erosion
advertisement
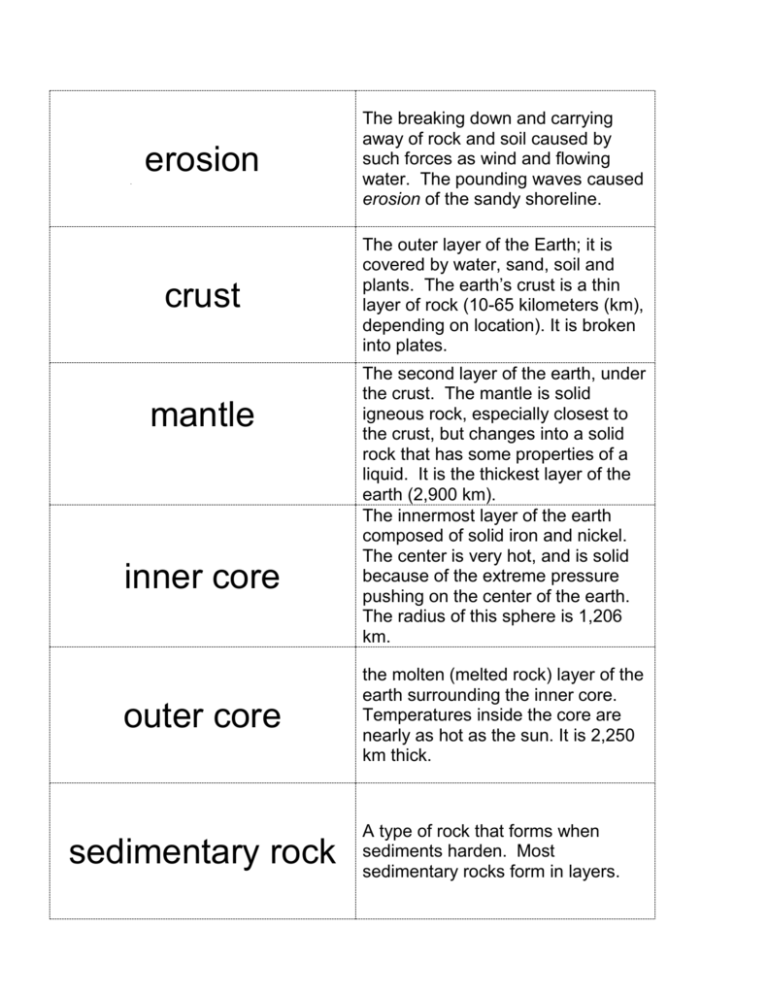
erosion The breaking down and carrying away of rock and soil caused by such forces as wind and flowing water. The pounding waves caused erosion of the sandy shoreline. crust The outer layer of the Earth; it is covered by water, sand, soil and plants. The earth’s crust is a thin layer of rock (10-65 kilometers (km), depending on location). It is broken into plates. mantle inner core outer core sedimentary rock The second layer of the earth, under the crust. The mantle is solid igneous rock, especially closest to the crust, but changes into a solid rock that has some properties of a liquid. It is the thickest layer of the earth (2,900 km). The innermost layer of the earth composed of solid iron and nickel. The center is very hot, and is solid because of the extreme pressure pushing on the center of the earth. The radius of this sphere is 1,206 km. the molten (melted rock) layer of the earth surrounding the inner core. Temperatures inside the core are nearly as hot as the sun. It is 2,250 km thick. A type of rock that forms when sediments harden. Most sedimentary rocks form in layers. igneous rock A type of rock that forms from melted rock that cools and hardens. Obsidian is an igneous rock that forms when lava cools quickly. metamorphic rock A type of rock that forms from existing rocks because of changes caused by heat, pressure, or chemicals. Slate is a metamorphic rock that forms from the sedimentary rock shale. magma Melted rock material that forms deep within Earth. Some igneous rocks, such as granite, form from magma. lava liquid rock that reaches the surface of the earth, through vents called volcanoes minerals A solid element of compound from Earth’s crust that has a definitive chemical composition and crystal structure. plate tectonics the process of crustal plate movement volcano places on the earth’s surface where hot, liquid rock seeps or explodes out. earthquake a shaking of the ground caused by plates moving under the surface of the earth. plates the huge slabs of rock that make up the earth’s crust (like pieces of a puzzle) fossil The remains or traces of a living thing from the past, preserved in rock. Fossils can include imprints of animal skeletons pressed into rock. fault lines points at which the earth’s crust cracks Pangaea the theory that shows how once all the continents were connected and have drifted apart over time. tsunami an enormous ocean wave caused by earthquakes or volcanoes.






