Same substance = same density
advertisement

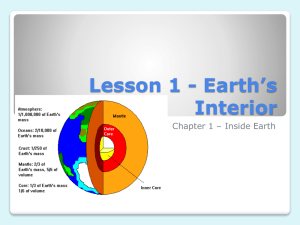
EARTH SCIENCE: NEED TO KNOW FACTS . . . Maps and Measurements A sphere is the best model of Earth’s shape (Earth “appears” round). Its real shape is an oblate spheroid. Altitude (angle of how high in sky) of Polaris = your northern hemisphere latitude. Polaris is at the horizon at the equator (0), directly above your head at the North Pole (90) Latitude is North or South of the Equator, Longitude is East or West of Prime Meridian Longitude is based on sun. Sun moves 15/hr in sky. (360/24 hrs = 15) Each time zone is about 15. Topographic maps show elevation- how high something is! When contour lines are close together = steep slope/gradient In the gradient formula, change in field values means you find the difference between the two elevations. Contour lines bend when they cross rivers and point upstream (uphill). Rivers always flow downhill (downstream), towards lower elevation numbers. A cross section/profile is a SIDE VIEW of something. Compass direction means: north, south, east, west, northeast, southeast, northwest, southwest. Rocks and Minerals Minerals make up rocks. Their properties depend on their internal structure of atoms. Luster is their shine- it can be metallic or non-metallic. Streak is the color of the powder that is left behind when a mineral is scratched against a plate. Hardness is tested by scratching glass; if something is harder than glass, it can scratch it. Diamond is the hardest mineral- it can scratch all the others. Cleavage means they break in flat layers, Fracture means they just look broken. Sedimentary rocks: made of sediments deposited, buried, and cemented together, usually in horizontal layers, can contain fossils, fragments/clasts of other rocks Igneous rocks: Extrusive- lava, above ground, cools fast- small/no crystals (fine, glassy or vesicular) Intrusive- magma, underground, cools slow- large crystals (coarse to very coarse) Metamorphic rocks: Other rocks are re-crystallized due to heat and pressure, banding, foliated (stripes) o Contact Metamorphism: An igneous intrusion heats up surrounding rock and causes it to recrystallize, turning it into metamorphic rock. o Regional Metamorphism: Plates converge, creating a lot of heat and pressure which recrystallizes a large area of rock and turns it metamorphic. Rock Cycle: All three rock types can turn into one another by melting, weathering, erosion, heat, pressure. Weathering, Erosion and Landscapes Weathering is the breaking down of rock. Physical is broken down, Chemical is changed chemically. o Weathering of rocks is affected by climate, surface area, and composition of the rock. o Climate: Warmer and Wetter climates have more weathering o The greater the surface area, the more weathering. o Softer minerals weather more easily. Calcite (found in limestone and marble) weathers faster because it reacts with acid. o Water expands when it freezes (frost wedging) Erosion is the transportation of sediments by wind, water, glaciers, waves, gravity/mass movement. Deposition is placement of sediment in a new location. Gravity is behind all erosion. (mass movement, wind, running water, glaciers, ocean waves) Streams are the number one agent of erosion! They make rocks round and smooth (abrasion) Stream velocity is faster when the gradient (slope) and discharge (amount of water in stream) are higher. Velocity is faster on outside of meander (bend). Erosion occurs there and it is deepest. Velocity is slower on inside of meander (bend). Deposition occurs there and it is more shallow. Heavy, dense, and round particles get deposited first in water. Streams slow down when they enter oceans and sediments are sorted by size- biggest to smallest. Stream deposits are sorted, round, smooth, make V shaped valleys. Glacial sediments are unsorted, scratched, grooved, make U shaped valleys and can carry boulders. Glaciers formed NY! They leave behind moraines (unsorted piles of sediment) and make finger lakes. Porosity (amount of holes) - size doesn’t matter (when sorted) Permeability (holes connected) – the bigger the particle size, the faster water goes through Impermeable- water cannot penetrate (rock particles are close together) Capillarity (movement upward) – increases as particle size decreases Landscapes: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains Arid (dry) landscapes: steep slopes; Humid landscapes: smooth round slopes. Seasons and Insolation The seasons are caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis (23.5 and its revolution around the sun! Insolation is incoming solar radiation, heat from the sun Duration of insolation is how LONG we get heat from the sun. (12 hrs always at equator, 24 hrs at N. Pole in summer, 24 hrs at S. Pole in winter) Intensity of insolation is how direct the angle is. (90 at equator in Spring/Fall, Tropic of Cancer in Summer, Tropic of Capricorn in Winter.) Equator = no seasons = always has 12 hours of daylight Low latitudes are regions near the equator and have high temperatures and high moisture levels. High latitudes are regions near the poles and have low temperatures and low moisture levels. If the Earth’s tilt was GREATER than 23.5, we would have colder winters and warmer summers (a larger range in seasons) If the Earth’s tilt was LESS than 23.5, we would have warmer winters and cooler summers (a smaller range in seasons) Day Date Vertical ray Summer solstice June 21 Tropic of Cancer Autumn equinox September 23 Equator Winter solstice December 21 Tropic of Capricorn Spring equinox March 21 Equator Sunrise Sunset Day length 23 1/2 N 0 N of E N of W Longest East West 12 hours 23 1/2 S 0 S of E S of W East West Shortest 12 hours Dark/black/rough surfaces absorb the most heat; white/smooth surfaces reflect the most heat. A good absorber of energy is a good radiator of energy. Heat and energy move in different ways: o Conduction: heat transferred directly from molecule to molecule (heating a pan on stove) o Radiation: heat moves through space ex: solar radiation o Convection: due to differences in density (atmosphere-weather, asthenosphere– plates move) o Infrared radiation: reradiated from Earth, turns into long wave radiation Meteorology Atmosphere: the gas layer that surrounds the earth. Made mostly of Nitrogen and Oxygen, subdivided into the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere. Heat from the sun causes weather- temperature differences create density differences. Cloud formation: Warm, moist air rises, expands and cools to the dew point. Condensation occurs. Relative Humidity: How much moisture is in the air compared to how much it can hold. Saturation: Air is completely filled with water vapor. When relative humidity is 100%. Dewpoint: Temperature at which condensation occurs (when relative humidity is 100%) A sling psychrometer is used to measure dewpoint and relative humidity. The Water Cycle Hydrosphere: All of the liquid water on earth! Made mostly of hydrogen and oxygen (H2O!) Condensation: water vapor changing into liquid water (remove heat, cool it down) Evaporation: liquid water changing to water vapor (add heat), boiling Transpiration: when water evaporates directly off trees and other plants. Precipitation: rain, snow, sleet, hail; happens when temperature and dewpoint are THE SAME. Runoff: excess water not able to infiltrate (seep into) the ground. Wind is a horizontal movement of air caused by uneven heating of Earth’s surface High Pressure Low Pressure Wind Blows Wind Blows Outward, towards edges Inward, towards center Clockwise Counter-clockwise H Cold Warm No clouds, clear skies Clouds, Storms No precipitation / dry Precipitation / wet Name of Front Cold Front: pushes out warm air and forces it to rise because it is less dense. Creates thunderstorms. Warm Front: Warm air pushes cold air away. Creates precipitation. Occluded Front: cold air pushes out warm front, forcing warm air upward in between. Stationary Front: Two air masses meet and stop moving. Symbol L Diagram Cold air Warm air Warm air Cool air Warm air Cold air Warm air Cool air Cool air When isobars are close together, the wind is blowing quickly. An anemometer is used to measure wind speed. Units are in knots, or km/hr. A barometer is used to measure air pressure. Units are in millibars (mb), atmospheres, mm of Mercury. Air mass– region of atmosphere with uniform temperature and humidity (moisture) Continental Polar, Continental Tropic, Maritime Polar, Maritime Tropic, Continental Arctic. Front– boundary between two air masses Passing of a front = precipitation and change in temperature and wind direction Cold fronts move fastest Weather moves NE in NY because of “prevailing winds,” which means the way the winds normally move. Warm air rises because it is less dense!!! Climate Climate means long term weather patterns in an area. Things that determine climate. o Latitude: Low latitude = warm temperatures, High latitude = cool temperatures o Elevation: higher elevations = cooler temperatures o Mountain barriers (Orographic lift): windward = cool and moist / leeward = warm and dry o Ocean currents: warm = warmer temperatures / cool = cooler temperatures o Nearness to a large body of water (being on coast) moderates temperatures by creating cooler summers and warmer winters. Ex: NY has cooler summers and warmer winters than Chicago, which is inland. Specific Heat: Water has a higher specific heat than land, which means it takes LONGER to change temperature. (That’s why the water at the beach doesn’t get warm until the end of summer!) Sea Breeze: During the day, cool air over the ocean moves inland (towards land) and creates a sea breeze. Land Breeze: During the night, cool air on the land makes warm air over the ocean rise because it is less dense. Ultraviolet radiation: comes directly from Sun – short wave radiation, when it hits earth it turns into long wave radiation. Dangerous UV radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer. Greenhouse gases: absorb long wave radiation ex: Carbon Dioxide Global Warming: caused by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane absorbing heat. Deforestation: cutting down trees, also called logging. Increases global warming because trees absorb carbon dioxide. The Dynamic Earth Earth’s Interior Layers: o Crust- Rocky outer layer of Earth o Lithosphere- The major plates and solid upper mantle, mostly composed of silicon and oxygen. o Asthenosphere- Molten (melted) top layer of the mantle where convection currents occur. Also called the plastic mantle, which means that it moves around a lot, NOT that it’s made of plastic. o Outer Core- Made of liquid iron and nickel o Inner Core- Made of solid iron and nickel. o Heat and pressure increase as depth inside the earth increases. Theory of Plate Tectonics: Earth’s upper layers are made of about 12 huge slabs of rock called plates that move around. Convergent- plates move together, Divergent- plates move apart, Transform- plates slide past each other Convection Currents in the mantle make the plates move. (Heat rises because it is less dense, cools down, and sinks, and this happens over and over) Oceanic crust is made of basalt; Continental crust is made of granite. Oceanic Crust/Basalt is thinner and more dense than Continental Crust/granite which is thicker and less dense, so oceanic crust gets subducted into the mantle at convergent plate boundaries. Types of Convergent Boundaries: o Continental-Continental Convergence: Orogeny, which means mountains are uplifted. Ex: Himalayas o Continental-Oceanic Convergence: Deep trench (subduction zone) beside continental volcanic mountain ranges. Ex: Peru-Chile Trench and Andes Mountains o Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence: Volcanic Island Arcs and trenches. Ex: Aleutian Islands/Trench. Types of Divergent Boundaries o Continental-Continental Divergence: Rift Valley (Deep hole in continent) o Oceanic-Oceanic Divergence: Mid-Ocean Ridge, where new crust is created. Mid-ocean ridges: new, young, crust created; Trenches: holes where crust is subducted into mantle. Ring of Fire: Convergent boundaries around Pacific Plate where most earthquakes and volcanoes occur. Hot Spot: a spot where Earth’s crust is unusually thin so magma from the mantle rises straight through it and forms a volcanic island above it. As the plates move due to Plate Tectonics, new islands form in a line, called volcanic island chains. Ex: Hawaii Magnetic Reversals: The magnetic material in oceanic basalt alternates from + (Normal Polarity) to – (Reversed Polarity). This can help us figure out how old earth is. Seis- means earthquake. Seismic Waves- energy waves (P and S) released by an earthquake, seismologist- a person who studies earthquakes, seismograph- instrument that detects seismic waves. P Waves: Primary Waves, travel faster, arrive at locations first, travel through solids, liquids, and gases. S Waves: Secondary Waves, travel slower, arrive second, travel through SOLIDS only. P waves travel through solids and liquids while S waves only through solids. This is the reason why S waves can’t go through the outer core. Difference in arrival time between P and S Waves can tell how far the seismograph is from the epicenter. You need 3 seismometer stations to locate an earthquake’s epicenter (the point where the earthquake begins) where all 3 circles cross. This is called triangulation. Geologic History Relative Dating: How old something is compared to something else (older vs. younger) o Superposition: Age: Bottom rock layer is oldest and top layers are younger o Original Horizontality: rocks were originally deposition in Horizontal Layers o Cross-Cutting: An igneous intrusion that cuts through other layers is younger than the layers it cuts through. o Igneous intrusions, tilting, faults, and folding are younger than the rock they cut through. o Correlation: Matching up rocks by their characteristics in order to figure out how old they are. o Unconformity: gap in geologic time – buried erosional surface o Marine (sea) fossils on mountain tops indicate that the land has been uplifted/moved to a new area because of Plate Tectonics. o Good index fossils lived for a short geologic time, over a large geographic area, and are used to figure out the age of rocks. Absolute Dating: How old something is in years. o Radioactive Dating: Using the predictable decay in half-lives of a radioactive isotope to figure out how old something is in YEARS. After each half-life, half of the material turns from radioactive to stable. After 5 or 6 half-lives, there isn’t enough material to detect. o Carbon-14 dates recent, once living objects, within 30,000 years old because it has a shorter halflife; Uranium-238 dates oldest rocks because it has a longer half-life. Half-Life % of Material Remaining Carbon-14 Age Original (0) 100% Just Formed 1 50% 5,700 years old 2 25% 11,400 years old 3 12.5% 17,100 years old 4 6.25% 22,800 years old 5 3.125% 28,500 years old. The solar system and Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago. Early volcanoes erupted and shot out gases that formed our early atmosphere (called outgassing). 3.5 billion years ago, early bacteria evolved and by 2.5 billion years ago, had released enough oxygen to form our atmosphere. Mass Extinction: an unusually large amount of organisms become extinct over a short period of time. Ex: 65.5 million years ago, the extinction of the dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous period. Astronomy and Earth’s Motions Earth rotates counterclockwise, west to east, (1 day), 15 / hr Evidence of rotation: Coriolis Effect – deflects to the right (N Hemisphere) Foucault Pendulum – constantly swings due to earth’s rotation Day and Night, Sunrise and Sunset Celestial objects appear to move 15 across sky every hour (sun, stars, etc.) Earth revolves counterclockwise, (one year), 1 / day Evidence of revolution: We see different constellations each season We have four seasons, seasons are caused by REVOLUTION and TILT of earth’s axis The Solar System The solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago. Geocentric – Earth in center of solar system. (WRONG) / Heliocentric – Sun in center. (CORRECT) Ellipse: an oval with two foci, the true shape of the orbits in our solar system. Eccentricity: a measure of how oval an ellipse is. High eccentricity= very oval, low eccentricity= circular Earth is closer to the sun in winter (perihelion); revolves fastest (greatest orbital velocity) Earth is farther from the sun in summer (aphelion) and revolves slowest (least orbital velocity) The closer a planet is to the sun, the greater the orbital velocity. Perihelion= highest orbital velocity. The smaller the distance between two objects, the greater the gravitational attraction. The larger the mass of an object, the greater the gravitational attraction. Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars; are all small, dense, rocky Jovian Planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune; are all larger, not dense, gaseous/icy. Sun, Moon, and Earth Lunar Eclipse: Earth blocks sunlight from hitting the moon. Sun, Earth, Moon in a row. Solar Eclipse: Moon blocks sunlight from hitting the earth. Sun, Moon, Earth in a row. Neap Tides: When the moon, earth and sun are at right angles to one another, causing lower high tides and higher low tides. Spring Tides: When the moon, earth, and sun are aligned, causing higher high tides and lower low tides. Tides are cyclical; this means they happen over and over again. The Universe The universe is everything that exists. The Big Bang, the theory of our universe being created is thought to have happened 10-15 billion years ago, and causes everything in the universe to move away from a single point. This is called the Doppler Effect, or redshift. Galaxies, such as ours, the Milky Way, are collections of billions of stars. All galaxies are moving away from one another at extremely high speeds. Star Life Cycles: H-R Diagram in Reference Table Stars do NUCLEAR FUSION to create energy! They fuse hydrogen into helium! Main Sequence: Where normal-sized stars spend most of their lives. Ex: Sun Red Giant: Normal-sized stars turn into this when they lose their energy. Ex: Future sun! Super Giant: The biggest stars turn into this when they lose their energy. Ex: Betelgeuse Supernova: Giant explosion created when supergiants die. Black Hole: What the biggest supergiants create when they die. So much gravity, not even light can escape. Our sun will NEVER become one because it is NOT big enough. Luminosity: Brightness of a star compared to the sun