Earth Science
advertisement

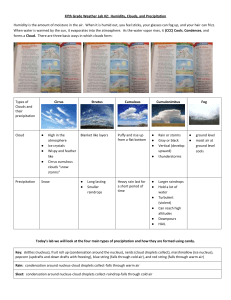
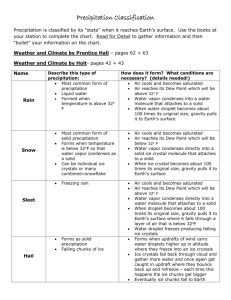
Earth Science Chapter 16 Section 5 A. Precipitation: Precipitation is any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches the Earth’s surface. Precipitation always comes from clouds. In order for precipitation to occur, cloud droplets or ice crystals must grow heavy enough to fall away from the cloud and reach the ground. B. Types of precipitation: 1. Rain: Falls mostly from nimbostratus and cumulonimbus clouds. - The bulk of rain originates as snowflakes or hailstones, which melt on the way down as they descend through air that is above 32 F. - Most commonly, raindrop diameters are in the range of 1 to 6 mm. At larger diameters the drops become unstable and break up. 2. Freezing Rain: forms a coating of ice that sometimes grows thick and heavy enough to bring down limbs, snap power lines and disrupt traffic. - Freezing rain develops when rain falls from a relatively mild air layer aloft into a shallow layer of subfreezing air at ground level . The drops become super cooled and then freeze immediately on contact with cold surfaces 3. Snow: An assemblage of ice crystals in the form of flakes. The form of snowflake varies with water vapor concentration and temperature and may consist of plates, stars, columns or needles. 4. Sleet, are actually frozen raindrops. They develop in much the same way as freezing- rain with one difference: 1. The surface layer of cold air is so deep that raindrops freeze prior to hitting the ground. ** We can readily distinguish ice pellets from freezing rain, because ice pellets bounce when striking the ground and freezing rain does not. 5. Hail: Consists of rounded or jagged lumps of ice often characterized by concentric layers resembling the internal structure of an onion. - Hail develops within intense thunderstorms where strong convection currents carry ice pellets up into the middle of the cumulonimbus cloud. - Along the way, ice pellets grow larger by collecting super cooled water droplets and eventually becoming heavy enough to fall to earth. C. Measuring Precipitation: Meteorologists measure rainfall with a rain gauge. A rain gauge is an open-ended can or tube that collects rainfall. The amount of rainfall is measured by dipping a ruler into the water or by reading a marked scale. D. Controlling Precipitation: Cloud seeding = an attempt to stimulate natural precipitation processes by injecting nucleating agents into clouds. The objective of seeding cold clouds is to stimulate the Bergeron process in clouds that are deficient in ice crystals. The seeding agent is either Silver Iodide (AgI), which has crystal properties similar to those of ice, or Dry ice which is solid Carbon Dioxide (CO) which has a temperature of about -80 C ( -112 F ). Silver Iodide crystals are freezing nuclei that are active at -4 C (25 F) and below. Dry ice pellets are so cold that within a cloud they cause surrounding super cooled water droplets to freeze. Dry ice is also used to disperse fog around airports. Dry ice cause ice crystals to form increasing visibility.