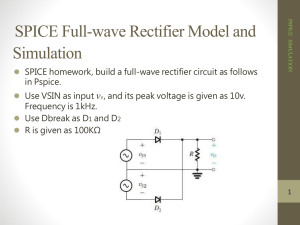
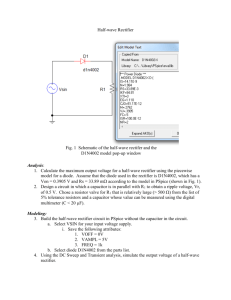
ECT-246 For the power supply circuit shown above, we have 40
advertisement

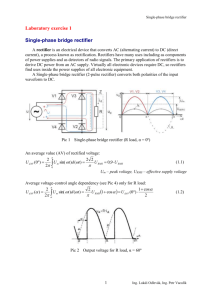
ECT-246 T1 LINE VOLTAGE C1 VREG COMMON 1. For the power supply circuit shown above, we have 40 points Vin = 120 vac, transformer turns ration is 10:1, C1 = 100µF, Voltage regulator is LM 7805, RL = 100 Ω Calculate: (a) Secondary rms voltage. Vs(rms) = 120 /10 = 12 V (b) Secondary peak voltage Vs(pk) = Vs(rms) / 0.707 = 12V / 0.707 = 16.97 V (c) Peak voltage at the output of the bridge rectifier. VL(pk) = Vs(pk) – 1.4 = 16.97 – 1.4 = 15.57 V if voltage drop across the diodes is considered. (d) DC voltage across the load resistor Idc Vdc Vm 4f C Here Vdc=?, Vm = 15.57V, Idc = Vdc/R = Vdc/100, f = 60Hz, C = 100μF Vdc 15.57 0.4167Vdc Hence, Vdc 15.57 100 4 60 100 106 15.57 10.99 , say 11 volts. Or, Vdc 1.4167 (e) DC current through the load resistor. DC current through load = Vdc/R = 11/100 = 0.11 amps. (f) Primary peak current Primary peak current = secondary peak current/10 = 0.607/10 = 0.0607 amps. 1 RL (g) Secondary peak current 1 2C 2 2 R Im Vm 15.57 1 (2 60) 2 (100 106 ) 2 0.607 amps. 2 100 (h) DC voltage at the output of bridge rectifier with no filter. Vave = 2VL(pk) / π = 2*15.57 / π = 9.91 V 2. What is the ripple frequency for the given rectifiers: 9 points (a) Half wave rectifier: ripple frequency = 60Hz In the half-wave rectifier, one pulse of DC output is generated for one cycle of AC input. The ripple frequency of a half-wave rectifier circuit powered by 60Hz AC is measured to be 60 Hz. (b) Full-wave rectifier: ripple frequency = 120Hz In the full-wave rectifier, two pulses of DC output are generated for each cycle of AC input. Since there is double the number of pulses in the full-wave rectifier's output, the ripple frequency of a full-wave rectifier circuit, powered by the exact same 60 Hz AC line voltage, is measured to be 120 Hz. (2*AC input frequency = 2*60Hz = 120Hz) (c) Bridge rectifier: ripple frequency = 120Hz The bridge rectifier also produces two pulses per cycle…..therefore, ripple frequency = 2*60Hz = 120Hz. 3. What is the effect of increasing the value for resistor and capacitor on the ripple voltage at the output of a bridge rectifier? Express your answer in terms of increase or decrease. Explain your answer with the help of a formula. 6 points (a) Capacitor Idc Vdc Vm . Vdc Vm Vdc 1 4f C 4 fR C 1 4 fRC We see that 2nd term will decrease if C is increased and Vdc will increase. Vdc will become almost equal to Vm if C becomes too large but this cannot be done as current surge will become excessive and supply may not be capable to deliver that much current. Vdc Vm 2 (b) Resistor Idc Vdc Vm . Vdc Vm Vdc 1 4f C 4 fR C 1 4 fRC Here also, 2nd term deceases with increase in R and Vdc increases. Vdc Vm 4. If one diode is shorted in a bridge rectifier, what effect it would have on the output waveform? Draw the waveform . 5 points If one diode of the bridge rectifier is shorted, the output of the bridge rectifier is halfwave rectification and no longer full-wave rectification. “picture is from week 1 summary in Doc sharing” 5. What is the function of a bridge rectifier? 5 points The bridge rectifier is a full wave rectifier that alternates conduction between two diode pairs. The purpose of a bridge rectifier is to convert AC voltage (sine wave) to (fullwave) pulsating DC voltage. Also peak inverse voltage of the diode becomes half. 6. What is the function of the filter at the output of bridge rectifier? 5 points The function of the filter at the output of the bridge rectifier is to convert the ripple voltage to smooth DC (it reduces ripple voltage). 7. What is the function of voltage regulator at the output of bridge rectifier and filter in a power supply? 5 points The function of the voltage regulator is to regulate the DC output voltage of the supply against variations caused by changes in the load current, as well as the changes in the AC supply voltage. 8. What is the effect of variation in input frequency in a power supply on: 9 points (a) Output ripple voltage Idc Vdc Vr . We see that output ripple voltage decreases with the increase in 2 f C 2 f RC frequency. (b) Ouput DC voltage 3 Vm . We see that if frequency f increases, 2nd term in denominator will 1 1 4 fRC decrease and Vdc will increase. (c)Output DC current Vdc Vm . Here also, Idc will increase with increase in frequency f. Idc R 1 R 1 4 fRC Vdc 9. The peak voltage at the output of a bridge rectifier is 15 V. What would be the DC voltage ? 5 points Vave = 2*VL(pk) / π = 2*15V / π = 30 / π = 9.55V 10. What are the differences between Full-wave rectifier and bridge rectifier? 5 points Full-wave rectifiers use two diodes where one conducts on the positive half cycle of the AC (wave) and the other conducts on the negative half cycle. Bridge rectifiers use four diodes, where two conduct on the positive half cycle, and the other two conducts on the negative half cycle. The bridge rectifier does not require the use of a center tapped transformer, whereas, the full-rectifier does require a center tapped transformer, therefore it cannot be connected directly to an AC line input. The bridge rectifier provides twice the average output voltage and current and can be directly connected to an AC line input. Peak inverse voltage of the diodes required in case of center tap connection is double of the peak inverse voltage of the diodes required in case of bridge rectifier. As a result, bridge rectifier is commonly used. 4