mm bp
advertisement

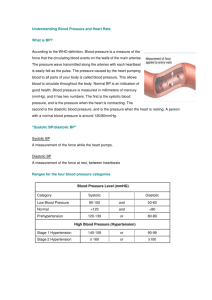
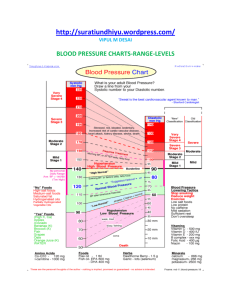
Student Review Questions, Porth Chapter 23, Disorders of Blood Pressure Regulation 1. Multiple Choice In a patient with a systolic pressure of 146 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure of 82 mm Hg, the pulse pressure would be calculated as: 228 mm Hg. *64 mm Hg. 73 mm Hg. 41 mm Hg. Rationale: The pulse pressure is calculated by deducting the diastolic pressure (82) from the systolic pressure (146). The difference is the pulse pressure. 2. Multiple Choice When a person moves from a lying to a standing position, which of the following is most responsible for an increase in heart rate? *Stretching of baroreceptors in the heart and brain Arterial chemoreceptors in the carotid arteries Fluid shift to the lower extremities Carbon dioxide and oxygen demand Rationale: With position changes, the blood pressure changes due to the stretching of the baroreceptors with a resultant increase in heart rate and sympathetically induced vasoconstriction that causes an increase in peripheral vascular resistance. 3. Multiple Choice Long-term regulation of blood pressure is primarily performed by: neural mechanisms. humoral response. hormonal mechanisms. *kidney action. Rationale: Long-term regulation of blood pressure is performed by the kidneys. Short-term regulation of blood pressure is regulated by neural and hormonal mechanisms. 4. Multiple Choice While obtaining a blood pressure (BP) for an obese patient, it is appropriate to ensure that the BP cuff is not too small, which would result in: a reading that is too low. a decreased pulse pressure reading. *a reading that is too high. an accurate BP assessment. Rationale: A cuff that is too small for the patient will result in an overestimation of the BP. It will not give you an accurate assessment or pulse pressure. 5. Multiple Choice Which of the following is a constitutional risk factor for the development of hypertension? Obesity Increased alcohol consumption History of smoking *Race Rationale: Constitutional risk factors include a family history of hypertension, race, and greater age. The other options are lifestyle risk factors. 6. Multiple Choice A patient is taking a medication to treat hypertension that acts to decrease heart rate and cardiac output. Which classification of medications is the drug the patient is taking in? Diuretics ACE inhibitors *ß-adrenergic blockers Calcium channel blockers Rationale: ß-adrenergic blockers work to decrease the heart rate and cardiac output. Diuretics lower BP by decreasing the vascular volume, while ACE inhibitors work to reduce vasoconstriction. Calcium channel blockers reduce BP by reducing vascular smooth muscle tone. 7. Multiple Choice Systolic hypertension is of concern to health care professionals because it is related to the risk for the development of: *left ventricular hypertrophy. right-sided heart failure. obesity. renal damage. Rationale: Elevated pressures during systole favor the development of left ventricular hypertrophy, increased myocardial oxygen demands, and eventual left-sided heart failure. 8. Multiple Choice Which of the following is characteristic with a preeclampsia or eclampsia diagnosis? Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg and glucose in the urine during the 36th week of pregnancy *Blood pressure of 160/100 mm Hg and proteinuria during the 30th week of pregnancy Blood pressure of 130/88 mm Hg and hyperglycemia during the 22nd week of pregnancy Blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg and proteinuria in the second trimester Rationale: Preeclampsia and eclampsia are defined as an elevation in blood pressure (systolic > 140 mm Hg or diastolic >90 mm Hg) and proteinuria (300 g or greater in 24 hours) developing after 20 weeks of gestation. 9. Multiple Choice As the aging process occurs, stiffening of the large arteries occurs and results in: decreased systolic pressure and increased diastolic pressure. no change in the blood pressure. *increased systolic pressure and decreased diastolic pressure. narrowing of the pulse pressure. Rationale: The stiffening of the large arteries results in a systolic pressure increase while the diastolic pressure remains unchanged or actually decreases. The pulse pressure widens, rather than narrows, because of the changes in the systolic and diastolic readings. 10. Multiple Choice Which of the following patients is at greatest risk for orthostatic hypotension? *66-year-old postsurgery patient who’s been immobile 23-year-old pregnant patient at 36 weeks’ gestation 42-year-old male patient with a history of pulmonary embolism 70-year-old female who has taken the same hypertension medication for 10 years Rationale: Patients who have been immobile and are postsurgery are at greater risk for developing orthostatic hypotension. The other patients are not at great risk.