o Hematuria is the most consistent sign, and it is only present 50-60% of the time o Flank pain, but by the time the flank pain shows up it is a considerably large lesion. o ¼ of all patients with renal cell carcinoma have evidence of metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Typically it moves to the lungs- repeat episodes of pneumonia. Exam 2 10/18/2005 9:51:00 AM Urinary Tract Infection Second most common infection in the US Not much morbidity Divide into upper and lower UTI Lower is much more common Upper includes kidney Lower is bladder Most commonly an older person problem Over the age of 65 4-10% Below this age is 1-4% Mainly an adult problem Young group is pediatric females—diapers to toilet training This is a hygiene problem o Wearing diapers too long o Wiping front to back or back to front o Bubble baths—urethra has bacterostatic chemicals 80-90% have E. coli at the base of the problem UTI's are ascending infections Ration of men to women is 1:10 Subcategories o Blockage of one ureter o Catheter 5%/day risk of getting a UTI of a hospital stay o Now at 1% o Coated w/tephalon o Less frequent changing of catheter 18-27 y/o women—sexually active o Honeymoon cystitis o Peri-urethral swelling o Increase urethral outlet pressure o Harder to urinate o Urinary stasis o Good medium for bacterial growth Pregnant women Diabetes Mellitus o Reduced immune status o Enhanced environment for bacteria—glucose in urine Obstruction of any type o Hypertrophy of prostate o Floor of pelvis tightened—women How to o Surgery o Stenosis of urethra Obstruction leads to stasis Hypertension o Upper urinary tract—kidneys o Form of renal failure Neurogenic bladder o Lost ability to contract bladder decide if Lower or Upper If common UTI, can be treated conservatively Have to be more cautious w/upper Upper UTI is sicker o 102 to 104 o Shaking chills o Unilateral flank pain (can be B/L) o Casts Historical—what happened wks ago Bloody casts o Epithelial cells (renal) o Pt looks ill o Urine labs are abnormal o Very unusual for Dysuria Lower o Change in urinary output o Burning pain w/urethritis o Females do not have strong urethritis (pain is not prominent) o Males are more likely to have pain and copious discharge Fever is present is low grade Cystitis—low grade ESR slightly elevated if bladder, none w/urethritis Urine labs abnormal Combination of bacterial and WBC Bacterial or WBC alone consider contamination o Double catch for women o Triple catch for men o Blood may be in urine o o o o Kidney and upper UTI Medullary portion affected first Can occur from ascension Build up of urine from stenosis of ureter Cortex affect primarily or only—can't talk about ascension o Look at vascular tree o Patchy infiltrate of infection o Septicemia—look at both kidneys o This is worse than medullary—environment is hostile due to osmolality Investigate Pt IVP and retro exam Include abdominal US Tx Only one's that look for spinal cause and susceptibility to infection Don't know why have UTI but do Hydrating the pt will help the pt—flush out the organisms Cranberry juice o Not b/c acidifier o A component that makes it difficult for the bacteria to grab onto the wall o Reduced bacterial adhesions We do not know for sure how much to drink Recommend 4-8oz glasses per day—Dr. Kuhn got results w/this If this is going to work, it will tend to work quickly If this does not work, look at the water that they are drinking Recommend steamed, distilled water