Human Behavior Course Syllabus: Topics & Objectives
advertisement
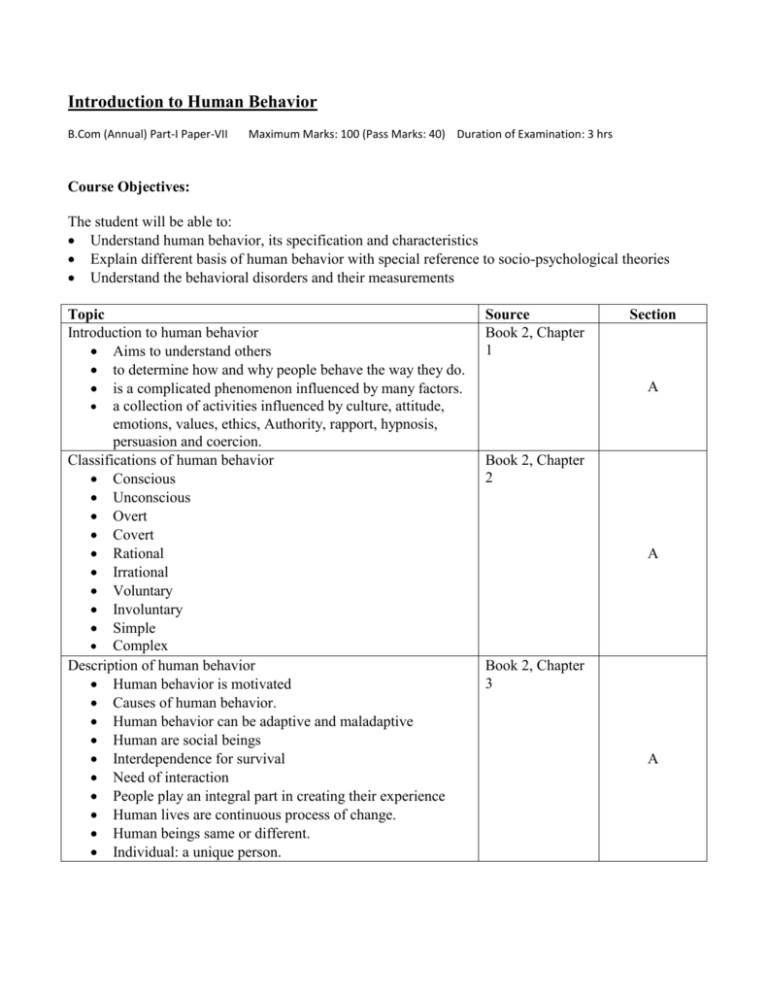
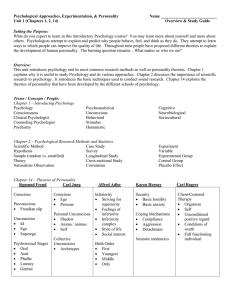
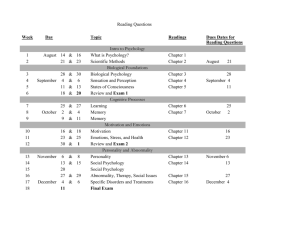
Introduction to Human Behavior B.Com (Annual) Part-I Paper-VII Maximum Marks: 100 (Pass Marks: 40) Duration of Examination: 3 hrs Course Objectives: The student will be able to: Understand human behavior, its specification and characteristics Explain different basis of human behavior with special reference to socio-psychological theories Understand the behavioral disorders and their measurements Topic Introduction to human behavior Aims to understand others to determine how and why people behave the way they do. is a complicated phenomenon influenced by many factors. a collection of activities influenced by culture, attitude, emotions, values, ethics, Authority, rapport, hypnosis, persuasion and coercion. Classifications of human behavior Conscious Unconscious Overt Covert Rational Irrational Voluntary Involuntary Simple Complex Description of human behavior Human behavior is motivated Causes of human behavior. Human behavior can be adaptive and maladaptive Human are social beings Interdependence for survival Need of interaction People play an integral part in creating their experience Human lives are continuous process of change. Human beings same or different. Individual: a unique person. Source Book 2, Chapter 1 Section A Book 2, Chapter 2 A Book 2, Chapter 3 A Psychology of behavior Theory of behavior Basic drives and motives Social influences Emotions Biological base of behavior The nervous system Genetic influences Influences of hormones Biological rhythms Daily behavior Gestures Influencing daily behavior Body language Examples of body language Reading body signals Theoretical approaches Psychodynamic approach humanistic approach behavioral approach cognitive approach biological approach Human needs theory by: maslow Psychoanalytic theory (sigmund freud) Level of awareness conscious preconscious / subconscious unconscious Book 6, Chapter 1 Organization of the mind id ego superego conscience Social theory Erik erikson Psychosocial theory stages of development development goal or task psychosocial crisis the process of coping. Book 2, Chapter 4 A Book 6, Chapter 2 B Book 6, Chapter 3 B Book 2, Chapter 4 B Book 2, Chapter 4 B B Book 2, Chapter 5 C Carl jung conscious (ego) collective unconscious- “psychic inheritance” personal unconscious Archetypes persona anima & animus shadow Personality orientations introversion extroversion Behavioral disorders Defining abnormal behavior Addiction Split-brain Personality disorders Alzheimer's disease Autism Phobias Book 2, Chapter 6 C Book 2, Chapter 7 C Book 6, Chapter5 C Recommended Books 1. W. R. Hobbs: 2010. Introduction to Human Behavior 2. Jeffrey Eric Criste Introduction to Human Behavior 3. John S. Wodarski. 1985. Introduction to human behavior 4. Linda M. Levine. 2003. Introduction to human behavior 5. Tracy M. Laulhe .2000 .Introduction to Human Behavior .Pearson Custom Publishing, 6. Quinn Sartain Aaron.; John,North Alvin.; Roy Strange Jack. 2005. Psychology Understanding Human Behavior Additional Books 1. Theodore Millon and Melvin J. Lerner. Hand Book of Psychology, Volume 5, Personality and social Psychology. Canada: John Wilet & sons Inc. 2. Body Language Magic 3. Allen Pease. 1981. Body Language, How to read other’s thoughts by their gestures. 4. George Stricker and Thomas Widiger. 2003. Hand Book of Psychology, Vol. 8. Clinical Psychology, Canada: John Wiley & sons Inc. 5. Richard M. Ryckman. 2008. Theories of Personality. Australia: Thomson & Wadsworth. 6. Robert A. Baron. Psychology, 4th Edition.