Foreign Language
advertisement
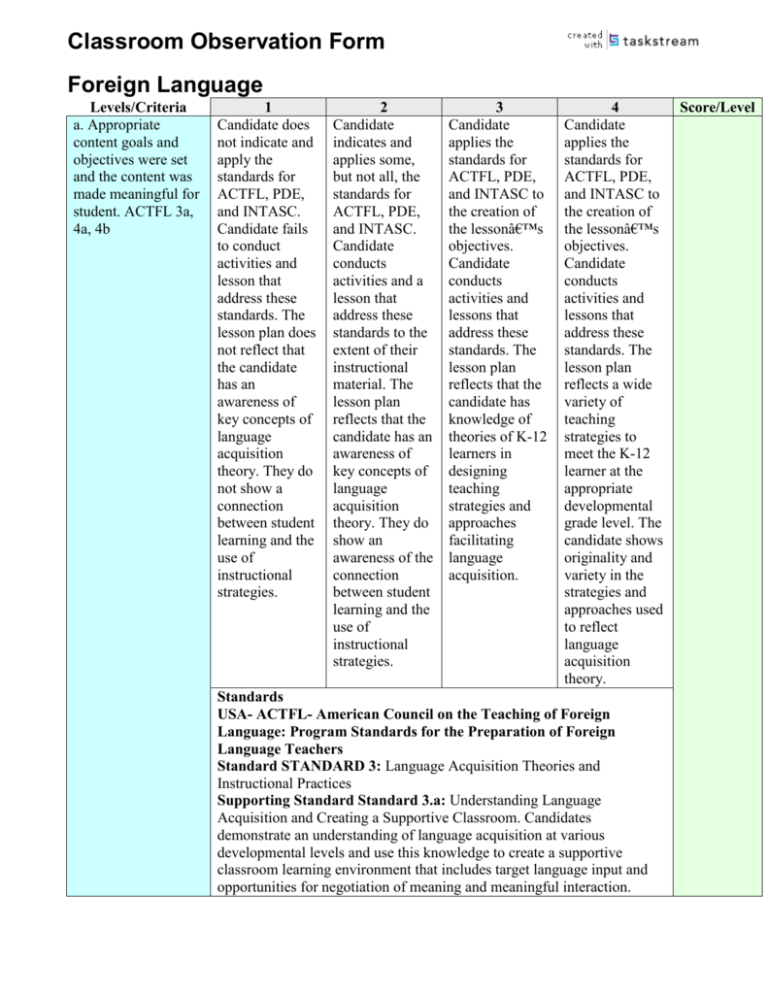
Classroom Observation Form Foreign Language Levels/Criteria a. Appropriate content goals and objectives were set and the content was made meaningful for student. ACTFL 3a, 4a, 4b 1 Candidate does not indicate and apply the standards for ACTFL, PDE, and INTASC. Candidate fails to conduct activities and lesson that address these standards. The lesson plan does not reflect that the candidate has an awareness of key concepts of language acquisition theory. They do not show a connection between student learning and the use of instructional strategies. 2 Candidate indicates and applies some, but not all, the standards for ACTFL, PDE, and INTASC. Candidate conducts activities and a lesson that address these standards to the extent of their instructional material. The lesson plan reflects that the candidate has an awareness of key concepts of language acquisition theory. They do show an awareness of the connection between student learning and the use of instructional strategies. 3 Candidate applies the standards for ACTFL, PDE, and INTASC to the creation of the lesson’s objectives. Candidate conducts activities and lessons that address these standards. The lesson plan reflects that the candidate has knowledge of theories of K-12 learners in designing teaching strategies and approaches facilitating language acquisition. 4 Candidate applies the standards for ACTFL, PDE, and INTASC to the creation of the lesson’s objectives. Candidate conducts activities and lessons that address these standards. The lesson plan reflects a wide variety of teaching strategies to meet the K-12 learner at the appropriate developmental grade level. The candidate shows originality and variety in the strategies and approaches used to reflect language acquisition theory. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.a: Understanding Language Acquisition and Creating a Supportive Classroom. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of language acquisition at various developmental levels and use this knowledge to create a supportive classroom learning environment that includes target language input and opportunities for negotiation of meaning and meaningful interaction. Score/Level Levels/Criteria b. Lesson was well paced (INTASC 2) c. Entire class monitored and more than one activity/group was attended to at a time and classroom management techniques (e.g., proximity) used effectively (INTASC 2,5) 1 2 3 4 Score/Level Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.a: Understanding and Integrating Standards In Planning. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of the goal areas and standards of the Standards for Foreign Language Learning and their state standards, and they integrate these frameworks into curricular planning. Supporting Standard Standard 4.b: Integrating Standards in Instruction. Candidates integrate the Standards for Foreign Language Learning and their state standards into language instruction. Failed to pace Sometimes Sometimes Always paced lesson so that it paced lesson too paced lesson too the lesson well was neither too fast for some fast for some by fast for individuals but individuals but individualizing individuals nor too slow for the too slow for the instruction and too slow for the group group keeping students group from falling behind but also kept the group from going too slow Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Individuals and Individuals and Individuals and Individuals and groups were groups were groups were groups were never kept on sometimes kept mostly kept on always kept on task and a on task and a task and a task and a sequence from sequence from sequence from sequence from least invasive least invasive least invasive least invasive (e.g., eye (e.g., eye (e.g., eye (e.g., eye contact and contact and contact and contact and proximity) to proximity) to proximity) to proximity) to most invasive most invasive most invasive most invasive interventions interventions interventions interventions was not used to was used was always used was used keep students on inconsistently to (but used consistently and task keep students on sometimes effectively to task unsuccessfully) keep students on to keep students task on task Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, Levels/Criteria d. Attention gained (INTASC 1,2,4) ACTFL 4b A strategy was used to gain the students’ attention at the beginning of the lesson as well as other relevant times during the lesson to maintain/regain attention. ▪Strategies related directly to the learning in the lesson. ▪Visuals, ambiguity, curiosity, noise, or other ways were effectively used Uses cultural products, practices, perspectives 1 2 3 4 social and personal development. Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and selfmotivation. A strategy was A strategy was A strategy was A strategy was never used to sometimes used often used to always used to gain the to gain the gain the gain the students’ students’ students’ students’ attention at the attention at the attention at the attention at the beginning of the beginning of the beginning of the beginning of the lesson as well as lesson as well as lesson as well as lesson as well as other relevant other relevant other relevant other relevant times during the times during the times during the times during the lesson to lesson to lesson to lesson to maintain/regain maintain/regain maintain/regain maintain/regain attention. attention. attention. attention. Visuals, Visuals, Visuals, Visuals, ambiguity, ambiguity, ambiguity, ambiguity, curiosity, noise, curiosity, noise, curiosity, noise, curiosity, noise, or other ways or other ways or other ways or other ways were not used were not used were used were always effectively. effectively. effectively. used effectively. There is no use Candidate Candidate Candidate used of products, includes one or includes an the productspractices, and more of the opportunity for practicesperspectives areas of the student to perspectives mentioned to set products, explore the framework as the stage for the practices, target language the basis for class. perspectives in culture by using planning and setting the stage products, implementing for the lesson. practices, and instruction perspectives. during the lesson. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.b: Integrating Standards in Instruction. Candidates integrate the Standards for Foreign Language Learning and their state standards into language instruction. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Score/Level Levels/Criteria e. Previous knowledge recalled (INTASC 2,4). f. Purpose/Objective of the lesson made clear (INTASC 1,4) ACTFL 4b 1 2 3 4 Score/Level Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Strategies were Strategies were Strategies Strategies not used to build sometimes related directly related directly on prior related directly to the learning to the learning knowledge nor to the learning in the lesson and in the lesson and did they relate in the lesson and often debunked debunked directly to the often debunked common common learning in the common preconceptions preconceptions lesson and often preconceptions that would have that would have debunked that would have hampered hampered common hampered learning for learning for preconceptions learning for understanding. understanding. that would have understanding. hampered learning for understanding. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. It was not clear It could be It could clearly Objectives were what students somewhat be inferred what clearly posted were to be inferred what students were to for all to see and learning and students were to be learning and there was a clear why they were be learning but it could be discussion of learning it. The no discussion of inferred as to why they were candidate does why they were why they were important to not understand learning it. The learning it. The know. The the connection candidate candidate design candidate uses among the understands the opportunities for the interpersonal, connection students to interpersonalinterpretive, and among the communicate by interpretivepresentational interpersonal, using the presentational modes of interpretive, and interpersonal, framework as communication. presentational interpretive, and the basis for One mode at a modes of presentational planning and time is focused communication, modes in an implementing on for but only focuses integrated classroom instruction and on one of these manner. communication. Levels/Criteria g. Teacher Input Provided (ACTFL 2a, 3a) 1 2 3 4 activities. at a time. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.b: Integrating Standards in Instruction. Candidates integrate the Standards for Foreign Language Learning and their state standards into language instruction. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Skills or Skills or Skills or Skills or concepts of the concepts of the concepts of the concepts of the lesson were lesson were lesson were lesson were never introduced sometimes always always and explained introduced and introduced and introduced and by using clear explained by explained by explained by examples and using somewhat using clear using clear language and the clear examples examples and examples and sequence and and language language but the language that organization of and the sequence and debunked instruction was sequence and organization of student not appropriate. organization of instruction was preconceptions The candidate instruction was not appropriate. and the uses the target not appropriate. The candidate sequence and language for The candidate uses the target organization of specific parts of uses the target language to the instruction the classroom language for maximum extent introduced new lesson at the specific parts of in class at all principles of levels of the the classroom levels of increasing students, but lesson at the instruction. complexity. The avoids levels of the There is time candidate spontaneous students, but allotted for structures the interaction with avoids spontaneous class to the students in spontaneous interaction in the maximize the the target interaction with target language. use of the target language. The the students in A variety of language at all candidate does the target strategies are levels of not use language. The used to help instruction. A strategies to help candidate uses students key component students strategies to help understand oral of the class is Score/Level Levels/Criteria h. Teacher guided practice was adequate and 1 understand oral and written input. The candidate does not include examples of cultural practices, products, or perspectives. 2 students understand oral and written input. The candidate cites examples of cultural practices, products or perspectives, but it is clear that the candidate is drawing from a limited knowledge base. 3 and written input. The candidate includes key cultural perspectives. 4 Score/Level spontaneous interaction with students in the target language. The candidate assists students in developing a repertoire of strategies for understanding oral and written input. The target language is used to teach a variety of content. The candidate shares with students the view that the target culture is a system in which its perspective is reflected through practices and products. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 2: Cultures, Literatures, Cross-Disciplinary Concepts Supporting Standard Standard 2.a: Demonstrating Cultural Understandings. Candidates demonstrate that they understand the connections among the perspectives of a culture and its practices and products, and they integrate the cultural framework for foreign language standards into their instructional practices. Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.a: Understanding Language Acquisition and Creating a Supportive Classroom. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of language acquisition at various developmental levels and use this knowledge to create a supportive classroom learning environment that includes target language input and opportunities for negotiation of meaning and meaningful interaction. The teacher and The teacher and The teacher and The teacher and students never students students always students always worked through sometimes worked through worked through Levels/Criteria appropriate (INTASC 2,4) ACTFL 3a i. Repetition of key concepts occurred 1 examples together as needed and students were not expected to do similar problems on their own. The candidate plans most interaction in the classroom. The candidate teaches some phrases in the target language to negotiate meaning. 2 worked through examples together as needed but students were not expected to do similar problems on their own. The candidate plans most of the interaction in the classroom. The candidate assists students in negotiating meaning through the use of expressions in the target language. 3 examples together as needed but students were not always expected to do similar problems on their own. The candidate provides opportunities for students to negotiate meaning through spontaneous interaction. Students are taught a variety of ways to negotiate meaning. 4 Score/Level examples together as needed, the teacher provided scaffolding that addressed individual student needs and students were not expected to do similar problems on their own. Negotiating meaning is an integral part of the classroom interaction. The candidate teaches students to integrate negotiation of meaning strategies into their communication with others. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.a: Understanding Language Acquisition and Creating a Supportive Classroom. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of language acquisition at various developmental levels and use this knowledge to create a supportive classroom learning environment that includes target language input and opportunities for negotiation of meaning and meaningful interaction. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. No repetition Some repetition Repetition took Repetition took place took place but place and occurred, Levels/Criteria throughout the lesson (INTASC 2,4) j. A variety of instructional materials were used to actively engage the students. (INTASC 2,3,4,6) ACTFL 2a, 2b, 4c 1 2 no more than the students’ natural memory was used to help students learn and remember 3 mnemonic devices use to help students learn and remember 4 mnemonic devices were used, chunking and other concepts used to help students learn and remember essential facts and concepts Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. No instructional Instructional A variety of A variety of materials were materials were instructional instructional used. used (such as materials (such materials (such maps, texts, as maps, texts, as maps, texts, pictures, graphs, pictures, graphs, pictures, graphs, interactive interactive interactive computer-based computer-based computer-based activities, activities, activities, timelines, oral timelines, oral timelines, oral histories, histories, histories, primary primary primary documents and documents and documents and artifacts, etc.) artifacts, etc.) artifacts, etc.) but their use was were used and were used and not aligned with they were they were the lesson aligned with the aligned with the objectives. The lesson lesson candidate relies objectives. The objectives and on ready candidate they help to available (in investigates and create a text) cultural includes “hands-onanalyses. The materials that minds-on― candidate uses contain cultural experiences that materials that questions or motivated are based on assumptions. students to apply short-term The candidate the lesson instructional uses knowledge concepts to an objectives rather of standards and authentic than standards curricular goals problem. The or curricular to evaluate, candidate uses Score/Level Levels/Criteria 1 2 goals. Materials used have been designed for formal classroom use. Texts used elicit a literal interpretation. 3 select, and design materials, including visuals, realia, authentic printed and oral materials, cultural texts and other resources obtained through technology. Students are assisted in strategies for understanding and interpreting authentic texts. 4 Score/Level instructional material that poses significant cultural questions or that illustrate cultural changes. The candidate uses knowledge of the standards philosophy and curricular goals to evaluate, select, and design materials, including a creative use of visuals, realia, authentic printed and oral materials, cultural texts, and other resources obtained through technology. They justify the use of these materials. Students are engaged in acquiring new information by exploring these materials. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 2: Cultures, Literatures, Cross-Disciplinary Concepts Supporting Standard Standard 2.a: Demonstrating Cultural Understandings. Candidates demonstrate that they understand the connections among the perspectives of a culture and its practices and products, and they integrate the cultural framework for foreign language standards into their instructional practices. Supporting Standard Standard 2.b: Demonstrating Understanding of Literary and Cultural Texts and Traditions. Candidates recognize the Levels/Criteria k. All of the students were actively engaged in the learning throughout the lesson. (INTASC 2,4) ACTFL 3a 1 2 3 4 Score/Level value and role of literary and cultural texts and use them to interpret and reflect upon the perspectives of the target cultures over time. Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.c: Selecting and Designing Instructional Materials. Candidates use standards and curricular goals to evaluate, select, design, and adapt instructional resources. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. All students Most students All students All students were off task. were off task. appeared to be appeared to be The students The activities engaged in the engaged in the were not and contexts of lesson activities. lesson activities engaged in the the class are The candidate and their learning process. those that occur designs performances in instructional activities in (answers to materials. which students questions, Exercises and will have results of activities require opportunities to projects/papers, students to interact etc.) provide meaningfully demonstrated predictable with each other. their and/or correct The majority of engagement. answers. The activities and Meaningful candidate tasks are interaction is at assumes a standards-based the heart of traditional role and reflect instruction. The of teacher. curricular candidate Feedback is themes and engages students primarily students’ in evaluative in interests. The communicative nature. candidate uses activities and exercises and tasks regularly activities that throughout the require students lesson. to provide open- Interaction is ended, personalized to Levels/Criteria l. Students were encouraged to understand, question, and interpret ideas from diverse perspectives. (INTASC 4) ACTFL 2a 1 2 3 personalized responses. The candidate acts as a facilitator for the classroom. Feedback focuses on meaning and accuracy. 4 Score/Level the interests of students and reflects curricular goals. The candidate is a facilitator in the classroom. The candidate engages students in monitoring their own progress. The candidate rewards students for taking risks in using the target language. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.a: Understanding Language Acquisition and Creating a Supportive Classroom. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of language acquisition at various developmental levels and use this knowledge to create a supportive classroom learning environment that includes target language input and opportunities for negotiation of meaning and meaningful interaction. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Open-ended Open-ended Open-ended Open-ended questions were questions were questions were questions were never used, and sometimes used, always used always used diverse and diverse when when perspectives perspectives appropriate, and appropriate, and were never were never diverse diverse explored. explored. The perspectives perspectives candidate bases were sometimes were always the cultural explored. The explored and work of the candidate students were students on integrates encouraged to familiar and cultural insights ask their own Levels/Criteria m. Higher order thinking skills were used. (INTASC 4) ACTFL 3b 1 2 factual cultural content. 3 with the target language in its communicative and content areas. Knowledge of culture shared with students comes through independent work and interactions with native speakers. 4 questions. The candidate emphasizes cultural concepts as they teach language, analyze and synthesize cultural information from authentic sources in various media. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 2: Cultures, Literatures, Cross-Disciplinary Concepts Supporting Standard Standard 2.a: Demonstrating Cultural Understandings. Candidates demonstrate that they understand the connections among the perspectives of a culture and its practices and products, and they integrate the cultural framework for foreign language standards into their instructional practices. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Higher levels of Higher levels of Higher levels of Higher levels of Bloom’s Bloom’s Bloom’s Bloom’s Taxonomy such Taxonomy such Taxonomy such Taxonomy such as analysis, as analysis, as analysis, as analysis, application, application, application, application, creating, and creating, and were reached creating, and evaluation were evaluation were but creating, and evaluation were never reached. sometimes evaluation were always reached The candidate reached. The not reached when implements few candidate when appropriate. The activities and implements appropriate. The candidate those activities activities that candidate rewards students have a limited have a limited implements for engaging in number of number of activities that critical thinking answers and answers and promote critical and problem allow little room allow little room thinking and solving. for critical for critical problem-solving thinking and/or thinking and/or skills. problem solving. problem solving. Standards Score/Level Levels/Criteria n. Evaluation of student comprehension occurred throughout the lesson and appropriate feedback provided. (INTASC 8) ACTFL 3b, 5a 1 2 3 4 Score/Level USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Students were Students were Students were Students were never asked sometimes always asked always asked questions or asked questions questions or questions or asked to perform or asked to asked to perform asked to perform a task that perform a task a task that a task that would that would would would demonstrate demonstrate demonstrate demonstrate student student student student understanding understanding understanding understanding during the during the during the during the lesson. No lesson. The lesson when lesson when formative candidate uses appropriate but appropriate and assessments short-answer the appropriate the appropriate took place questioning as feedback was feedback was during the class. the primary not always always given strategy for given. The and eliciting candidate accommodations language from recognizes that were made when students. The questioning necessary. The candidate strategies and candidate attempts to task-based integrates the assess students, activities serve appropriate use but the different of questioning assessment is instructional strategies and not formative or objectives. The task-based does not yield candidate uses activities based the information tasks as they on instructional needed about the appear in their objectives and students to instructional the nature of further plan. The materials. The language use assessments candidate that they want to used were conducts a elicit from the prepared by formative students. The others or assessment that candidate Levels/Criteria o. The lesson ended with closure/review that focused on the main objectives of the lesson. (INTASC 3,4) 1 2 prepared for pedagogical purposes. 3 is tied to the objectives. The teacher uses a performance assessment that measures the students’ abilities to comprehend and interpret text and oral activities. 4 conducts a formative assessment that is tied to the objectives. The teacher uses a performance assessment that measures the students’ abilities to comprehend and interpret text and oral activities. Some of these activities allow students to develop selfassessment skills. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. Standard STANDARD 5: Assessment Of Languages and Cultures Supporting Standard Standard 5.a: Knowing assessment models and using them appropriately. Candidates believe that assessment is ongoing, and they demonstrate knowledge of multiple ways of assessment that are age- and level-appropriate by implementing purposeful measures. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 8: The teacher understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. No summary The teacher The students The students took place. candidate were asked to were asked to summarized the summarize the summarize the lesson. learning. learning and it focused on the main objectives of the lessons Score/Level Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 and included an opportunity to practice speaking the target language. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. p. Variety of Failed to any of Failed to use an An appropriate An appropriate teaching the following appropriate amount of the amount of the methods/instructional strategies: direct combination of following following strategies were used instruction, the following strategies were strategies were to reach different discovery strategies so that used so that used so that all types of learners. learning, the need of the most of the of the diverse (INTASC 2,4,8) cooperative diverse students diverse students’ ACTFL 3b, 4.c learning, role could be met: students’ needs for playing, direct needs for learning were discussions, instruction, learning were met: direct technology discovery met direct instruction, simulations, learning, instruction, discovery “handscooperative discovery learning, on/minds-on― learning, role learning, cooperative materials, paired playing, cooperative learning, role students, etc. discussions, learning, role playing, The entire technology playing, discussions, lesson is largesimulations, discussions, technology group “handstechnology simulations, instruction. on/minds-on― simulations, “handsmaterials, paired “handson/minds-on― students, etc. on/minds-on― materials, paired The candidate materials, paired students, etc. attempts to tailor students, etc. The candidate instruction to The candidate uses a variety of students’ uses a variety of instructional developmental instructional models and needs. The models and techniques candidate techniques to tailored to meet identifies the accommodate the needs of the individual ways the differences students. The student learns of their students. candidate and attempts to The candidate implements a plan for this. identifies variety of The class is multiple ways to instructional Score/Level Levels/Criteria 1 2 taught primarily with large-group instruction. Pairand small-group activities generally consist of students grouped together but working individually. 3 address the different styles of learning. The candidate conducts activities in which the students work collaboratively in pairs and small groups. The candidate defines and models the task, gives a time limit and expectations for follow-up, groups students, assigns roles, monitors the group, and conducts followup. 4 models and strategies to accommodate different ways of learning. The candidate conducts activities in which the students work collaboratively in pairs and small groups. The candidate includes strategies for students to assume roles, monitor their own progress, and evaluate their own performance. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.c: Selecting and Designing Instructional Materials. Candidates use standards and curricular goals to evaluate, select, design, and adapt instructional resources. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Principle: 8: The teacher understands and uses formal and informal Score/Level Levels/Criteria q. Relevant subject areas & “real world― problems were integrated into the lesson. (1,2,3,7) ACTFL 2c,4b 1 2 3 4 Score/Level assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. No reference to A brief It was clear how Students were the application reference was the subject could engaged in real of the content made be applied to world problem was made concerning the “real solving by application of world― applying lesson the content. The problems. The content to the candidate candidate solution of real integrates integrates world problems. discrete pieces concepts from The candidate from other other subject uses a contentsubject areas as areas. Strategies based approach they appear in for learning the to integrate instructional content in a language and materials. The foreign language subject area candidate uses are addressed. content. resources that Authentic Authentic accompany the resources resources instructional appropriate for appropriate for materials. The their students the students are candidate are used. The used. Students connects with candidate are assisted in target-language provides an acquiring new communities opportunity for information through the use students to from the other of video and/or connect to target disciplines in the native speaker language target language. presentations. communities The candidate through a provides an variety of means opportunity for such as students to technology and connect to target authentic language materials. communities through a variety of means such as technology and authentic materials. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 2: Cultures, Literatures, Cross-Disciplinary Concepts Supporting Standard Standard 2.c: Integrating Other Disciplines In Instruction. Candidates integrate knowledge of other disciplines into Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level foreign language instruction and identify distinctive viewpoints accessible only through the target language. Standard STANDARD 4: Integration Of Standards Into Curriculum and Instruction Supporting Standard Standard 4.b: Integrating Standards in Instruction. Candidates integrate the Standards for Foreign Language Learning and their state standards into language instruction. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 7: The teacher plans instruction based upon knowledge of subject matter, students, the community, and curriculum goals. r. Inclusion of special No IEP’s IEP’s were IEP’s were IEP’s were needs student were referenced, referenced, but referenced, and referenced, occurred. (INTASC no no some accommodations 2,3) ACTFL 3b accommodations accommodations accommodations were made, were made, and were made, and were made, but many pathways many pathways many pathways not enough to learning were to learning were to learning were pathways to provided. not provided. not provided. learning were provided. The candidate The candidate The candidate plans for does not recognizes that The candidate students’ recognize that all students have implements a special needs by all students have different needs variety of planning for different needs (cognitive, instructional alternative (cognitive, physical, models and classroom physical, linguistic, techniques to activities as linguistic, social, address the necessary. social, emotional, etc.), specific special emotional, etc.). but fails to needs of their adequately students. address these needs. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Levels/Criteria s. Individual differences were addressed. (INTASC 2,3,5) ACTFL 3b 1 2 3 4 Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Individual Some Instruction Instruction differences were instruction built clearly built on clearly built on not addressed. on students’ students’ students’ prior knowledge prior knowledge prior knowledge and experiences and experiences, and experiences, and some however, more and differentiated differentiated differentiated instruction took instruction instruction took place. geared to the place so that the particular needs particular needs The candidate of the students of the students attempts to was needed. in the class were address the wide More pathways clearly met. range of to learning need Multiple language levels, to be geared to pathways were language students’ provided and backgrounds differing they met the and learning learning styles. needs of the styles by using a students’ limited variety The candidate learning styles. of instructional implements a strategies. variety of instructional models and techniques to address student differences in students’ language levels, language backgrounds, and learning styles. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Score/Level Levels/Criteria t. Classroom instruction and assignments provided for Limited English Proficiency (LEP) students. 1 2 3 4 Score/Level Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and selfmotivation. No standardsSome standards- Standards-based Standards-based based practices based practices practices and practices and and strategies and strategies strategies related strategies related related to related to to planning, to planning, planning, planning, implementing, implementing, implementing, implementing, and managing and managing and managing and managing ESL and content ESL and content ESL and content ESL and content instruction, instruction, instruction, instruction, and including including including no integration of classroom classroom classroom language skills, organization, organization, organization, and adapted were clearly were clearly were used, and classroom used and some used and the no integration of resources were integration of integration of language skills, used. language skills, language skills, and adapted and adapted and adapted classroom Limited classroom classroom resources were adjustments are resources were resources were used. made to used. used effectively. accommodate Adjustments are the level of the Adjustments are The student not made to student if the made to whose native accommodate target language accommodate language is the the level of the of the class is the level of the target language student if the the native student if the of the class is target language language of the target language fully integrated of the class is student. of the class is into the lesson at the native the native the appropriate language of the language of the level of the Levels/Criteria 1 student. u. Diversity issues were addressed in an appropriate manner. (INTASC 2,3,6,10) ACTFL 3b Students were not at the center of their learning and did not have appropriate choices for applying course content to issues important to them and examples and illustrations that were not inclusive of multi-cultures were consistently used. The candidate does not adapt instruction to address students’ needs. 2 3 4 Score/Level student. student and to benefit other students in the class. Students were Students were Students were sometimes at the mostly at the always at the center of their center of their center of their learning and learning and learning and had sometimes had mostly had appropriate appropriate appropriate choices for choices for choices for applying course applying course applying course content to issues content to issues content to issues important to important to important to them and them and them and examples and examples and examples and illustrations that illustrations that illustrations that were inclusive were inclusive were inclusive of multi-cultures of multi-cultures of multi-cultures were used. were not were sometimes consistently used. The candidate used. creates a climate The candidate that values The candidate adapts diversity in the implements instruction to classroom. The specific address special needs of instructions students’ the students are given to them to needs. addressed. address students’ needs. Standards USA- ACTFL- American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Language: Program Standards for the Preparation of Foreign Language Teachers Standard STANDARD 3: Language Acquisition Theories and Instructional Practices Supporting Standard Standard 3.b: Developing Instructional Practices That Reflect Language Outcomes and Learner Diversity. Candidates develop a variety of instructional practices that reflect language outcomes and articulated program models and address the needs of diverse language learners. USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are Levels/Criteria v. Displayed Enthusiasm. (INTASC 1,6) w. Exhibited Confidence. x. Displayed empathy. (INTASC 5,9,10) 1 2 3 4 Score/Level adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being. Voice inflection, Voice inflection, Voice inflection, Voice inflection, smiling, gestures smiling, gestures smiling, gestures smiling, gestures were never used were sometimes were mostly were always when used when used when used when appropriate appropriate appropriate appropriate and students responded with their own enthusiasm Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. Never projected Sometimes Always Always voice, or led the projected voice, projected voice projected voice class by but did not lead when when example the class by appropriate, and appropriate, and example mostly led the always led the class by class by example example Never listened Sometimes Always listened Always listened to students and listened to to students when to students when never served as students and appropriate and appropriate and students’ served as sometimes always served as advocate student advocate served as students’ students’ advocate when advocate when appropriate determining, for (e.g., when example, that determining that factors in the factors in the students’ students’ environment environment outside of outside of school may be school may be influencing the influencing the students’ students’ Levels/Criteria y. Acted and appeared in a professional manner. (INTASC 9,10) 1 2 3 life and learning 4 life and learning) Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and selfmotivation. Principle: 9: The teacher is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being. Failed to start Started and and/or end on ended on time time and failed and wore to wear professional professional attire. attire. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 9: The teacher is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being. Score/Level King’s College Secondary Foreign Language Teacher Candidate Observation Rubric Aligned with ACTFL Standards and INTASC Principles Teacher Candidate’s Name:_________________________________ Date:________ Name of Observer: ________________________ Title: __________________ Lesson Topic: ________________________ Rating scale: 1=unsatisfactory (i.e, non of the criteria were met), 2=satisfactory (i.e, some of the criteria were met), 3=superior (i.e, most of the criteria were met), , 4=exemplary (i.e, all of the criteria were met), , NA=not applicable (circle one) (See grading rubric Appendix Student Teaching Handbook for criteria) I. Efficient Use of Instructional Time a. Appropriate goals and objectives were set (INTASC 1,2,7) b. Lesson was well paced (INTASC 2) c. Entire class monitored and more than one activity/group was attended to at a time and classroom management techniques (e.g., proximity) used effectively (INTASC 2,5) II. Instruction d. Attention gained (INTASC 1,2,4) e. Previous knowledge recalled (INTASC 2,4) f. Purpose/Objective of the lesson made clear (INTASC 1,4) g. Teacher Input Provided (INTASC 6) h. Teacher guided practice was adequate and appropriate (INTASC 2,4) i. Repetition of key concepts occurred throughout the lesson (INTASC 2,4) j. A variety of instructional materials were used to actively engage the students. (INTASC 2,3,4,6) Rating 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA k. All of the students were actively engaged in the learning throughout the lesson. (INTASC 2,4) 1 2 3 4 or NA l. Students were encouraged to understand, question, and interpret ideas from diverse perspectives. (INTASC 4) Open-ended questions were used, diverse perspectives were explored. 1 2 3 4 or NA Comments m. Higher order thinking skills were used. (INTASC 4) 1 2 3 4 or NA 1 2 3 4 or NA n. Evaluation of student comprehension occurred throughout the lesson and appropriate feedback provided. (INTASC 8) 1 2 3 4 or NA o. The lesson ended with closure/review that focused on the main objectives of the lesson. (INTASC 3,4) The students were able to summarize the learning rather than the student teacher having to do this for them. 1 2 3 4 or NA p. Variety of teaching methods/instructional strategies were used to reach different types of learners. (INTASC 2,4,8) e.g., direct instruction, discovery learning, cooperative learning, role playing, discussions, technology simulations, “hands-on/minds-on” materials, paired students, etc. 1 2 3 4 or NA q. Relevant subject areas & “real world” problems were integrated into the lesson. (INTASC 1,2,3,7) 1 2 3 4 or NA r. Inclusion of special needs student occurred. (INTASC 2,3) 1 2 3 4 or NA s. Individual differences were addressed. (INTASC 2,3,5) 1 2 3 4 or NA t. Classroom instruction and assignments provided for Limited English Proficiency (LEP) students. (INTASC 2,3) 1 2 3 4 or NA u. Diversity issues were addressed in an appropriate manner. (INTASC 2,3,6,10) 1 2 3 4 or NA III. Personal and Professional Characteristics 1 2 3 4 or NA v. Displayed Enthusiasm. (INTASC 1,6) w. Exhibited Confidence. (INTASC 1 2 3 4 or NA 1) x. Displayed empathy. (INTASC 5,9,10) 1 2 3 4 or NA y. Acted and appeared in a professional manner. (INTASC 9,10) 1 2 3 4 or NA z. Use of the target language is appropriate and proficient The unit’s definition of diversity is simply that in every setting there is diversity because no two people are alike. Thus, in every class there is student diversity – not only in cultural background, but also in motivation, skills for learning, beliefs what learning involves, and preferences for different ways of learning. (McKeachie and Svinciki 2006)