Biotechnology notes
advertisement

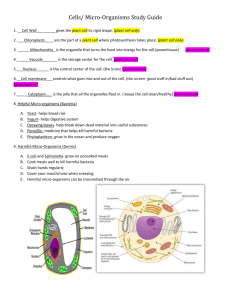
Living Factories Identify yeast as a single-celled fungus which can use sugar as food Yeast is a microscopic fungus found naturally on many types of fruit such as grapes. A yeast cell is made of a single cell. Yeast can use sugar (glucose) as a food supply. Using a word equation, state the process of fermentation of glucose by yeast Yeast is used to make many useful products. Its usefulness comes from its ability to use glucose as a source of energy. It does this in a process called fermentation. The word equation for fermentation is: Glucose energy + carbon dioxide + ethanol State that the raising of dough and the manufacture of beer and wine depend on the activities of yeast When yeast ferments, it makes two important products, ethanol and carbon dioxide. In baking the carbon dioxide bubbles make the dough rise. The ethanol is burned off during the baking process. State that the souring of milk is a fermentation process 1 State that the manufacture of cheese and yoghurt depends on the activities of bacteria Cheese and yoghurt are made by curdling milk. Lactic acid is needed to curdle the milk. Manufacturers add certain strains of bacteria to the milk. Different types of bacteria are used to give the different types of cheese and yoghurt. Problems and profit with Waste Describe some examples of the damage caused to the environment by disposal of untreated sewage Sewage is mostly organic waste and it is produced in large amounts by humans. To avoid disease, it must be dealt with safely and quickly. The release of untreated sewage into waterways causes the pH of the water to decrease and also causes a fall in the oxygen content of the water. Give examples of diseases which may be spread by untreated sewage In the first half of the 19th Century, disease and death in Britain as a result of untreated sewage entering water. Even in modern Britain, natural disasters like flooding could disrupt the sewage treatment systems and the threat of such disease could return. Some of the diseases which can be spread by untreated sewage or failure to wash hands after a visit to the toilet are: typhoid diptheria polio food poisoning 2 cholera State that the main process in the treatment of sewage is its breakdown by the action of decay micro-organisms to products harmless to the environment Describe how the oxygen required by micro-organisms can be provided during sewage treatment Oxygen is required by the micro-organisms and this is usually provided at the treatment works using compressed air or by trickling the sewage over stones which trap pockets of air. 3 Describe the principle precautions to be taken during laboratory work with microorganisms Microbes can help in the production of food and drink, the treatment of sewage or can cause disease. Micro-organisms are found everywhere so precautions must be taken to prevent unwanted microbes from growing (contamination). Safe-practice Petri dishes of agar jelly must be kept closed until you are ready to use them to stop microbes from the air contaminating the plates. you wash your hands before and after the experiment to stop you contaminating the agar plates and then to stop you spreading the microbes around. Petri dishes are sealed with tape after being inoculated to stop microbes escaping. After use the petri dishes are treated in an autoclave to kill the microbes. Explain the importance of such precautions in biotechnological processes whenever relevant Contamination is the presence of unwanted, perhaps harmful, micro-organisms. Beer production is one area where contamination may occur. Between batches beer manufacturers’ sterilise their equipment. State that alcohol and methane are products of fermentation Methane and alcohol can be used as fuels and are known as fermentation on fuels. Explain the advantages of deriving fuel through fermentation rather than from fossil sources There are advantages in using fermentation fuels rather than fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are coal, oil and gas. 4 Fermentation fuels Fossil fuels Harmless to the environment Harmful to the environment Easy to obtain Difficult to obtain Cheap to obtain Expensive to obtain Renewable Non - renewable Give 2 examples of useful products and the waste materials from which they are gained through the action of micro-organisms and explain the economic importance of this technology Upgrading waste is a means of obtaining useful products from unwanted waste material which would otherwise have to be disposed of and might harm the environment. Two examples of useful products are: 1 Biogas This can be made from the degradation of farm manure and household rubbish by microbes. The biogas can then be used as a source of energy. 2 Whey and fruit pulp Whey is the waste from cheese making and fruit pulp the waste from making fruit juice. Both of these food left-overs can be converted by micro-organisms to high quality protein foods for e.g. cattle feed. State that under suitable conditions, micro-organisms can reproduce very rapidly by asexual means Most micro-organisms can reproduce much faster than plant and animal cells can by asexual reproduction. State that micro-organisms may be harvested to provide protein rich food for animals or man Large quantities of micro-organisms can be used to provide protein rich food for animals and man e.g. single cell protein or mycoprotein. 5 Reprogramming Microbes State that the normal control of bacterial activity depends on its chromosomal material Bacterial cells are much smaller than animal cells. Both bacteria and animal cells have a nucleus. Some bacterial cells have extra chromosome material called plasmids that can be transferred from one bacterial cell to another. Just like other cells, the normal control of the bacterial cell’s activities depend on its chromosomal material. Bacterial cell Chromosome plasmid State that pieces of chromosome can be transferred from a different organism and so allow bacteria to make new substances Genetic engineering alters microbes so that they will make products they would not normally make. A number of steps are involved: 1 The chromosomal material is removed from an animal cell 2 One gene is removed 3 A plasmid is carefully removed from a bacterial cell and the ring is carefully opened 4 The gene from the animal cell is inserted into the plasmid 5 The altered plasmid is placed back into the bacterial cell 6 Give some examples of the products of genetic engineering and their applications, e.g. insulin Growth hormone is given to children who would not otherwise grow properly. Insulin is used to treat diabetics who cannot make their own. State that “biological” detergents contain enzymes produced by bacteria Some detergents are called biological detergents as they contain enzymes Comparing non-biological and biological washing powders Temperature (C) 20 40 100 Biological powder Stain gone Stain gone Stain present Non-biological powder Stain partly present Stain partly present Stain gone State that an antibiotic is a chemical which prevents growth of micro-organisms In 1928 a Scotsman called Alexander Fleming discovered that a substance made by a fungus prevented the growth of some bacteria. This substance was named penicillin and was the first known antibiotic. Since then many other antibiotics have been discovered and used against diseases caused by bacteria. 7