Supplemental Figure 1
advertisement

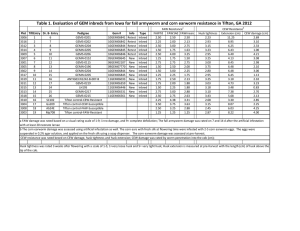
Salcedo et al. 2007 Supplemental Figure 1. Ideogram of the X chromosome showing the five loci sequenced in this study. Physical and genetic map positions are based on data from NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and MGI (http://www.informatics.jax.org/), and are listed in parentheses below each locus name. Gene structures are presented at right, and the approximate genomic length of each gene is given. Solid boxes indicate coding exons; empty boxes indicate untranslated regions. The region of each gene that was sequenced in this study is indicated by a horizontal line. Supplemental Figure 2. Polymorphic sites for five loci X-linked in M. musculus and M. domesticus, in order from centromere to telomere. Catalogue numbers, inbred strain names, or species names are shown at left; Md – M. domesticus, Mm – M. musculus. Inferred ancestral sequence presented at top; dots indicate match to this sequence, blanks indicate missing data, and dashes indicate insertion/deletion polymorphisms. Numbers at top represent position of polymorphic sites relative to alignment of all sequences within each locus. Supplementary Figure 3. Gene genealogies for classical inbred strains and wild mice, for (A) Xlinked and (B) autosomal loci. AL, CR, mu = M. musculus; D, MC, IS, do = M. domesticus; classical inbred strain names are as in Table 1. Supplemental Figure 4. Haplotype networks colored by geography for M. domesticus. Each circle represents a haplotype; circle size is proportional to number of chromosomes. Hatch marks represent mutational steps (base substitutions only). Mainland Italy is represented in grey, Sicily in black, Greece in white, and Spain in yellow.