Syllabus for DSC 321: Quantitative Analysis of Business Problems
advertisement

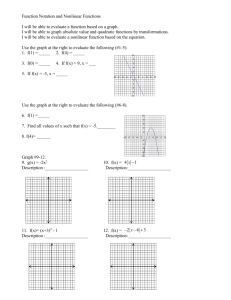
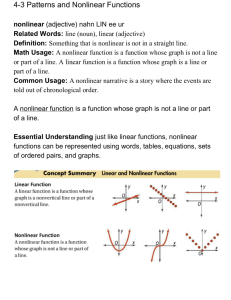
Syllabus for DSC 321: Quantitative Analysis of Business Problems Course Goals Course Goals 1. To present concepts that are useful for problem solving. 2. To demonstrate the role of mathematical modeling in the problem solving process. This includes the use of abstraction and simplification to gain a better understanding of a system or process. 3. To show the role and limitations of the language of mathematics as a representational form for a process or system. 4. To demonstrate that there are a number of different equally valid models that might be used to represent a particular system and that the model form chosen is influenced by the needs and perspective of the modeler. 5. To present the students with the opportunity to work together on group projects to demonstrate that we learn from each other as well as in the classroom or from the "expert." 6. To encourage the student to remember that the purpose of analysis is action and that the goal is to change systems so that they better meet some defined need. Topics Time (Lectures) Introduction to Decision Making and Management Science 1 An Introduction to Corporate Planning Models (The use of logically and statistically derived functional relationships in models of complex systems) 2 The Linear Programming Model Introduction Graphical Solution Method Formulation of Linear Programming Models Logical and Statistical Modeling Methods Use of Computer Software to Solve Linear Programming Models The Simplex Method for Solving Linear Programming Models Sensitivity Analysis for Linear Programming Models Network Models The Transportation Problem The Assignment Problem 1 1 2 1 2 4 3 1 1 An Introduction to Nonlinear Programming Models Formulation of Nonlinear Models Using Logical and Statistical Modeling Methods Use of Computer Software to Solve Nonlinear Programming Models Choosing a Linear or Nonlinear Function to Model a Relationship 2 1 1 Methods for Incorporating Multiple Decision Criteria into a Model Goal Programming Models 3 A. Methods for Decision Analysis Under Conditions of Uncertainty Use of Payoff Tables Use of Decision Trees Expected Value and Expected Utility as Decision Criteria 7* B. Analytical Queuing Models Single Server Queues Multiple Server Queues Economic Evaluation of Queuing Systems C. Analytical Inventory Models Deterministic Models Probabilistic Models * Seven lectures for one or more of topics A, B, and C at the instructor’s discretion. Simulation Models Models of Queuing Systems Models of Inventory Systems Evaluating Decision Alternatives Using Simulation Models Using Regression Analysis to Evaluate Alternatives Combining Modeling Methodologies The Use of Simulation and Regression Analysis to Build a Mathematical Programming Model, An Example TOTAL 3 2 1 1 1 42