Advanced Electrical Machine Analysis
advertisement
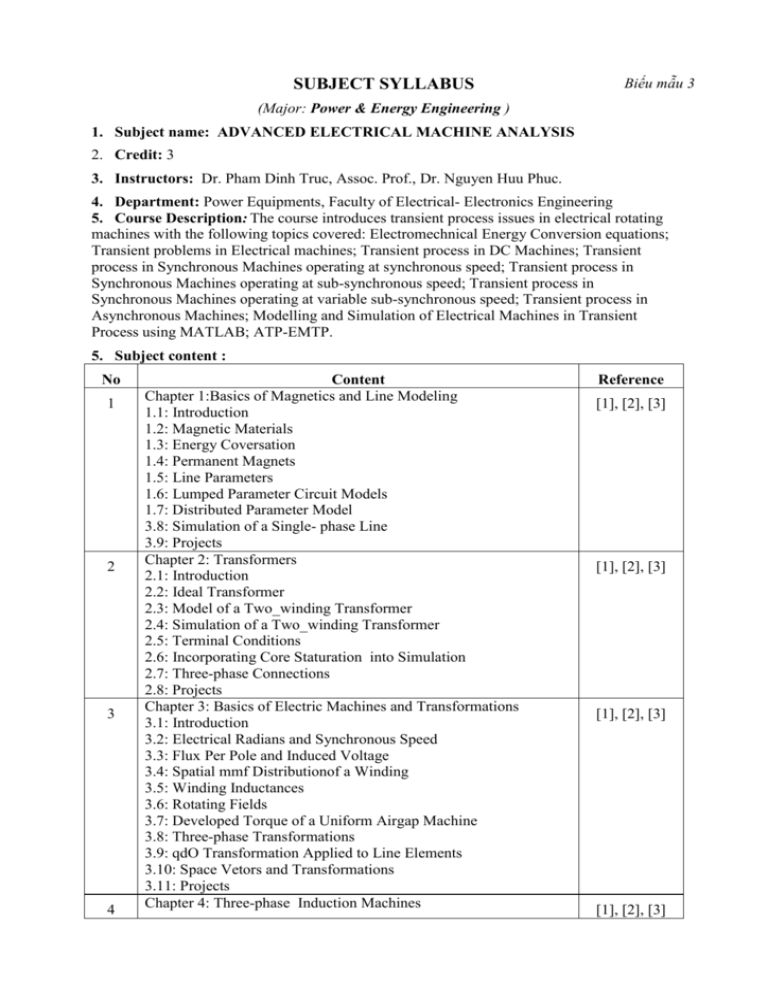
SUBJECT SYLLABUS Biểu mẫu 3 (Major: Power & Energy Engineering ) 1. Subject name: ADVANCED ELECTRICAL MACHINE ANALYSIS 2. Credit: 3 3. Instructors: Dr. Pham Dinh Truc, Assoc. Prof., Dr. Nguyen Huu Phuc. 4. Department: Power Equipments, Faculty of Electrical- Electronics Engineering 5. Course Description: The course introduces transient process issues in electrical rotating machines with the following topics covered: Electromechnical Energy Conversion equations; Transient problems in Electrical machines; Transient process in DC Machines; Transient process in Synchronous Machines operating at synchronous speed; Transient process in Synchronous Machines operating at sub-synchronous speed; Transient process in Synchronous Machines operating at variable sub-synchronous speed; Transient process in Asynchronous Machines; Modelling and Simulation of Electrical Machines in Transient Process using MATLAB; ATP-EMTP. 5. Subject content : No 1 2 3 4 Content Chapter 1:Basics of Magnetics and Line Modeling 1.1: Introduction 1.2: Magnetic Materials 1.3: Energy Coversation 1.4: Permanent Magnets 1.5: Line Parameters 1.6: Lumped Parameter Circuit Models 1.7: Distributed Parameter Model 3.8: Simulation of a Single- phase Line 3.9: Projects Chapter 2: Transformers 2.1: Introduction 2.2: Ideal Transformer 2.3: Model of a Two_winding Transformer 2.4: Simulation of a Two_winding Transformer 2.5: Terminal Conditions 2.6: Incorporating Core Staturation into Simulation 2.7: Three-phase Connections 2.8: Projects Chapter 3: Basics of Electric Machines and Transformations 3.1: Introduction 3.2: Electrical Radians and Synchronous Speed 3.3: Flux Per Pole and Induced Voltage 3.4: Spatial mmf Distributionof a Winding 3.5: Winding Inductances 3.6: Rotating Fields 3.7: Developed Torque of a Uniform Airgap Machine 3.8: Three-phase Transformations 3.9: qdO Transformation Applied to Line Elements 3.10: Space Vetors and Transformations 3.11: Projects Chapter 4: Three-phase Induction Machines Reference [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] 5 6 7 8 4.1: Introduction 4.2: Rotating Magnetic Field and Slip 4.3: Circuit Model of a Three-phase Induction Machine 4.4: Machine Model in Arbitrary qdO Reference Frame 4.5: qdO Stationary and Synchronous Reference Frames 4.6: Steady-State Model 4.7: Transient Model 4.8: Simulation of an Introduction Machine in the Stationary Reference Frame 4.9: Linearized Model 4.10: Single-phase Introduction Model 4.11: Projects Chapter 5: Synchronous Machines 5.1: Introduction 5.2:Mathematical Model 5.3: Currents in Terms of Flux Linkages 5.4: Steady- state Operation 5.5: Simulation of Three-phase Synchronous Machines 5.6: Machine Parameters 5.7: Calculating Machine Parameters 5.8: Higher-order Models 5.9: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors 5.10: Synchronous Machine Projects Chapter 6: DC Machines 6.1: Introduction 6.2: Armature Windings 6.3: Field Excitation 6.4: Induced Voltage of the Armature Winding 6.5: Electromagnetic Torque 6.6: Armature Reaction 6.7: Commutation 6.8: Models of Operation 6.9: Feasible Torque-speed Region 6.10: Braking 6.11: Speed Control 6.12: Four-quadrant Operation 6.13: Staring a Shunt dc Generator 6.14: Starting a Shunt dc Motor 6.15: Projects Chapter 7: Control of Induction Machines 7.1: Introduction 7.2: Speed Control 7.3: Constant Airgap Flux Operation 7.4: Constant Volts/Hertz Flux Operation 7.5: Induction Machine Drives 7.6: Field-orientation Methods 7.7: Inderect Field Orientation Methods 7.9: Projects Chapter 8: Synchronous Machine in Power Systems and Drives 8.1: Introduction 8.2: Synchronous Generators in Power Systems 8.3: Transient Model with.7 d and q Field Windings [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] [1], [2], [3] 8.4: Sub-transient Model with Field and Damper Windings 8.5: Specific Cases 8.6: Excitation Systems 8.7: Shaft Torsional 8.8: Synchronous Motor Drives 8.9: Projects 6. Reference Literature : [1]. Response Analysis of AC Electrical Machines, Computer Models and Simulation; John R.Smith; John Wiley & Sons 1990. [2]. Three-Phase Electrical Machine Systems, Computer Simulation; John R.Smith, Meng-Jen Chen; John Wiley & Sons 1993. [3]. Introduction aø l’eùlectrotechnique approfondie; J. Lesenne, F.Notelet, G. Seùguier; TEC DOC 1990. 7. Evaluation: No Method Number of test Weight(%) 1 Mid-term test 0 2 Practice, Experiment 0 3 Seminar, Assignment in classes 8 50 4 Final test (Report assignment) 1 50 Instructors