Precipitation
advertisement

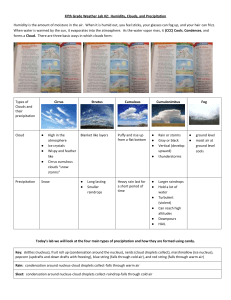
Precipitation Clouds made of water droplets < 10 micrometers in diameter Fall incredibly slow Formation of precipitation 1. Bergeron process a. Temperature in cloud is below freezing – supercooled water b. Ice crystals collect water vapor c. Large snowflakes form and fall as snow or melt and form rain d. Mid and High latitudes 2. Collision-coalescence a. Warm clouds b. Large condensation nuclei form large drops c. Droplets collide with other droplets d. Tropical regions Forms of precipitation 1. Rain and drizzle a. Rain - droplets > .5 mm b. Drizzle < .5 mm 2. Snow – ice crystals, or groups of ice crystals 3. Sleet and glaze a. Sleet – small particles of ice Warmer air over colder air -- water falls hits colder air and freezes b. Glaze – rain freezes on impact with cold object 4. Hail a. b. c. d. Frozen ice balls Formed in layers within cumulonimbus clouds Strong winds blow frozen drops up to be coated by more ice Eventually falls when wind cannot keep hail from falling 5. Rime a. Freezing of supercooled fog Precipitation measured by Rain gauge Funnel and cylinder in proper ratio Snow a. Depth b. Melted units -- St. Louis area 10 inches snow = 1 inch melted Varies by location (ex. Wet snow versus dry snow)