LAB: How Does Exercise Affect Cellular Respiration
advertisement

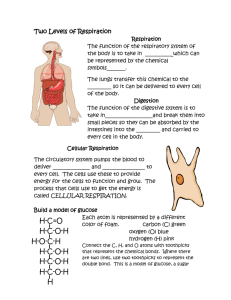
Exercise & Cellular Respiration Lab Objective To observe the effects of exercise on cellular respiration. To identify the role of heart rate in determining the rate of cellular respiration. Background Cellular respiration (see chemical reaction below) is a chemical reaction that occurs in your cells to create energy; when you are exercising your muscle cells are creating ATP to contract. Cellular respiration requires oxygen (which is breathed in) and creates carbon dioxide (which is breathed out). C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP (energy) This lab will address how exercise (increased muscle activity) affects the rate of cellular respiration. You will measure heart rate as an indicator of the need for oxygen. You will measure these indicators at rest (with no exercise) and after 1, 2 and 3 minutes of exercise. Materials stop watch PreLab 1. Title and date of the lab (remember to include your lab partners names, write in pen, and add this lab to your table of contents) 2. Purpose 1-2 sentences describing the overall goal of the experiment; use complete sentences 3. Hypothesis Write an if/then statement for this lab hypothesizing how exercise will impact the rate of cellular respiration/heart rate. Include WHY you think this. 4. Lab Procedure (see below) First list the materials needed for this lab. Next, write a procedure for the experiment. Use your own words to describe the steps in this lab. You should be able to do the experiment from what you write without using this lab sheet. You may do a numbered list here. 5. Variables State the independent variable, dependent variable, and control for this experiment. 6. PreLab Questions See Below; copy each question and ANSWER it BEFORE doing the lab OR answer in complete sentences. 7. Data (see below) Copy the data table into your lab notebook. Give the data table an appropriate title. **ANOTHER OPTION FOR THIS LAB IS TO CUT OUT AND TAPE THE DATA TABLES INTO YOUR LAB NOTEBOOK** PreLab Questions 1. What is the equation for cellular respiration? Label which items are the reactants and the products. 2. In what part of the cell does cellular respiration occur primarily? Draw and label the parts of this cell organelle. 3. Write a prediction/hypothesis of how exercise will affect the body’s rate of cellular respiration. Procedure Assign each member in your group as one of the following: Recorder Exerciser 1 Exerciser 2 Exerciser 3 PART A: Resting (no exercise) 1. Take your pulse by counting the number of beats in 30 seconds and multiply that number by 2. Record this in your table for each member in your group. 2. Average the numbers for each member of your group to get an average heart rate. Record this in your data table. PART B: Increased Muscle Activity (Exercise) 1. Have exerciser’s 1, 2 and 3 exercise for exactly 1 minute by doing jumping jacks. 2. After 1 minute of exercise, each person should immediately take their pulse for 30 seconds. Again, multiply this number by 2 and record in your data table. 3. Repeat steps 1 & 2 again – but exercising for 2 minutes. 4. Repeat steps 1 & 2 again – but exercising for 3 minutes. Data Table Record the heart rate/pulse: Exerciser 1 Exerciser 2 Exerciser 3 Average Resting 1 minute exercise 2 minutes exercise 3 minutes exercise Analysis and Conclusion Questions Answer the questions below using your BACKGROUND information in the lab & notes, as well as your lab data. ANSWER THE QUESTIONS IN COMPLETE SENTENCES 1. How did exercise affect the heart rate? 2. What does this indicate about the amount of oxygen needed in the muscles? 3. What can you conclude about the effect of exercise on the amount of carbon dioxide that is present in your exhaled breath? Why is this so? 4. What type of muscle fiber do you think you were primarily using during jumping jacks – explain. 5. Do you think doing push-ups, sprints and/or weight lifting would provide accurate results – explain why or why not. 6. State whether your hypothesis was correct or incorrect and why. In doing so, discuss what you think is going on in the muscles of the body as muscle activity is increased. Explain how your results about heart rate are related to cellular respiration.