EM Spectra Study Guide: Astronomy, Wavelengths & More

Astronomy Name ____________ Key ____________
EM Spectra – Study Guide
1.
How many types of spectra are there?
3 Types: Continuous (like a rainbow), Emission (bright colored lines) and Absorption
(dark lines on colored background)
How are these spectra alike? Lines (either colored or dark) appear in same locations specific for star or element
How are they different? Lines are in a unique location for a star or an element
2.
What is the order of electromagnetic spectrum waves from the shortest wavelength to the longest?
Gamma < X Ray < Ultraviolet < Visible < Infrared < Microwave < Radio
Shortest Wave
Highest Frequency
Longest wave
Lowest Frequency
3.
The longest wavelengths have the ____ Lowest ___ frequencies and _ lower _ energy.
4. The shortest wavelengths have the __ highest __ frequencies and ___ higher __ energy.
5.
Which wavelengths are considered the most dangerous? Why?
GAMMA AND X-RAYS, because they have the highest frequency (and energy)
6.
Which wavelengths are completely blocked by our atmosphere?
Gamma and x-rays
7.
Which wavelengths can completely penetrate our atmosphere?
Radio and visible
8.
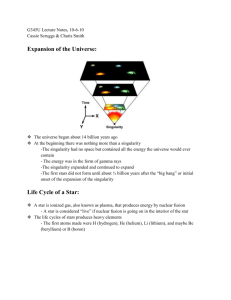
What type of information can be obtained by studying a star’s spectrum?
Temperature and Composition (what elements it contains); if it is moving to or away from us; its age; its size, and brightness.
9.
What type of EM waves are used in TV remotes? __ Infrared __
10.
What type of EM waves are used in radar? ____ microwave ____
11.
Which EM waves travel the fastest? They all travel at the SAME speed (Light speed) IN
A VACUUM!
12.
Spectra are unique for ___ elements __ and ___ stars ____.
13.
Light radiation acts as both ___ particle ____ and ____ wave ____.
14.
Given an element’s and a star’s spectra, how can you tell if the element is present in the star? (You will have to do this problem on quiz!) See Star Spectra Activity
15.
What type of light (EM radiation) is best to see molecular hydrogen gas? …stars?
…Supernova remnants? (The test problems will use this information.)
Use your “spin-a-spectrum”
16.
Why do we put telescopes in space? ( Hint: see questions 5-7 above.
)
Some parts of the EM Spectrum do NOT make it to Earth’s surface (Gamma and x-rays, most of UV and IR); also telescopes in space do not suffer from atmospheric distortion
17.
According to Annie Jump Cannon’s classification, which stars are coolest? M
Which are hottest? O Types: O B A F G K M
18.
Why are stars different colors? Which color star is hottest? …. Coolest?
The color of a star depends on where its peak energy wavelength is; hottest stars are Blue
(their peak is near or in the UV range); coolest are RED (peak near or in Infrared)
19.
How can you tell is a star is moving to or away from us?
How its spectra is shifted—toward us is BLUE shifted; away from us is RED shifted.
20.
Our eyes can only see ____VISIBLE____ light.
21.
Name TWO instruments that are used to break light into its different color parts.
Prisms and diffraction gratings
22.
If the electromagnetic spectrum were 60 octaves wide, visible light would be less than
__ 1 _ octave(s) wide.
****Look over your Electromagnetic Quick Quiz and Brain Pop Questions!
Mini-Essay: How is the story Seven Blind Mice like using the electromagnetic spectrum?
Each mouse only got part of the picture; but together they could see it all. Each part of the electromagnetic spectrum can give us part of the picture of stars, but we need all parts to understand it fully.
Bonus Questions:
1. How many light years across is our Milky Way?
100,000 LY
BONUS Question: Make up a mneumonic for the EM Spectrum order.
For example: G ood e X amples U se V ery I mpressive M emory R hymes
Gamma X -Ray U ltraviolet V isible I nfrared Microwave R adio