Context: To develop positive attitudes to reading and understanding
advertisement

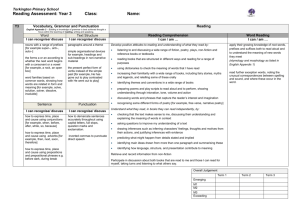
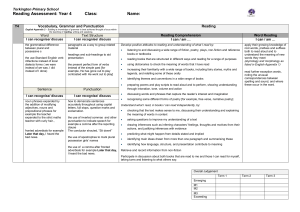
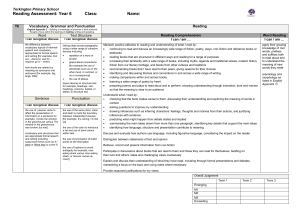
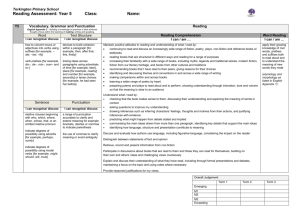
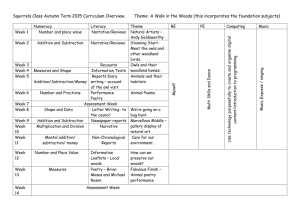
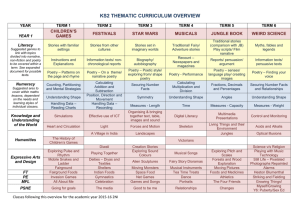
Context: To develop positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what they read by listening to and discussing a wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks Inference & Deduction skim & scan retell fairy stories draw inferences such orally as inferring find & copy characters' feelings, words identify main ideas thoughts and motives drawn from one from their actions, identify the paragraph and justifying inferences main point of summarise these with evidence a simple paragraph retrieve and record predict what might information from happen from details read using non-fiction stated and implied punctuation A . ! ? “” COMPREHENSION General Literal Word Reading (link to spelling) read aloud words from Appendix 1 (spelling) Non Narrative Instructions - timetables & route-finders Reports - non chronological Recounts - letters, diaries, historical Reference books & textbooks Text Features & Layout discuss words and phrases that capture the reader’s interest and imagination: alliteration, similes, adverbials, noun phrases, vocabulary Other poetry plays Vocabulary use dictionaries to identify how language, structure, and presentation contribute to check the meaning (see also non narrative layout guidance) meaning of words that fairy tales: good v evil, rags to riches, magic, talking animals, they have opening phrases, 3,7, repetition, talking to the reader, names, read patterns, alliteration, similes, begin to identify & Instructions: imperative verbs with adverbs, time connections, comment on different bullet points, numbers, boxes, points of view in a text. Reports: present/past tense, openings & endings, paragraphs, headings & subheadings understand what a writer Recounts: personal pronouns, letter conventions, paragraph might be thinking e.g. he themes, openings & endings thinks Miss Trunchbull is Reference books: alphabetical order, headings & mean subheadings, line breaks, glossary, contents etc. Responding to the text check that the text makes sense to them recognise and identify root words, suffixes and prefixes & use this knowledge to understand new words. ask questions to improve their understanding of a text recognise exception words and discuss this e.g. said. participate in discussion about both books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, taking turns and listening to what others say. use phonic knowledge to attempt to read any word Narrative fairy stories familiar settings adventure picture books Authorial Intent discuss their understanding explain the meaning of words in context Text s English Curriculum Reading Year 3 identify themes and conventions Performance use intonation, tone, volume and action when performing poetry, plays or when reading to an audience. Poetry & Playscripts Performing & Learning Reading prepare poems and play scripts to read aloud and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action discuss the choice of words and their impact including the use of sound effects: similes, alliteration, rhyme and rhythm. describe the effect of a poem and its purpose & feeling. Poetry to Learn: On the Ning Nang Nong – Spike Milligan Simple Simon – traditional The Owl & The Pussycat – Edward Lear English Curriculum Reading Year 4 COMPREHENSION Text s Narrative Non Narrative Other adventure stories Report: (Non Chronological) poetry fantasy stories Recounts/Chronological Reports: newspapers & plays – Context: To develop positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what characterisation magazines, diaries conventions they read by listening to and discussing a wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, settings Persuasion: advert, persuasive techniques & layout non-fiction and reference books or textbooks myths & legends fables General Literal Inference & Deduction Authorial Intent Text Features & Layout Vocabulary skim & scan retell stories orally draw inferences such as discuss words and identify themes and conventions use & in summarised inferring characters' phrases that capture dictionaries to find & copy form in writing feelings, thoughts and the reader’s interest identify how language, structure, and presentation contribute to check the meaning (see also non narrative layout guidance) words & motives from their actions, and imagination: meaning of phrases identify main and justify inferences with words that they ideas drawn from evidence find & comment on have read & a Reports: present/past tense, openings & endings, Identify main more than one alliteration, thesaurus to paragraphs, headings & subheadings point of a paragraph and predict what might happen onomatopoeia, similes, Newspaper: title (no articles), past tense, fronted adverbials find synonyms paragraph summarising from details stated and sensory words, of time, exaggeration, powerful verbs, openings & endings these implied adverbials, noun Persuasion: exaggeration, 3s, data/experts, science, threat, read using phrases, vocabulary dare, rhetorical questions, emotive words & pictures punctuation retrieve and suggest the mood & Reference books: alphabetical order, headings & A . ! ? “” , record information atmosphere of a story comment on how an subheadings, line breaks, glossary, contents, index, from non-fiction from details about the author wants the Visual sections: captions, diagram, illustration, photographs setting & language used reader to respond Word Reading (link to spelling) read aloud words from Appendix 1 (spelling) Responding to the text check that the text makes sense to them discuss their understanding recognise and identify root words, suffixes and prefixes use knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes to understand new words. recognise exception words and discuss this e.g. said. explain the meaning of words in context ask questions to improve their understanding of a text participate in discussion about both books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, taking turns and listening to what others say. Performance use intonation, tone, volume and action when performing poetry, plays or when reading to an audience. comment on their own and others’ performance and suggest simple improvements. Poetry Performing & Learning Reading prepare poems and play scripts to read aloud and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action comment on the choice of words and their impact including the use of imagery: similes, onomatopoeia, alliteration, rhyme and rhythm. describe the effect of a poem and its purpose & feeling. Poetry to Learn: The Crocodile – Lewis Carroll The King’s Breakfast – A A Milne Matilda – Hillaire Belloc English Curriculum Reading Year 5 COMPREHENSION Text s Narrative modern fiction, Context: To maintain positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what fiction from our they read by continuing to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of literary heritage fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks. Science Fiction Mystery General Literal Inference & Deduction Authorial Intent skim & scan summarise the draw inferences such as identify how language, main ideas drawn inferring characters' structure & presentation find & copy words & from more than feelings, thoughts and contribute to meaning phrases one paragraph, motives from their actions, identifying key and justifying inferences discuss and evaluate distinguish between details that with evidence from across how authors use statements of fact and support the main a text language, including opinion ideas figurative language & predict what might imagery, considering the explain and discuss their retrieve, record happen from details impact on the reader understanding of what and present stated and implied they have read and information from recognise and discuss provide reasoned non-fiction different points of view justifications for their views. recognise if a viewpoint read using a range of is positive, negative or punctuation neutral Word Reading (link to spelling) use knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes to understand new words – both meaning & pronunciation accurate and fluent reading of complex sentences using context, read homophones correctly Responding to the text recommend books that they have read to their peers, giving reasons for their choices making comparisons within and across books checking that the book makes sense to them, discussing their understanding and exploring the meaning of words in context asking questions to improve their understanding participate in discussions about books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, building on their own and others’ ideas and challenging views courteously Non Narrative Other Report: (Non Chronological) poetry Recount: events plays Instructions: “how to use”, incl warnings & advice Explanations Persuasive writing: letters, articles etc. Text Features & Layout Vocabulary identifying and discussing themes and when reading conventions in and across a wide range of writing with or to e.g. pupils, loss, heroism, courage, perseverance, attention cooperation, honesty, overcoming fear, loyalty, should be paid sacrifice to new vocabulary – Recognise how suspense is built up in a text both a word’s meaning(s) comment on how language, structure, and and its correct presentation contribute to meaning (see also non pronunciation. narrative layout guidance) Science Fiction: scientific vocabulary, specific characters & settings Mystery: sentence length & structure, settings, atmosphere, show don’t tell, description Performance show understanding by using intonation, tone and volume so that the meaning is clear to an audience when performing or reading aloud explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read, including through formal debates and presentations, maintaining a focus on the topic and using notes where necessary Poetry Performing & Learning Reading Prepare poems and plays Explain the choice of language to read aloud and to and its impact including imagery: perform, showing similes, onomatopoeia, understanding through alliteration, personification, intonation, tone and assonance, metaphor volume so that the Describe viewpoint meaning is clear to an Explain the purpose of a poem audience Poetry to Learn: Daffodills – William Wordsworth The Wiitches Chant from Macbeth – William Shakespeare The Listeners – Walter de la Mare Leisure – W H Davies Context: To maintain positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what they read by continuing to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks. General Literal COMPREHENSION skim & scan find & copy words & phrases distinguish between statements of fact and opinion explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read provide reasoned justifications for their views. Word Reading (link to spelling) use knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes to understand new words – both meaning & pronunciation summarise the main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph, identifying key details that support the main ideas retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction Inference & Deduction draw inferences such as inferring characters' feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, and justifying inferences with evidence predict what might happen from details stated and implied Responding to the text recommend books that they have read to their peers, giving reasons for their choices make comparisons within and across books check that the book makes sense to them, discussing their understanding and exploring the meaning of words in context read texts not ask questions to improve their understanding written in modern or standard English participate in discussions about books that are read to them and those they can read for read abbreviations, themselves, building on their own and others’ colloquialisms and ideas and challenging views courteously specialist vocabulary Text s English Curriculum Reading Year 6 Narrative Variety of genres Non Narrative All genres Other poetry plays Authorial Intent Text Features & Layout Vocabulary identify how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning identify and discuss themes and conventions in and across a wide range of writing e.g. loss, heroism, courage, perseverance, cooperation, honesty, overcoming fear, loyalty, sacrifice when reading with or to pupils, attention should be paid to new vocabulary – both a word’s meaning(s) and its correct pronunciation. discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language & imagery, considering the impact on the reader recognise explicit and implicit points of view in a text comment on how language, structure, and presentation contribute to meaning (see also non narrative layout guidance) identify & comment on the structure/layout, language, audience & purpose of all writing with justifications from the text. Performance show understanding by using intonation, tone and volume so that the meaning is clear to an audience when performing or reading aloud explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read, including through formal presentations and debates, maintaining a focus on the topic and using notes where necessary Poetry Performing & Learning Reading Prepare poems and plays Explain the impact of the choice to read aloud and to of language and its impact perform, showing including imagery: similes, understanding through onomatopoeia, alliteration, intonation, tone and personification, assonance, volume so that the metaphor meaning is clear to an Describe viewpoint & themes audience Explain structure & meaning Poetry to Learn: Tyger – William Blake If – Rudyard Kipling Macavity the Mystery Cat – T S Eliot If Pigs Could Fly – James Reeves