Cell Size Lab
advertisement

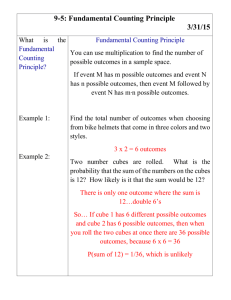
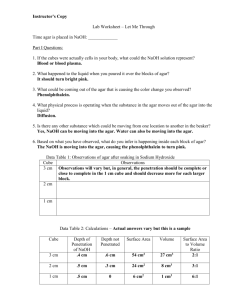
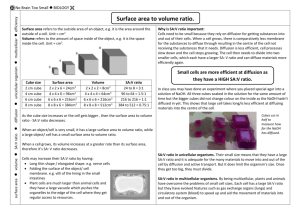
Cell Size Lab INTRODUCTION: It is through the cell membrane that food, oxygen, and water enter the cell and waste products leave the cell. How quickly this exchange takes place depends on the surface area of the cell membrane. The amount of food and oxygen needed and the amount of waste produced depends on the volume of the cell. When cells grow to a certain size, their rate of growth slows down and then stops. They have reached their size limit. When one of these larger cells divides into two smaller cells, the rate of growth again increases. In this investigation you will experiment to determine why this is so. EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS: 250 ml beakers agar-agar Plastic spoon millimeter ruler Phenolphthalein razor blade 11" X 13" pan 4% NaOH solution paper towels PROCEDURE: 1. Obtain an agar block from your teacher. 2. With a razor blade, cut your block in half. Set one half aside and cut the remaining block in half again. Set one half aside and repeat this process until you have five different sized blocks. 3. As you cut the blocks, measure and record their length, width, and height on the data table. 4. When all the blocks have been measured and recorded, submerge them in NaOH solution. Use caution with NaOH-it is caustic. If NaOH gets on you, wash it off immediately. 5. Allow the cubes to soak for 5 minutes, then pour the NaOH down the sink and rinse the cubes with water. Use care that you do not pour your agar cubes out of the beaker. Now remove the agar cubes with a spoon and blot them dry with a paper towel. 7. With your razor blade, cut the agar cubes in half and measure the depth of the colored area. This is known as the amount of absorption and should be recorded in the mm Absorbed column. Observations: Using your measurements, determine the surface area, volume, and surface area to volume ratio of each block and record it on the data table. Surface area (mm2) = L x W 6 numbers together. of each side, then + the Volume (mm3) = L x W x H Surface area to volume ratio = surface area / volume DATA TABLE Cube Surface Dimension Area L, W, H (mm2) (mm) Volume (mm3) L x W x H S.A./Volume mm ratio Absorbed QUESTIONS: 1. Which cube has the greatest surface area? 2. Which cube has the greatest surface area to volume ratio? 3. What evidence is there that sodium hydroxide is being absorbed by the agar cubes? 4. Explain how cells “feed” themselves.(obtain nutrients and get rid of wastes) 5. If the sodium hydroxide were some vital substance, such as food, and the agar cubes were cells,which cell would be “fed” the most efficiently? 6. What happens to the surface area to volume a cell as the cell grows? 7. What happens to the cell’s ability to feed and get rid of waste as it grows? 8. What happens to the surface area to volume you divide the cell in half? 9. Make a statement which explains why cells limited in the size to which they can grow. ratio of itself ratio if are