Elementary - Madison County Schools
advertisement
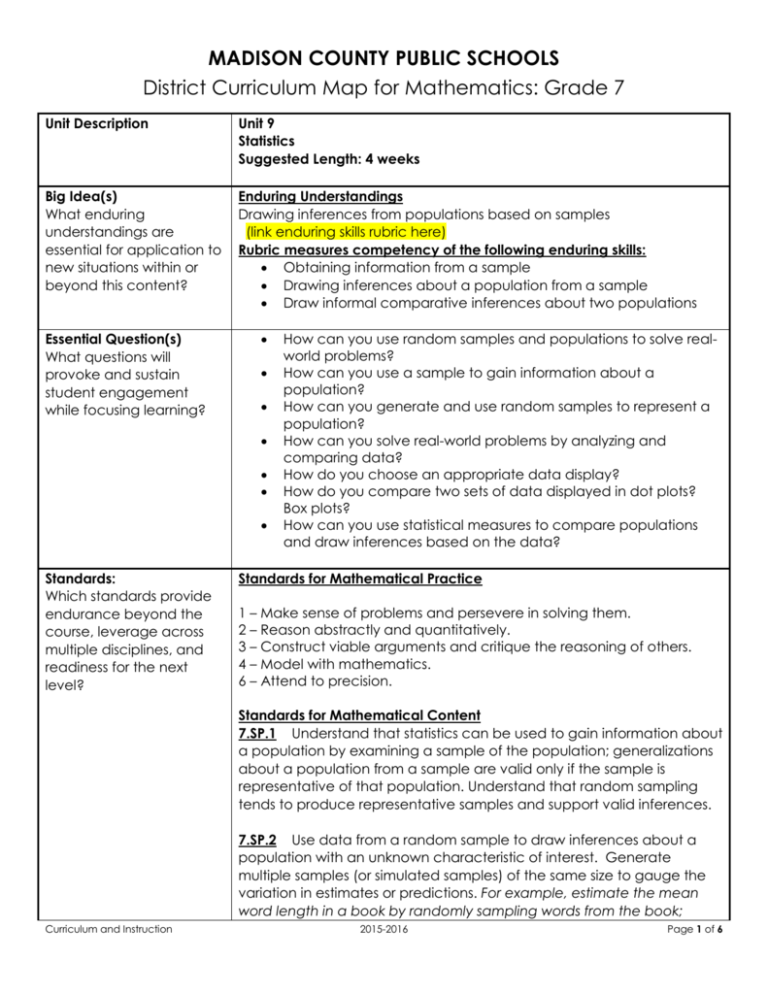
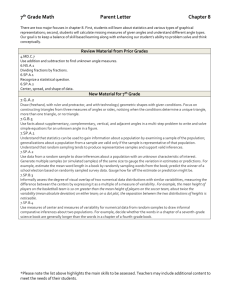
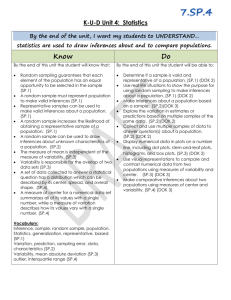
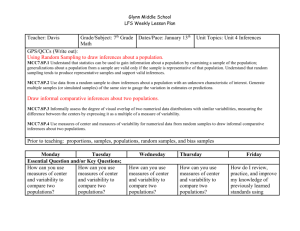
MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 Unit Description Unit 9 Statistics Suggested Length: 4 weeks Big Idea(s) What enduring understandings are essential for application to new situations within or beyond this content? Enduring Understandings Drawing inferences from populations based on samples (link enduring skills rubric here) Rubric measures competency of the following enduring skills: Obtaining information from a sample Drawing inferences about a population from a sample Draw informal comparative inferences about two populations Essential Question(s) What questions will provoke and sustain student engagement while focusing learning? Standards: Which standards provide endurance beyond the course, leverage across multiple disciplines, and readiness for the next level? How can you use random samples and populations to solve realworld problems? How can you use a sample to gain information about a population? How can you generate and use random samples to represent a population? How can you solve real-world problems by analyzing and comparing data? How do you choose an appropriate data display? How do you compare two sets of data displayed in dot plots? Box plots? How can you use statistical measures to compare populations and draw inferences based on the data? Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 – Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 – Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 – Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4 – Model with mathematics. 6 – Attend to precision. Standards for Mathematical Content 7.SP.1 Understand that statistics can be used to gain information about a population by examining a sample of the population; generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only if the sample is representative of that population. Understand that random sampling tends to produce representative samples and support valid inferences. 7.SP.2 Use data from a random sample to draw inferences about a population with an unknown characteristic of interest. Generate multiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size to gauge the variation in estimates or predictions. For example, estimate the mean word length in a book by randomly sampling words from the book; Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 1 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 predict the winner of a school election based on randomly sampled survey data. Gauge how far off the estimate or prediction might be. 7.SP.3 Informally assess the degree of visual overlap of two numerical data distributions with similar variabilities, measuring the difference between the centers by expressing it as a multiple of a measure of variability. For example, the mean height of players on the basketball team is 10 cm greater than the mean height of players on the soccer team, about twice the variability (mean absolute deviation) on either team; on a dot plot, the separation between the two distributions of heights is noticeable. 7.SP.4 Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science book are generally longer than the words in a chapter of a fourth-grade science book. Supporting Standard(s): Which related standards will be incorporated to support and enhance the enduring standards? Instructional Outcomes What must students learn and be able to do by the end of the unit to demonstrate mastery? Curriculum and Instruction 7.EE.3 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. (NOTE: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions.) I am learning to… Define statistics terms such as population, sample, sample size, random sampling, generalizations, valid, biased and unbiased. (not a test item) Recognize sampling techniques such as convenience, random, systematic, and voluntary. (not a test item) Identify and generate unbiased statistical questions. (not a test item) Identify an appropriate sample for a population. (7.SP.1) Use the data from a sample to make generalizations about the population. (7.SP.1) Know that generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only if the sample is representative of that population. (7.SP.1) Make predictions, draw conclusions, and verify results from statistical data. (7.SP.1) Analyze and interpret data from a random sample to draw 2015-2016 Page 2 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 inferences about a population with an unknown characteristic of interest. (7.SP.2) Generate multiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size. (7.SP.2) Determine the reliability of a sample using multiple samples from the same population. (7.SP.2) Compare two numerical data distributions on a graph by visually comparing their displays and assessing the degree of visual overlap (overall shape). (7.SP.3) Identify and find measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode). (7.SP.4) Identify and find measures of variation including upper quartile, lower quartile, upper extreme-maximum, lower extrememinimum, range, interquartile range (IQR), and mean absolute deviation (MAD), box-and-whisker plots (box plots), line plots, and dot plots. (7.SP.4) Compare the measures of center in data distributions by measuring the difference between the centers and expressing it as a multiple of a measure of variability. (7.SP.4) Analyze and interpret data using measures of central tendency and variability. (7.SP.4) Draw formal comparative inferences about two populations from random samples. Vocabulary What vocabulary must students know to understand and communicate effectively about this content? (7.SP.4) Essential Vocabulary Biased, box and whiskers plot, data, degree of visual overlap, graph, inferences, mean absolute deviation (MAD), measure of center, measure of variation, outlier, population, prediction, sample, random sample, range, reliability, representative sample, simulation, spread, statistical variability, statistics, stem and leaf plot, unbiased, valid Supporting Vocabulary Equation Resources/Activities What resources could we use to best teach this unit? Curriculum and Instruction Resources/Activities From https://www.georgiastandards.org/Pages/default.aspx Use the following unit to access tasks and instructional strategies specific to percent proportions. (insert link to Georgia standards frameworks unit 4) Dan Meyer – Yellow Starbursts (also for SP.6) http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/yellowstarbursts/ Ann Shannon Formative Assessment Lessons (search by standard) http://map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?gradeid=22 Shodor Activities by Content Strand http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/standards/organization/354 / 2015-2016 Page 3 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 Common Misconceptions Curriculum and Instruction EngageNY Lessons by Strand https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-7-mathematics NCTM Illuminations – search for games, lessons and interactives by grade level and content http://illuminations.nctm.org Remember there are other sources in your school that may not be listed on this common resources list due to variation in each individual school. Examples of other great resources your school may have access to include: GoMath, Connected Math, IXL, Compass, MobyMax, Laying the Foundation, Carnegie, etc. The Kentucky Numeracy Project is also a great resource that can be searched by CCSS and grade level K-4 for RTI and gap closure purposes. Find this resource at http://knp.kentuckymathematics.org/#!/page_knphome. Kentucky teachers can use it for free. Just put in your school email address and the username “mathfun”, and password is “859”. Students can confuse the different measures of center. Students may have difficulty calculating the median when that data set has an even number of data points. Students may struggle using data to be persuasive to both sides of an argument. Students struggle to understand the concept of reliability. Students struggle with generalizations from the sample to the entire population. Students struggle to determine when a sample is appropriate and when a sample is random. 2015-2016 Page 4 of 6 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 5 of 6 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 6 of 6