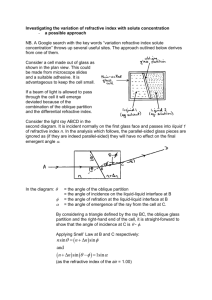
Practice 1 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Topic: Refraction Section A 1 The
advertisement

Practice 1 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Topic: Refraction Section A 1 The diagram below shows the path of a light ray as it enters a semi-spherical glass block. The refractive index of the glass is o 45 o 62 o 28 A 0.80 2. B 0.73 C 1.51 The diagram shows a ray of light moving from air to plastic. What is the refractive index of the plastic? A. 0.82 B. 1.22 3. 4. D 1.61 C. 1.41 D. 1.50 Red light travelling in glass strikes a glass-air boundary. Some light is reflected and some is refracted. Which diagram correctly shows the reflection and refraction? The diagrams show the passage of light through glass blocks. Which diagram is correct? 1 Practice 1 Section B 1 The figure below shows a ray of light incident on the water surface of a tank at an angle of incidence of 45 °. At the bottom lies a plane mirror AB. a. Explain the meaning of refractive index. [1] b. Calculate the angle of refraction if the refractive index of water is 1.3 [2] c. Draw on the figure as accurately as possible, the subsequent path of the ray until it emerges into air again [2] 2. The diagram below shows a light ray coming out from a glass block to the air. 140 60 (a) State the angle of incidence. [1] a (b) State the angle of refraction. [1] 2 Practice 1 a (c) Calculate the refractive index of the glass block. [2] (d) The speed of light in air is 3 108 m s-1. What is the speed of light in the glass block? [2] Section C 1. (a) State the laws of reflection. [2] (b) Describe an experiment using a plane mirror to show the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. Include a labeled diagram in your answer. [5] (c) A ray of light is incident upon a piece of glass of refractive index 1.61, at an angle of 50. (i) Calculate the angle of refraction. (ii) Why is the angle of incidence not equal to the angle of refraction ? [2] [1] Suggested Answers Section A 1. C 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Section B 1a. Refractive index = ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in medium b. sin r = sin 45o / 1.3 = 0.544 r = 33o 2 (a) The angle of incidence is 90 – 60 = 30 . [1] (b) The angle of refraction is 140 – 90 = 50 . [1] (c) n = sin 50 sin 30 [1] = 1.53 (to 3 s.f.) 3 [1] Practice 1 (d) v = c n 8 -1 3 10 m s = [1] = 1.96 108 m s-1 1.532 [1] Section C 1(a) ▪ The angle of incidents is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane. (b) Labeled diagram line XY at angle (e.g. 30) to the normal (c) i) Draw a straight line AB on a piece of plain paper. Draw the normal NN’ to line AB and line XY at angle (e.g. 30) to the normal. Place a plane mirror vertically on line AB. Place pins P1 and P2 on incident ray XY. View the images of P1 and P2 and place pins P3 and P4 in line with the images. Join points P3 and P4 to obtain the reflected ray. Measure the angle P3P4 made with normal NN’. Repeat with line P1P2 at a different angle and obtain the corresponding angle made by P3P4 with the normal. The angles P1P2 and P3P4 made with the normal are equal. sin i =n sin r sin r = sin 50 o sin i = 1.61 n r = 28.4o ii) Ray undergoes refraction when it enters a different medium. speed / ms-1-1 speed/ms 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 4 0.1 time / s time/s 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14