Diffraction of Water Waves Activity
advertisement

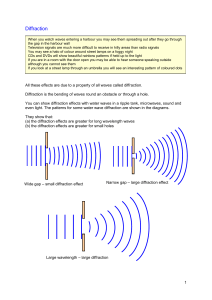
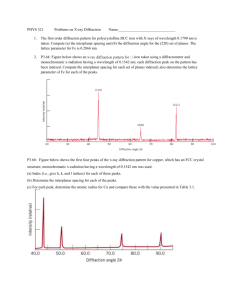
Diffraction of Water Waves Activity Diffraction – if waves pass by a sharp edge or through a small opening they bend - this bending is called diffraction Purpose: the purpose of the following activity is to study the diffraction of a wave around an obstacle, by and edge, and through an opening Materials: ripple tank wax blocks chart paper (1 piece) straight wave generator light source electrical circuit Basic Set-up: 1. Attach the legs to your ripple tank. 2. Place your light source above the ripple tank so it shines directly down through the glass. 3. Place the chart paper on the floor below the tank to act as a screen. 4. Put water in the ripple tank to a depth of 1 cm. Level the tank to ensure that the water depth is uniform. 5. Set up the electrical circuit with the variable power supply, wires, rheostat and motor as demonstrated by Mrs. Clarke. Diffraction Around an Object 1. Place one wax block in the centre of the ripple tank. 2. Start the wave generator and observe the diffraction of the waves around the block (this is easier to observe by watching the shadows on your chart paper on the floor). Sketch a diagram of the diffraction around the block. Be sure to indicate the direction of the waves. 3. Decrease the wavelength of your waves by adjusting your wave generator (using the rheostat). 4. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? 5. Increase the wavelength of your waves so it is longer than in #2. 6. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? #4? 7. What conclusions can you draw about how wavelength is related to diffraction around an object? Diffraction by an Edge 1. Use your wax blocks so they extend from one edge of the tank to approximately half way across the tank. 2. Start the wave generator and observe the diffraction of the waves around the end of the barrier. Sketch a graph of the diffraction, be sure to indicate the direction of the waves. 3. Decrease the wavelength of your waves by adjusting your wave generator. 4. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? 5. Increase the wavelength of your waves so it is longer than in #2. 6. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? #4? 7. What conclusions can you draw about how wavelength is related to diffraction around the edge of a barrier? Diffraction Through an Opening 1. Place your wax blocks in the tank so you have a small opening between them (approximately 10 cm). 2. Start the wave generator and observe the diffraction of the waves through the space between the blocks. Sketch the diffraction. Indicate the direction of the waves. 3. Decrease the wavelength of your waves by adjusting your wave generator. 4. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? 5. Increase the wavelength of your waves so it is longer than in #2. 6. Observe the diffraction pattern on the floor again. How does it differ from the diffraction pattern in #2? #4? 7. What conclusions can you draw about how wavelength is related to diffraction through an opening in a barrier? 8. Readjust your wave generator back to the original wavelength and observe the diffraction pattern again. 9. Make the opening in your barrier smaller and observe the diffraction pattern again. How does it differ from #8? 10. Make the opening in your barrier larger than in #8 and observe the diffraction pattern again. 11. How does the pattern differ from in #8 and #9? 12. What conclusion can you draw about the relationship between amount of diffraction and size of opening in a barrier?